By Y. Varoufakis, S. Holland AND J.K. Galbraith
1. Prologue
Europe is fragmenting. While in the past year the European Central Bank has managed to stabilise the bond markets, the economies of the European core and its periphery are drifting apart. As this happens, human costs mount and disintegration becomes an increasing threat.
It is not just a matter for the Eurozone. The fallout from a Eurozone breakup would destroy the European Union, except perhaps in name. And Europe’s fragmentation poses a global danger.
Following a sequence of errors and avoidable delays Europe’s leadership remains in denial about the nature of the crisis, and continues to pose the false choice between draconian austerity and a federal Europe.
By contrast, we propose immediate solutions, feasible within current European law and treaties.
There are in this crisis four sub-crises: a banking crisis, a public debt crisis, a crisis of under-investment, and now a social crisis – the result of five years of policy failure. Our Modest Proposal therefore now has four elements. They deploy existing institutions and require none of the moves that many Europeans oppose, such as national guarantees or fiscal transfers. Nor do they require treaty changes, which many electorates anyway could reject. Thus we propose a European New Deal which, like its American forebear would lead to progress within months, yet through measures that fall entirely within the constitutional framework to which European governments have already agreed.
2. The nature of the Eurozone crisis
The Eurozone crisis is unfolding on four interrelated domains. Banking crisis: There is a common global banking crisis, which was sparked off mainly by the catastrophe in American finance. But the Eurozone has proved uniquely unable to cope with the disaster, and this is a problem of structure and governance. The Eurozone features a central bank with no government, and national governments with no supportive central bank, arrayed against a global network of mega-banks they cannot possibly supervise. Europe’s response has been to propose a full Banking Union – a bold measure in principle but one that threatens both delay and diversion from actions that are needed immediately.
Better understood as a lack of credible deposit insurance, which logically requires that the entity that provides the insurance- the ECB in this case- is responsible for the regulation and supervision of its banks.
Debt crisis: The credit crunch of 2008 revealed the Eurozone’s principle of perfectly separable public debts to be unworkable. Forced to create a bailout fund that did not violate the no-bailout clauses of the ECB charter and Lisbon Treaty, Europe created the temporary European Financial Stability Facility (EFSF) and then the permanent European Stability Mechanism (ESM). The creation of these new institutions met the immediate funding needs of several member-states, but retained the flawed principle of separable public debts and so could not contain the crisis. One sovereign state, Cyprus, has now de facto gone bankrupt, imposing capital controls even while remaining inside the euro.
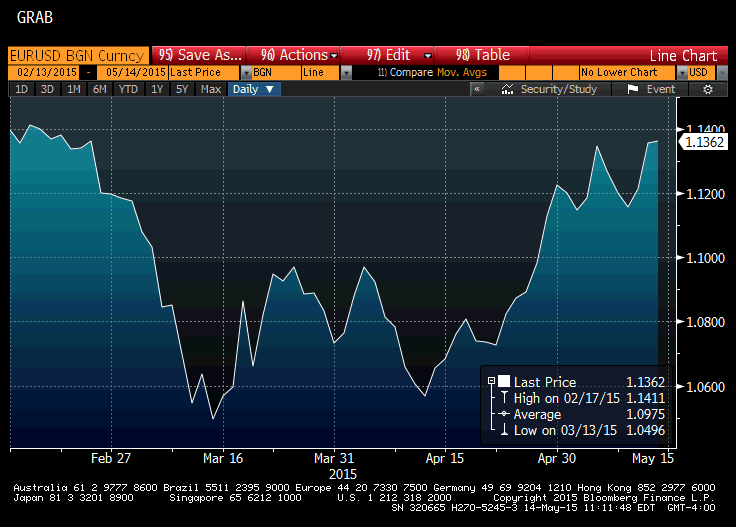
During the summer of 2012, the ECB came up with another approach: the Outright Monetary Transactions’ Programme (OMT). OMT succeeded in calming the bond markets for a while. But it too fails as a solution to the crisis, because it is based on a threat against bond markets that cannot remain credible over time. And while it puts the public debt crisis on hold, it fails to reverse it; ECB bond purchases cannot restore the lending power of failed markets or the borrowing power of failing governments.
