Stephanie Kelton: Consumers Need to Spend to Turn Economy Around
Category Archives: Employment
MMT to Obama- Use This Speech!
This is the speech I would make if I were President Obama:
My fellow Americans, let me get right to the point.
I have three bold new proposals to get back all the jobs we lost, and then some.
In fact, we need at least 20 million new jobs to restore our lost prosperity and put America back on top.
First let me state that the reason private sector jobs are lost is always the same.
Jobs are lost when business sales go down.
Economists give that fancy words- they call it a lack of aggregate demand.
But it’s very simple.
A restaurant doesn’t lay anyone off when it’s full of paying customers,
no matter how much the owner might hate the government,
the paper work, and the health regulations.
A department store doesn’t lay off workers when it’s full of paying customers,
And an engineering firm doesn’t lay anyone off when it has a backlog of orders.
Restaurants and other businesses lay people off when their customers stop buying, for any reason. So the reason we lost 8 million jobs almost all at once back in 2008 wasn’t because all of a sudden all those people decided they’d rather collect unemployment than work.
The reason all those jobs were lost was because sales collapsed.
Car sales, for example, collapsed from a rate of almost 17 million cars a year to just over 9 million cars a year.
That’s a serious collapse that cost millions of jobs.
Let me repeat, and it’s very simple, when sales go down, jobs are lost,
and when sales go up, jobs go up, as business hires to service all their new customers.
So my three proposals are specifically designed to get sales up to make sure business has a good paying job for anyone willing and able to work.
That’s good for businesses and all the people who work for them.
And these proposals are bipartisan.
They are supported by Americans ranging from Tea Party supporters to the Progressive left, and everyone in between.
So listen up!
My first proposal if for a full payroll tax suspension.
That means no FICA taxes will be taken from both employees and employers.
These taxes are punishing, regressive taxes that no progressive should ever support.
And, of course, the Tea Party is against any tax.
So I expect full bipartisan support on this proposal.
Suspending these taxes adds hundreds of dollars a month to the incomes of people working for a living. This is big money, not just a few pennies as in previous measures.
These are the people doing the real work.
Allowing them to take home more of their pay supports their good efforts.
Right now take home pay is barely enough to pay for food, rent, and gasoline, with not much left over. When government stops taking FICA taxes out of their pockets, they’ll be able to get back to more normal levels of spending.
And many will be able to better make their mortgage payments and their car payments,
which, by the way, is what the banks really want- people who can make their payments.
That’s the bottom up way to fix the banks, and not the top down bailouts we’ve done in the past.
And the payroll tax holiday is also for business, which reduces costs for business, which, through competition, helps keep prices down for all of us. Which means our dollars buy more than otherwise.
So a full payroll tax holiday means more take home pay for people working for a living,
and lower costs for business to help keep prices and inflation down,
so sales can go up and we can finally create those 20 million private sector jobs we desperately need.
My second proposal is for a one time $150 billion Federal revenue distribution to the 50 state governments with no strings attached.
This will help the states to fill the financial hole created by the recession,
and stay afloat while the sales and jobs recovery spurred by the payroll tax holiday
restores their lost revenues.
Again, I expect bipartisan support.
The progressives will support this as it helps the states sustain essential services,
and the Tea Party believes money is better spent at the state level than the federal level.
My third proposal does not involve a lot of money, but it’s critical for the kind of recovery that fits our common vision of America.
My third proposal is for a federally funded $8/hr transition job for anyone willing and able to work, to help the transition from unemployment to private sector employment.
The problem is employers don’t like to hire the unemployed, and especially the long term unemployed. While at the same time, with the payroll tax holiday and the revenue distribution to the states,business is going to need to hire all the people it can get. The federally funded transition job allows the unemployed to get a transition job, and show that they are willing and able to go to work every day, which makes them good candidates for graduation to private sector employment.
Again, I expect this proposal to also get solid bipartisan support.
Progressives have always known the value of full employment,
while the Tea Party believes people should be able to work for a living, rather than collect unemployment.
Let me add here that nothing in these proposals expands the role or scope of the federal government.
The payroll tax holiday is a cut of a regressive, punishing tax,
that takes the government’s hand out of the pockets of both workers and business.
The revenue distribution to the states has no strings attached.