Better understood as failure of the ECB to explicitly guarantee national govt bonds against default. It was only when Mario Draghi said the ECB would ‘do what it takes to prevent default of national govt debt’ that spreads narrowed and the national funding crisis faded. And it is only the threat that Greece will be allowed to default that is causing the current Greek funding crisis.
Investment crisis: Lack of investment in Europe threatens its living standards and its international competitiveness.
He doesn’t differentiate between public investment in public infrastructure, vs private investment that responds to prospects for profits.
As Germany alone ran large surpluses after 2000, the resulting trade imbalances ensured that when crisis hit in 2008, the deficit zones would collapse.
How is ‘collapse’ defined here? The funding crisis was a function of ECB policy that presumably would allow member nations to default, as when Draghi said that would not happen that crisis ended.
And the burden of adjustment fell exactly on the deficit zones, which could not bear it.
However, there were and remain alternatives to said ‘adjustments’ including the permission to run larger budget deficits than the current, arbitrary, 3% limit. Note that this ‘remedy’ is never even suggested or seriously discussed.
Nor could it be offset by devaluation or new public spending, so the scene was set for disinvestment in the regions that needed investment the most. Thus, Europe ended up with both low total investment and an even more uneven distribution of that investment between its surplus and deficit regions.
True, however it is not recognized that the fundamental cause is that the 3% deficit limit is too low.
Social crisis: Three years of harsh austerity have taken their toll on Europe’s peoples.
From Athens to Dublin and from Lisbon to Eastern Germany, millions of Europeans have lost access to basic goods and dignity. Unemployment is rampant. Homelessness and hunger are rising. Pensions have been cut; taxes on necessities meanwhile continue to rise. For the first time in two generations, Europeans are questioning the European project, while nationalism, and even Nazi parties, are gaining strength.
True
3. Political constraints for any solution.
Any solution to the crisis must respect realistic constraints on political action. This is why grand schemes should be shunned. It is why we need a modest proposal.
But immodest enough to do more than rearrange the deck chairs on the titanic.
Four constraints facing Europe presently are: (a) The ECB will not be allowed to monetise sovereigns directly.
Not necessary
There will be no ECB guarantees of debt issues by member-states,
They already said they will do what it takes to prevent default, meaning at maturity and when interest payments are due the ECB will make sure the appropriate accounts are credited. However this policy is discretionary, with threats Greece would be allowed to default.
no ECB purchases of government bonds in the primary market,
Not necessary
no ECB leveraging of the EFSF-ESM to buy sovereign debt from either the primary or secondary markets.
Not necessary
(b) The ECB’s OMT programme has been tolerated insofar as no bonds are actually purchased. OMT is a policy that does not match stability with growth and, sooner or later, will be found wanting.
And accomplishes nothing of consequence for the real economy.
(c) Surplus countries will not consent to ‘jointly and severally’ guaranteed Eurobonds to mutualise debt and deficit countries will resist the loss of sovereignty that would be demanded of them without a properly functioning federal transfer union which Germany, understandably, rejects.
Said eurobonds not necessary for fiscal transfers.
(d) Europe cannot wait for federation. If crisis resolution is made to depend on federation, the Eurozone will fail first.
Probably true.
The treaty changes necessary to create a proper European Treasury, with the powers to tax, spend and borrow, cannot, and must not, be held to precede resolution of this crisis.
Nor are they necessary to sustain full employment.
The next section presents four policies that recognise these constraints.
4. THE MODEST PROPOSAL – Four crises, four policies The Modest Proposal introduces no new EU institutions and violates no existing treaty. Instead, we propose that existing institutions be used in ways that remain within the letter of European legislation but allow for new functions and policies.
These institutions are:
· The European Central Bank – ECB
· The European Investment Bank – EIB
· The European Investment Fund – EIF
· The European Stability Mechanism – ESM
Policy 1 – Case-by-Case Bank Programme (CCBP)
For the time being, we propose that banks in need of recapitalisation from the ESM be turned over to the ESM directly – instead of having the national government borrow on the bank’s behalf.