The federal government does nothing more than write a check.
And the transition job is designed to move the unemployed, who are in fact already in the public sector, to private sector jobs.
There is no question that these three proposals will drive the increase in sales we need to
usher in a new era of prosperity and full employment.
The remaining concern is the federal budget deficit.
Fortunately, with the bad news of the downgrade of US Treasury securities by Standard and Poors to AA+ from AAA, a very important lesson was learned.
Interest rates actually came down. And substantially.
And with that the financial and economic heavy weights from the 4 corners of the globe
made a very important point.
The markets are telling us something we should have known all along.
The US is not Greece for a very important reason that has been overlooked.
That reason is, the US federal government is the issuer of its own currency, the US dollar.
While Greece is not the issuer of the euro.
In fact, Greece, and all the other euro nations, have put themselves in the position of the US states. Like the US states, Greece and other euro nations are not the issuer of the currency that they spend. So they can run out of money and go broke, and are dependent on being able to tax and borrow to be able to spend.
But the issuer of its own currency, like the US, Japan, and the UK,
can always pay their bills.
There is no such thing as the US running out of dollars.
The US is not dependent on taxes or borrowing to be able to make all of its dollar payments.
The US federal government can not go broke like Greece.
That was the important lesson of the S&P downgrade,
and everyone has seen it up close and personal and they all now agree.
And now they all know why, with the deficit at record high levels, interest rates remain at record low levels.
Does that mean we should spend without limit and not tax at all?
Absolutely not!
Too much spending and not enough taxing will surely drive up prices and inflation.
But it does mean that right now,
with unemployment sky high and an economy on the verge of another recession,
we can immediately enact my 3 proposals to bring us back to
a strong economy with good jobs for people who want them.
And some day, if somehow there are too many jobs and it’s causing an inflation problem,
we can then take the measures needed to cool things down.
But meanwhile, as they say, to get out of hole we need to stop digging,
and instead implement my 3 proposals.
So in conclusion, let me repeat these three, simple, direct, bipartisan proposals
for a speedy recovery:
A full payroll tax holiday for employees and employers
A one time revenue distribution to the states
And an $8/hr transition job for anyone willing and able to work to facilitate
the transition from unemployment to private sector employment as the economy recovers.
Thank you.
Payrolls/ISM
Karim writes:
Pretty bad payroll number that is likely to be enough to swing the Fed into action-at least Operation Twist, if not QE3
- Payrolls unch for August, though Verizon strike impact was 45k
- Net revisions -58k
- Unemployment rate unch at 9.1% on account of 331k gain in household survey (prior 2mths total -483k) and 366k gain in labor force
- Average hourly earnings -0.1% (0.5% prior mth)
- Index of aggregate hours -0.2%
- Manufacturing -3k from +36k
- Retail -8k from +26k
- Median duration of unemployment 21.8 weeks from 21.2
- U6 measure 16.2% from 16.1%
- Diffusion index 52.2 from 57.7
ISM yesterday showed production below 50, with other components holding up better. Anecdotes also show mixed results.
Possible that August was a temporary downturn, but Fed unlikely to take a chance on that and sit idle.
WHAT RESPONDENTS ARE SAYING…
“Earlier chemical price increases are beginning to soften.” (Chemical Products)
“Business is soft, confidence is down, and we are cutting inventory and expenses.” (Machinery)
“Exports continue to be strong — domestic weak.” (Computer & Electronic Products)
“Domestic sales are showing small improvements. International sales are showing larger improvements.” (Fabricated Metal Products)
“Demand remains constant and strong.” (Paper Products)
“Current headwinds in the national and international economic environment have increased uncertainty, and are affecting our customers’ willingness to commit to high-dollar equipment purchases.” (Transportation Equipment)
“We continue to post solid numbers, but the situation seems tenuous.” (Plastics & Rubber Products)
“Automotive business (represents 52 percent of our sales portfolio) continues to be strong. Core business has pulled back slightly.” (Apparel, Leather & Allied Products)
“Sales continue to be sluggish.” (Furniture & Related Products)
labor force participation rate
At least it took a break from going down.
I look at this as one of the better indicators of the output gap.
And don’t listen to that ‘it’s the demographics’ nonsense when it comes to this measure, thanks.
Serious heaps of slack out there.
EU Daily | Eurozone PMI at two-year low as new orders fall in all countries
Weakness and continued austerity. My guess is it will take serious blood in the streets before policy changes
IMF and eurozone clash over estimates
(FT) International Monetary Fund work, contained in a draft version of its Global Financial Stability Report, uses credit default swap prices to estimate the market value of government bonds of the three eurozone countries receiving IMF bail-outs – Ireland, Greece and Portugal – together with those of Italy, Spain and Belgium. Although the IMF analysis may be revised, two officials said one estimate showed that marking sovereign bonds to market would reduce European banks’ tangible common equity by about €200bn ($287bn), a drop of 10-12 per cent. The impact could be increased substantially, perhaps doubled, by the knock-on effects of European banks holding assets in other banks. The ECB and eurozone governments have rejected such estimates.
ECB Lends Euro-Area Banks 49.4 Billion Euros for Three Months(Bloomberg) The European Central Bank said it will lend euro-area banks 49.4 billion euros ($71.3 billion) in three-month cash. The ECB said 128 banks bid for the funds, which will be lent at the average of the benchmark rate over the period of the loan. The key rate is currently at 1.5 percent. Banks must repay 48.1 billion euros in previous three-month loans tomorrow. The ECB re-introduced an unlimited six-month loan this month and extended full allotment in its shorter-term operations through the end of the year as tensions on European money markets grew. ECB President Jean-Claude Trichet on Aug. 27 rejected the suggestion that there could be a liquidity crisis in Europe, citing the central bank’s non-standard measures.
Eurozone PMI at two-year low as new orders fall in all countries(Markit) Manufacturing PMI fell from 50.4 in July to 49.0 in August, its lowest level since August 2009 and below the earlier flash estimate of 49.7. National PMIs held just above the 50.0 no-change mark in Germany, the Netherlands and Austria, but signalled contractions in Ireland, France, Italy, Spain and Greece. Only the Irish PMI rose compared to July, but still remained in contraction territory. The weakness highlighted by the headline PMI reflected falling volumes of both output and new business in August. The Eurozone new orders-to-finished goods inventory ratio, which tends to lead the trend in production, fell to its lowest for almost two-and-a-half years.
European Central Bank Said To Purchase Italian Government BondsSept. 1 (Bloomberg) — The European Central Bank is buying Italian securities, according to two people with knowledge of the transactions. They declined to be identified because the transactions are confidential.
A spokesman for the ECB declined to comment.
Germans, Dutch, Finns to Meet on Crisis Amid Collateral SpatSept. 1 (Bloomberg) — The German, Dutch and Finnish finance ministers will meet on Sept. 6 in Berlin to discuss the euro-area debt crisis as a Finnish demand for collateral threatens to delay a second Greek bailout.
“We will discuss how to go forward with this crisis and the future,” Dutch Finance Minister Jan Kees de Jager told reporters in The Hague today. “It’s about fighting this fire, but more importantly, how do we prevent such a fire.”
Finland’s demand for collateral from Greece as a condition for contributing to a second rescue package has triggered calls for similar treatment from countries including Austria and the Netherlands. De Jager said an agreement on collateral shouldn’t take long to reach.
“I see room for a solution; there are proposals on the table to discuss,” De Jager said. “I think it will be possible to provide equal treatment for creditors without the disadvantage of the proposed deal between Finland and Greece, which is unthinkable because it uses extra money from the EFSF to provide collateral to Finland.”
The 440 billion-euro ($628 billion) European Financial Stability Facility is the euro region’s rescue fund.
Weidmann Says ECB Must Scale Back Crisis Measures to Reduce RiskSept. 1 (Bloomberg) — European Central Bank council member Jens Weidmann said the bank must scale back the additional risks it has shouldered to help counter the region’s debt crisis.
Measures taken by the ECB have “strained the existing framework of the currency union and blurred the boundaries between the responsibilities of monetary policy on one side and fiscal policy on the other,” Weidmann, who heads Germany’s Bundesbank, said at an event in Hanover today. Over time this can damage confidence in the central bank, he said. “It is therefore valid to scale back the extra risks monetary policy has taken on.”