‘In need of recapitalization’ is not defined. With credible deposit insurance banks can function in the normal course of business without capital, for example. That means ‘need of capital’ is a political and not an operational matter.
Banks from Cyprus, Greece and Spain would likely fall under this proposal. The ESM, and not the national government, would then restructure, recapitalize and resolve the failing banks dedicating the bulk of its funding capacity to this purpose.
Those banks are necessarily already ‘funded’ via either deposits or central bank credits, unless their equity capital is already negative and not simply below regulatory requirements, as for every asset there is necessarily a liability. And I have not been aware of the banks in question have negative capital accounts.
The Eurozone must eventually become a single banking area with a single banking authority.
Yes, with the provider of deposit insurance, the ECB, also doing the regulation and supervision.
But this final goal has become the enemy of good current policy. At the June 2012 European Summit direct bank recapitalisation was agreed upon in principle, but was made conditional on the formation of a Banking Union. Since then, the difficulties of legislating, designing and implementing a Banking Union have meant delay and dithering. A year after that sensible decision, the deadly embrace between insolvent national banking systems and insolvent member-states continues.
Today the dominant EU view remains that banking union must be completed before the ESM directly recapitalises banks.
Again, I don’t recall the problem being negative bank capital, but merely capital that may fall short of required minimums, in which case not only is no ‘public funding’ is required with regard to capital, but the concept itself is inapplicable as adding public capital doesn’t alter the risk to ‘public funds’
And that when it is complete, the ESM’s contribution will be partial and come only after a bail in of depositors in the fiscally stressed countries of the periphery. That way, the banking crisis will either never be resolved or its resolution be delayed for years, risking a new financial implosion.
Our proposal is that a national government should have the option of waiving its right to supervise and resolve a failing bank.
This carries extreme moral hazard, as it removes the risk of inadequate supervision from the national govt, and instead rewards lax supervision. Instead that right to supervise and regulate should immediately be transferred to the ECB for the entire national banking system in exchange for ECB deposit insurance.
Shares equivalent to the needed capital injection will then pass to the ESM, and the ECB and ESM will appoint a new Board of Directors. The new board will conduct a full review of the bank’s position and will recommend to the ECB-ESM a course for reform of the bank. Reform may entail a merger, downsizing, even a full resolution of the bank, with the understanding that steps will be taken to avoid, above all, a haircut of deposits.
That is functionally what I call sustaining credible deposit insurance which largely eliminates bank liquidity issues.
Once the bank has been restructured and recapitalised, the ESM will sell its shares and recoup its costs.
I agree with the resolution process.
The above proposal can be implemented today, without a Banking Union or any treaty changes.
The experience that the ECB and the ESM will acquire from this case-by-case process will help hone the formation of a proper banking union once the present crisis recedes.
POLICY 2 – Limited Debt Conversion Programme (LDCP)
The Maastricht Treaty permits each European member-state to issue sovereign debt up to 60% of GDP. Since the crisis of 2008, most Eurozone member-states have exceeded this limit. We propose that the ECB offer member-states the opportunity of a debt conversion for their Maastricht Compliant Debt (MCD), while the national shares of the converted debt would continue to be serviced separately by each member-state.
The ECB, faithful to the non-monetisation constraint (a) above, would not seek to buy or guarantee sovereign MCD debt directly or indirectly. Instead it would act as a go-between, mediating between investors and member-states. In effect, the ECB would orchestrate a conversion servicing loan for the MCD, for the purposes of redeeming those bonds upon maturity.
The conversion servicing loan works as follows. Refinancing of the Maastricht compliant share of the debt, now held in ECB-bonds, would be by member-states but at interest rates set by the ECB just above its bond yields. The shares of national debt converted to ECB-bonds are to be held by it in debit accounts. These cannot be used as collateral for credit or derivatives creation.6 Member states will undertake to redeem bonds in full on maturity, if the holders opt for this rather than to extend them at lower, more secure rates offered by the ECB.