The ECB is lending euro-area banks as much money as they need at its benchmark rate and has also re-started its bond purchase program — a step Weidmann opposed — in an attempt to stem the spreading debt crisis. While European leaders on July 21 re-tooled their 440-billion-euro ($629 billion) rescue fund, allowing it to buy government debt on the secondary market, national parliaments still need to ratify the changes.
“Decisions on taking further risks should be made by governments and parliaments, as only they are democratically legitimized,” Weidmann said.
He said one option for a long-term solution to Europe’s debt crisis could be “a real fiscal union.”
“Should one be unwilling or unable to take this path, then the existing no-bailout clause in the treaties, and the accompanying disciplining of fiscal policy, should be strengthened instead of being completely gutted,” he said.
Weidmann said his comments don’t relate to current economic developments or ECB policy, citing the one-week blackout prior to a rate decision. ECB officials will convene on Sept. 8 in Frankfurt.
German manufacturing PMI lowest since September 2009(Markit) At 50.9, down from 52.0 in July, the final seasonally adjusted Markit/BME Germany PMI was around one index point lower than the ‘flash’ figure of 52.0. Growth of German manufacturing output eased fractionally since the previous month and was the slowest since July 2009. Latest data pointed to a fall in intakes of new work for the second month running and the rate of contraction was the fastest since June 2009. The downturn in sales to export markets was highlighted by a further reduction in new business from abroad in August, with the rate of contraction also the sharpest for over two years. Meanwhile, stocks of finished goods at manufacturing firms accumulated at the steepest pace since the survey began in April 1996.
German Trade, Consumption Damped Second-Quarter GDP Growth(Bloomberg) Private consumption contracted 0.7 percent in the second quarter. GDP increased 0.1 percent from the first quarter, when it gained 1.3 percent, the office said, confirming its initial Aug. 16 estimate. Exports rose 2.3 percent from the first quarter, when they gained 2.1 percent. Imports surged 3.2 percent in the second quarter after rising 1.7 percent in the first. That resulted in net trade reducing GDP growth by 0.3 percentage point. Companies stocked up inventories, which contributed 0.7 percentage point to GDP growth. Gross investment also added 0.7 percentage point to growth. Private consumption subtracted 0.4 percentage point and a 0.9 percent decline in construction spending cut 0.1 percentage point off GDP.
Carrefour posts net loss in 1st half(AP) Europe’s largest retailer Carrefour SA posted an unexpected net loss in the first half and abandoned its growth target for the year amid the economic slowdown. The French retailer reported a net loss of euro249 million ($359 million) in the first six months of the year, compared with a profit of euro97 million a year earlier. Carrefour said it expects its operating profit to decline this year, reversing a target the retailer set in March when it said an ongoing and expensive “transformation plan” would raise profits this year. As it did last year, Carrefour booked what it calls “significant one-off charges” again in the first half. They amounted to euro884 million in the first half, over half of which went to writing down the value of Carrefour’s Italian assets.
Greece set to miss deficit target(AP) Greece is likely to miss its budget targets in 2011 even if it fully implements painful reforms a parliamentary panel of financial experts said. “The increase in the primary deficit in combination with a further drop in economic activity strengthens significantly the dynamics of debt, offsetting the benefits from the decisions of the summit of July 21, and distancing the possibility of stabilization of the debt to GDP in 2012,” the panel, known as the State Budget Office, wrote in a report. Citing government figures, it said the 2011 January-July deficit stands at euro15.59 billion ($22.53 billion) with a primary deficit of 2.4 percent of gross domestic product, as opposed to a euro12.45 billion ($17.99 billion) shortfall and 1.5 percent primary deficit in that period last year.
Italy Drops Pension Changes, Will Announce Budget Amendments(Bloomberg) The Italian government has dropped proposed changes to pension rules agreed to this week from a 45.5 billion-euro ($65.5 billion) austerity plan being discussed in parliament that aims to balance the budget by 2013. Giorgia Meloni, minister for youth and sport policy, told reporters that the government decided to withdraw the proposal agreed to by Prime Minister Silvio Berlusconi and Finance Minister Giulio Tremonti two days ago. On Aug. 29, Berlusconi’s office announced that the government had dropped a planned bonus tax on Italians earning more than 90,000 euros a year and reduced cuts in transfers to regional and local authorities. It did not provide details of how the lost deficit reduction of 4.5 billion euros from those changes would be compensated.
Crisis exposes weakness of Italian coalition(FT) Giulio Tremonti, finance minister, was said to be in “damage limitation” mode on Wednesday, seeking to assure Italy’s partners that a budget could still get through parliament’s twin chambers by the end of next week, despite prime minister Silvio Berlusconi’s decision to jettison some key proposals, including a wealth tax. Three weeks after the centre-right cabinet agreed an austerity package – with €45.5bn ($65.4bn) of savings intended to balance the budget by 2013 – the government on Wednesday missed its self-imposed deadline to present legislation to the senate, the first step towards parliamentary approval. Insiders admit, however, that the budget could amount to a stopgap measure, the second since July, and might need to be reinforced at a later date.
Spanish PM: deficit cap amendment essential(AP) “It is true that it is a reform done in a very short time span, because we need it,” Prime minister Jose Luis Rodriguez Zapatero said. The amendment of the 1978 constitution enshrines the principle of budgetary discipline into Spain’s constitution, but does not specify numbers. These will come in a separate law that is to be passed by June 2012. The Socialists and conservatives have agreed the law will stipulate that Spain’s deficit cannot exceed 0.4 percent of GDP, but that threshold will not take effect until 2020. Their support is enough for the bill to pass when it is voted on Friday in the lower house of Parliament and presumably next week in the Senate. Time is pressing because the legislature dissolves Sept. 27 in order to get ready for general elections Nov. 20.
Spain Expects ‘Chain’ of Market Turbulence, Valenciano Says(Bloomberg) “We’re probably going to get back into a chain of financial turbulence in September and October,” Elena Valenciano, Socialist party campaign chief, said in an interview. Valenciano said the constitutional amendment is necessary as Spain must avoid following Greece, Ireland and Portugal into seeking a European bailout. “We have to say this because sometimes talking of a rescue seems almost something positive: any kind of intervention in Spain would be a great misfortune for the country,” she said. Valenciano said authorities “didn’t expect August to be as bad as it was” and that the gap may widen again in the next two months, “not so much because of our own debt, but because of Italy’s debt.”
Portugal Raises Taxes to Meet Deficit Targets in Rescue Plan(Bloomberg) Portugal will raise capital gains tax and increase levies on corporate profit and high earners to reach the deficit-reduction goals in its 78 billion-euro ($112 billion) bailout. The government will impose a tax surcharge of 3 percent on companies with income above 1.5 million euros, add a bonus tax of 2.5 percent on the highest earners and raise the levy on capital gains by 1 percentage point to 21 percent, Finance Minister Vitor Gaspar said. The moves will help trim the budget deficit from 5.9 percent of gross domestic product this year to the European Union ceiling of 3 percent in 2013, he said. The shortfall will narrow to 0.5 percent in 2015. The government will reduce its deficit even as the economy contracts 2.2 percent this year and 1.8 percent next year, before expanding 1.2 percent in 2013, he said.
Ireland’s unemployment rate rises to 14.4 percent(AP) Ireland’s unemployment rate has risen to 14.4 percent. Ireland has been trying to escape its 3-year recession through export growth led by its multinational companies. But the domestic economy remains dormant because of weak consumer demand, high household debts and a collapsed real-estate market. The Central Statistics Agency said Wednesday that unemployment rose from July’s rate of 14.3 percent, the fourth straight monthly increase. A record-high 470,000 people in Ireland, a country of 4.5 million, are claiming welfare payments for joblessness. About 17 percent are foreigners, chiefly Eastern Europeans who immigrated during the final years of Ireland’s 1994-2007 Celtic Tiger boom.
Jackson Hole- comments tomorrow’s speech by Fed Chairman Bernanke
First, I see no public purpose in burning any crude oil to fly the Chairman and his entourage to make any speech.
He could just as easily deliver this one from the steps of the Fed in DC.
Congress should demand a statement of public purpose before endorsing any travel by its agents.
Next is what I expect from the speech.
The short answer is not much.
I don’t see more QE as the purpose of QE is to bring long rates down, and they are already down substantially. And the Fed now has sufficient evidence to confirm that long rates are mainly a function of expectations of future FOMC votes on rate settings.