Governments that wish to participate in the scheme can do so on the basis of Enhanced Cooperation, which needs at least nine member-states.7 Those not opting in can keep their own bonds even for their MCD. To safeguard the credibility of this conversion, and to provide a backstop for the ECB-bonds that requires no ECB monetisation, member-states agree to afford their ECB debit accounts super-seniority status, and the ECB’s conversion servicing loan mechanism may be insured by the ESM, utilising only a small portion of the latter’s borrowing capacity. If a member-state goes into a disorderly default before an ECB-bond issued on its behalf matures, then that ECB-bond payment will be covered by insurance purchased or provided by the ESM.
This can more readily be accomplished by formalizing and making permanent the ‘do what it takes to prevent default’ policy that’s already in place, and it will immediately lower the cost of new securities as well.
Why not continue with the ECB’s OMT? The ECB has succeeded in taming interest rate spreads within the Eurozone by means of announcing its Outright Monetary Transactions’ programme (OMT). OMT was conceived as unlimited support of stressed Euro-Area bonds – Italy’s and Spain’s in particular – so as to end the contagion and save the euro from collapse.
Instead I give credit for the low rates to the ‘do what it takes’ policy.
However, political and institutional pressures meant that the threat against bond dealers, which was implicit in the OMT announcement, had to be diluted to a conditional programme. The conditionality involves troika-supervision over the governments to be helped by the OMT, who are obliged to sign a draconian memorandum of understanding before OMT takes effect. The problem is not only that this of itself does nothing to address the need for both stability and growth, but that the governments of Spain and Italy would not survive signing such a memorandum of understanding, and therefore have not done so.
Thus OMT’s success in quelling the bond markets is based on a non-credible threat. So far, not one bond has been purchased. This constitutes an open invitation to bond dealers to test the ECB’s resolve at a time of their choosing. It is a temporary fix bound to stop working when circumstances embolden the bond dealers. That may happen when volatility returns to global bond markets once the Federal Reserve and the Bank of Japan begin to curtail their quantitative easing programmes.
There will be no funding issues while ‘do what it takes to prevent default’ policy is in force.
POLICY 3 – An Investment-led Recovery and Convergence Programme (IRCP)
In principle the EU already has a recovery and convergence strategy in the European Economic Recovery Programme 2020. In practice this has been shredded by austerity. We propose that the European Union launch a new investment programme to reverse the recession, strengthen European integration, restore private sector confidence and fulfill the commitment of the Rome Treaty to rising standards of living and that of the 1986 Single European Act to economic and social cohesion.
The Investment-led Recovery and Convergence Programme (IRCP) will be cofinanced by bonds issued jointly by the European Investment Bank (EIB) and the European Investment Fund (EIF). The EIB has a remit to invest in health, education, urban renewal, urban environment, green technology and green power generation, while the EIF both can co-finance EIB investment projects and should finance a European Venture Capital Fund, which was part of its original design.
A key principle of this proposal is that investment in these social and environmental domains should be europeanised. Borrowing for such investments should not count on national debt anymore than US Treasury borrowing counts on the debt of California or Delaware. The under-recognised precedents for this are (1) that no major European member state counts EIB borrowing against national debt, and (2) that the EIB has successfully issued bonds since 1958 without national guarantees.
EIB-EIF finance of an IRCP therefore does not need national guarantees or a common fiscal policy. Instead, the joint bonds can be serviced directly by the revenue streams of the EIB-EIF-funded investment projects. This can be carried out within member states and will not need fiscal transfers between them.
A European Venture Capital Fund financed by EIF bonds was backed unanimously by employers and trades unions on the Economic and Social Committee in their 2012 report Restarting Growth. Central European economies (Germany and Austria) already have excellent finance for small and medium firms through their Mittelstandpolitik. It is the peripheral economies that need this, to build new sectors, to foster convergence and cohesion and to address the growing imbalances of competitiveness within the Eurozone.
Rationale
The transmission mechanism of monetary policy to the periphery of Europe has broken down. Mr Mario Draghi admits this. He has gone on record to suggest that the EIB play a active role in restoring investment financing in the periphery. Mr Draghi is right on this point.
But, for the IRCP to reverse the Eurozone recession and stop the de-coupling of the core from the periphery, it must be large enough to have a significant effect on the GDP of the peripheral countries.
If EIB-EIF bonds are to be issued on this scale, some fear that their yields may rise. But this is far from clear. The world is awash in savings seeking sound investment outlets. Issues of EIF bonds that co-finance EIB investment projects should meet these demands, supporting stability and working to restore growth in the European periphery. We therefore submit that joint EIB-EIF bond issues can succeed without formal guarantees. Nonetheless, in fulfillment of its remit to support “the general economic policies in the Union”, the ECB can issue an advance or precautionary statement that it will partially support EIB-EIF bonds by means of standard central bank refinancing or secondary market operations. Such a statement should suffice to allow the EIB-EIF funded IRCP to be large enough for the purposes of bringing about Europe’s recovery.
Misleading arguments and unworkable alternatives:
There are calls for bonds to finance infrastructure, neglecting the fact that this has been happening through the European Investment Bank (EIB) for more than half a century. An example is a recent European Commission proposal for ‘Project Bonds’ to be guaranteed by member states. This assures opposition from many of them, not least Germany, while ignoring the fact that the EIB has issued project bonds successfully since 1958, without such guarantees.10
There is no high-profile awareness that EIB investment finance does not count on the national debt of any major member state of the EU nor need count on that of smaller states.11
There is a widespread presumption that public investment drains the private sector when in fact it sustains and supports it. There is similar presumption that one cannot solve the crisis by ‘piling debt on debt’. It depends on which debt for which purpose, and at what rates. Piling up national debt at interest rates of up to seven per cent or more without recovery is suicidal. Funding inflows from global surpluses to Europe to promote economic recovery through joint EIB-EIF bonds at interest rates which could be less than two per cent is entirely sustainable.
There is little awareness of the EIB’s sister organisation, the European Investment Fund (EIF), which has a large potential for investment funding of SMEs, high technology clusters and a variety of other projects, which it can cofinance with bonds, issued jointly with the EIB (see note 9). Why aren’t the EIB-EIF doing this now? Until the onset of the Eurozone crisis the EIB had succeeded in gaining national co-finance, or co-finance from national institutions, for its investments. But with the crisis and constraints on co-finance, total annual EIB financing fell from over €82bn in 2008 to only €45bn last year. The EIF can counterpart and thereby countervail this. It is a sister institution of the EIB within the EIB Group. Like EIB bonds, EIF bonds need not count on national debt nor need national guarantees. The EIB would retain control over project approval and monitoring. In sum, we recommend that:
The IRCP be funded by means of jointly issued EIB and EIF bonds without any formal guarantees or fiscal transfers by member states.
Both EIB and EIF bonds be redeemed by the revenue stream of the investment • projects they fund, as EIB bonds always have been.
If needed, the ECB should stand by to assist in keeping yields low, through direct purchases of EIB-EIF bonds in the secondary market.
I agree the role of the EIB could be expanded, however the political difficulties are substantial and the time to initial implementation will likely be a year or more- time the EU may not have.
POLICY 4 – An Emergency Social Solidarity Programme (ESSP)
We recommend that Europe embark immediately on an Emergency Social Solidarity Programme that will guarantee access to nutrition and to basic energy needs for all Europeans, by means of a European Food Stamp Programme modelled on its US equivalent and a European Minimum Energy Programme. These programmes would be funded by the European Commission using the interest accumulated within the European system of central banks, from TARGET2 imbalances, profits made from government bond transactions and, in the future, other financial transactions or balance sheet stamp duties that the EU is currently considering.
These revenues currently are returned to the member nations and without them compliance with the 3% deficit limit will reduce other spending and/or require additional taxes.
Rationale
Europe now faces the worst human and social crisis since the late 1940s. In member-states like Greece, Ireland, Portugal, but also elsewhere in the Eurozone, including core countries, basic needs are not being met. This is true especially for the elderly, the unemployed, for young children, for children in schools, for the disabled, and for the homeless. There is a plain moral imperative to act to satisfy these needs. In addition, Europe faces a clear and present danger from extremism, racism, xenophobia and even outright Nazism – notably in countries like Greece that have borne the brunt of the crisis. Never before have so many Europeans held the European Union and its institutions in such low esteem. The human and social crisis is turning quickly into a question of legitimacy for the European Union.