To that point, when the Fed announced QE, and market participants believed it would spur growth, and therefore FOMC rate hikes somewhere down the road, long rates worked their way higher. And when the Fed ended QE, and market participants believed the economy would be slower to recover, long rates worked their way lower. Not to mention China hates QE and it still looks to me there’s an understanding in place where China allocates reserves to $US as long as the Fed doesn’t do any QE.
The Fed could cut it’s target Fed funds rate, the cost of funds for the banking system, down to 0 and lower that cost of funds by a few basis points. But those few basis points can hardly be expected to have much effect on anything.
It’s not the Fed has run out of bullets, it’s that the Fed has never had any bullets of any consequence.
And with the few it’s fired, it hasn’t realized the odds are the gun has been pointed backwards.
For example, it still looks to me lower rates, if anything, reduce aggregate demand via the interest income channels.
And QE isn’t much other than a tax on the economy, that also removes interest income.
So look for a forecast of modest GDP growth with downside risks, core inflation remaining reasonably firm even as unemployment remains far too high, all of which support continued Fed ‘accommodation’ at current levels.
Spending Cuts, Not Tax Hikes, Best for Deficit: NABE
Spending cuts have higher multiples, but in any case it’s all beside the point.
The problem is the deficit is too small, not too large.
After the post S&P downgrade discussions, where all agree the US govt ‘prints the dollar’
the argument that there could be a Greek like financial crisis has quietly vanished.
The only remaining case against the deficit,
which no one is making,
for obvious reasons,
is that inflation from ‘overspending’ is too high, and even higher levels of unemployment are needed to fight inflation.
Spending Cuts, Not Tax Hikes, Best for Deficit: NABE
August 22 (AP) — The majority of economists surveyed by the National Association for Business Economics believe that the federal deficit should be reduced only or primarily through spending cuts.
The survey out Monday found that 56 percent of the NABE members surveyed felt that way, while 37 percent said they favor equal parts spending cuts and tax increases. The remaining 7 percent believe it should be done only or mostly through tax increases.
As for how to reduce the deficit, nearly 40 percent said the best way would be to contain Medicare and Medicaid costs. Nearly a quarter recommended overhauling the tax system and simplifying tax rates and exemptions. About 15 percent said the government should enact tough spending caps and cut discretionary spending.
The latest survey by the NABE was conducted in the two weeks ending Aug. 2, the day that the Senate passed and President Obama signed legislation to cut spending by more than $2 trillion and raise the nation’s debt ceiling.
The agreement managed to avert a potential default, but Standard & Poor’s downgraded U.S. credit from AAA to AA+, citing the political wrangling over the deal as a reason.
According to the survey of 250 economists who are members of NABE, nearly 49 percent of those responding said the country’s fiscal policy should be more restrictive, while nearly 37 percent said they believe the government should do more to stimulate the economy. The remainder said fiscal policy should remain the same.
At the same time, more than 70 percent of the people that responded said they expect U.S. fiscal policy to be more restrictive over the next two years.
payroll tax hike on the way?
GOP may OK tax increase that Obama hopes to block
By Charles Babington
August 22 (AP) — News flash: Congressional Republicans want to raise your taxes. Impossible, right? GOP lawmakers are so virulently anti-tax, surely they will fight to prevent a payroll tax increase on virtually every wage-earner starting Jan. 1, right?
Apparently not.
Many of the same Republicans who fought hammer-and-tong to keep the George W. Bush-era income tax cuts from expiring on schedule are now saying a different “temporary” tax cut should end as planned. By their own definition, that amounts to a tax increase.
Former Massachusetts Gov. Mitt Romney did not flatly rule out an extra year for the payroll tax cut, but he “would prefer to see the payroll tax cut on the employer side” to spur job growth, his campaign said.
Romney completely misses the point, unless he wants it known he’s for favoring employers over employees?
Jobs come mainly from sales, and cutting payroll taxes for workers increases spending, sales, and jobs.
Cutting payroll taxes for business also has benefits, as that reduces costs which puts downward pressure on prices which helps consumers and does thereby add to sales, but in a much smaller way.
I continue to propose we suspend FICA entirely.
Looks to me like this latest discussion will only strengthen suspicions that Republicans are trying to keep the economy from improving to hurt the President’s chances of winning next year.