Reason for TARGET2 funding
TARGET2 is a technical name for the system of internal accounting of monetary flows between the central banks that make up the European System of Central Banks. In a well balanced Eurozone, where the trade deficit of a member state is financed by a net flow of capital to that same member-state, the liabilities of that state’s central bank to the central banks of other states would just equal its assets.
Not true. Target 2 is about clearing balances that can cause banks to gain or lose liquidity independent of national trade balances.
Such a balanced flow of trade and capital would yield a TARGET2 figure near zero for all member-states.
Again, it’s not trade per se that alters bank liquidity issues.
And that was, more or less, the case throughout the Eurozone before the crisis.
However, the crisis caused major imbalances that were soon reflected in huge TARGET2 imbalances.
The clearing imbalances were caused by lack of credible deposit insurance exacerbated by potential bank failures, not trade per se.
As inflows of capital to the periphery dried up, and capital began to flow in the opposite direction, the central banks of the peripheral countries began to amass large net liabilities and the central banks of the surplus countries equally large net assets.
Yes, but not to confuse capital, which is bank equity/net worth, and liquidity which is the funding of assets and is sometimes casually called ‘capital’ the way ‘money’ is casually called capital.
The Eurozone’s designers had attempted to build a disincentive within the intraEurosystem real-time payments’ system, so as to prevent the build-up of huge liabilities on one side and corresponding assets on the other. This took the form of charging interest on the net liabilities of each national central bank, at an interest rate equal to the ECB’s main refinancing level.
The purpose of this policy rate is to make sure the ECB’s policy rate is the instrument of monetary policy, reflected as the banking system’s cost of funds.
These payments are distributed to the central banks of the surplus member-states, which then pass them on to their government treasury.
In practice, one bank necessarily has a credit balance at the ECB when another has a debit balance, and net debit balances exist to the extent there is actual cash in circulation that banks get in exchange for clearing balances. This keeps the banking system ‘net borrowed’ which provides the ECB with interest income. Additionally buying securities that yield more than deposit rates adds income to the ECB.
Thus the Eurozone was built on the assumption that TARGET2 imbalances would be isolated, idiosyncratic events, to be corrected by national policy action.
The system did not take account of the possibility that there could be fundamental structural asymmetries and a systemic crisis.
Today, the vast TARGET2 imbalances are the monetary tracks of the crisis. They trace the path of the consequent human and social disaster hitting mainly the deficit regions. The increased TARGET2 interest would never have accrued if the crises had not occurred. They accrue only because, for instance, risk averse Spanish and Greek depositors, reasonably enough, transfer their savings to a Frankfurt bank.
Yes, my point exactly, and somewhat counter to what was stated previously. Depositors can shift banks for a variety of reasons, with or without trade differentials.
As a result, under the rules of the TARGET2 system, the central bank of Spain and of Greece have to pay interest to the Bundesbank – to be passed along to the Federal Government in Berlin.
Which then pays interest to its depositors. The ECB profits to the extent it establishes a spread between the rate it lends at vs the rate paid to depositors. That spread is a political decision.
This indirect fiscal boost to the surplus country has no rational or moral basis. Yet the funds are there, and could be used to deflect the social and political danger facing Europe.
There is a strong case to be made that the interest collected from the deficit member-states’ central banks should be channelled to an account that would fund our proposed Emergency Social Solidarity Programme (ESSP). Additionally, if the EU introduces a financial transactions’ tax, or stamp duty proportional to the size of corporate balance sheets, a similar case can be made as to why these receipts should fund the ESSP. With this proposal, the ESSP is not funded by fiscal transfers nor national taxes.
The way I see it, functionally, it is a fiscal transfer, and not that I am against fiscal transfers!
My conclusion is that any improvement in the economy from these modest proposals, and as I’ve qualified above, will likewise be at least as modest. That is, the time and effort to attempt to implement these proposals, again, as qualified, will make little if any progress in fixing the economy as another generation is left to rot on the vine.
5. CONCLUSION: Four realistic policies to replace of five false choices Three years of crisis have culminated in a Europe that has lost legitimacy with its own citizens and credibility with the rest of the world. Europe is unnecessarily back in recession. While the bond markets were placated by the ECB’s actions in the summer of 2012, the Eurozone remains on the road toward disintegration.
While this process eats away at Europe’s potential for shared prosperity, European governments are imprisoned by false choices:
between stability and growth
between austerity and stimulus
between the deadly embrace of insolvent banks by insolvent governments, and an admirable but undefined and indefinitely delayed Banking Union
between the principle of perfectly separable country debts and the supposed need to persuade the surplus countries to bankroll the rest
between national sovereignty and federalism. These falsely dyadic choices imprison thinking and immobilise governments. They are responsible for a legitimation crisis for the European project. And they risk a catastrophic human, social and democratic crisis in Europe.
By contrast the Modest Proposal counters that:
The real choice is between beggar-my-neighbour deflation and an investmentled recovery combined with social stabilisation. The investment recovery will be funded by global capital, supplied principally by sovereign wealth funds and by pension funds which are seeking long-term investment outlets. Social stabilisation can be funded, initially, through the Target2 payments scheme.
Taxpayers in Germany and the other surplus nations do not need to bankroll the 2020 European Economic Recovery Programme, the restructuring of sovereign debt, resolution of the banking crisis, or the emergency humanitarian programme so urgently needed in the European periphery.
Neither an expansionary monetary policy nor a fiscal stimulus in Germany and other surplus countries, though welcome, would be sufficient to bring recovery to Europe.
Treaty changes for a federal union may be aspired by some, but will take too long , are opposed by many, and are not needed to resolve the crisis now. On this basis the Modest Proposal’s four policies are feasible steps by which to deal decisively with Europe’s banking crisis, the debt crisis, underinvestment, unemployment as well as the human, social and political emergency.
Version 4.0 of the Modest Proposal offers immediate answers to questions about the credibility of the ECB’s OMT policy, the impasse on a Banking Union, financing of SMEs through EIF bonds enabling a European Venture Capital Fund, green energy and high tech start-ups in Europe’s periphery, and basic human needs that the crisis has left untended.
It is not known how many strokes Alexander the Great needed to cut the Gordian knot. But in four strokes, Europe could cut through the knot of debt and deficits in which it has bound itself.
In one stroke, Policy 1, the Case-by-Case Bank Programme (CCBP), bypasses the impasse of Banking Union (BU), decoupling stressed sovereign debt and from banking recapitalisation, and allowing for a proper BU to be designed at leisure
By another stroke, Policy 2, the Limited Debt Conversion Programme (LDCP), the Eurozone’s mountain of debt shrinks, through an ECB-ESM conversion of Maastricht Compliant member-state Debt
By a third stroke, Policy 3, the Investment-led Recovery and Convergence Programme (IRCP) re-cycles global surpluses into European investments
By a fourth stroke, Policy 4, the Emergency Social Solidarity Programme (ESSP), deploys funds created from the asymmetries that helped cause the crisis to meet basic human needs caused by the crisis itself.
At the political level, the four policies of the Modest Proposal constitute a process of decentralised europeanisation, to be juxtaposed against an authoritarian federation that has not been put to European electorates, is unlikely to be endorsed by them, and, critically, offers them no assurance of higher levels of employment and welfare.
We propose that four areas of economic activity be europeanised: banks in need of ESM capital injections, sovereign debt management, the recycling of European and global savings into socially productive investment and prompt financing of a basic social emergency programme.
Our proposed europeanisation of borrowing for investment retains a large degree of subsidiarity. It is consistent with greater sovereignty for member-states than that implied by a federal structure, and it is compatible with the principle of reducing excess national debt, once banks, debt and investment flows are europeanised without the need for national guarantees or fiscal transfers.
While broad in scope, the Modest Proposal suggests no new institutions and does not aim at redesigning the Eurozone. It needs no new rules, fiscal compacts, or troikas. It requires no prior agreement to move in a federal direction while allowing for consent through enhanced cooperation rather than imposition of austerity.
It is in this sense that this proposal is, indeed, modest.