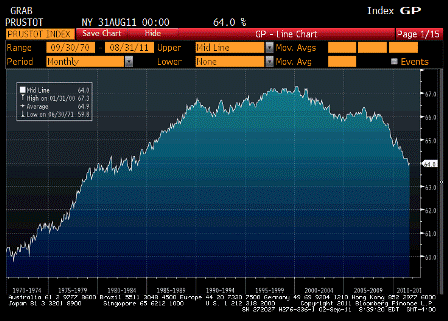
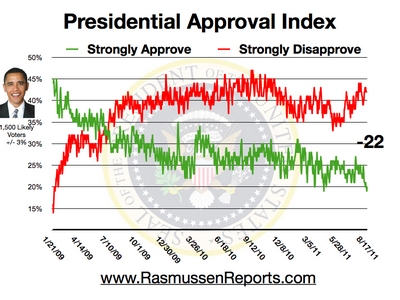
President Obama’s ratings slipping
As bad as it’s ever been.
I could turn it all around over a two day weekend.
Full FICA suspension
One time revenue distribution to the state govts of $500 per capita
$8/hr Federally funded transition job for anyone willing and able to work
(see my ‘proposals’ on this website)
Unemployment starts falling towards 4%
Stocks double in short order bailing out pension funds
Strong approve would go to 65%
Strong disapprove would go to less than 35%…
Jobless Claims Dip, Still in Range; Trade Deficit Jumps
As previously discussed, the real economy seems to be muddling through, and at firmer levels than the first half of the year.
The trade report will probably result in Q2 GDP being revised down to just below 1%, but up from the .4% reported for Q1
So Q3 still looks like it will be at least as strong as q2 and likely higher with lower gasoline prices and Japan coming back some.
With corporate profits still looking reasonably strong, corporations continue to demonstrate they can do reasonably well even with low GDP growth and high unemployment.
And with a federal deficit of around 9% of GDP continually adding income, sales, and savings I don’t see a lot of downside to GDP, sales, and profits, though a small negative print is certainly possible.
Jobless Claims Dip, Still in Range; Trade Deficit Jumps
August 11 (Reuters) — New U.S. claims for unemployment benefits dropped to a four-month low last week, government data showed on Thursday, a rare dose of good news for an economy that has been battered by a credit rating downgrade and falling share prices.
Initial claims for state unemployment benefits fell 7,000 to a seasonally adjusted 395,000, the Labor Department said, the lowest level since the week ended April 2.
Economists polled by Reuters had forecast claims steady at 400,000. The prior week’s figure was revised up to 402,000 from the previously reported 400,000.
The Federal Reserve said on Tuesday economic growth was considerably weaker than expected and unemployment would fall only gradually. The U.S. central bank promised to keep interest rates near zero until at least mid-2013.
Hiring accelerated in July after abruptly slowing in the past two months. However, there are worries that a sharp sell-off in stocks and a nasty fight between Democrats and Republicans over raising the government’s debt ceiling could dampen employers’ enthusiasm to hire new workers.
The continued improvement in the labor market could help to allay fears of a new recession, which have been stoked by the economy’s anemic growth pace in the first half of the year.
A Labor Department official said there was nothing unusual in the state-level claims data, adding that only one state had been estimated.
The four-week moving average of claims, considered a better measure of labor market trends, slipped 3,250 to 405,000. Economists say both initial claims and the four-week average need to drop close to 350,000 to signal a sustainable improvement in the labor market.
The number of people still receiving benefits under regular state programs after an initial week of aid dropped 60,000 to 3.69 million in the week ended July 30.
The number of Americans on emergency unemployment benefits fell 26,309 to 3.16 million in the week ended July 23, the latest week for which data is available.
A total of 7.48 million people were claiming unemployment benefits during that period under all programs, down 89,945 from the prior week.
Trade Gap Grows
The US. trade gap widened in June to its largest since October 2008, as both U.S. imports and exports declined in a sign of slowing global demand, a government report showed on Thursday.
The June trade deficit leapt to $53.1 billion, surprising analysts who expected it to narrow to $48 billion from an upwardly revised estimate of $50.8 billion in May.
Overall U.S. imports fell by close to 1 percent, despite a rise in value of crude oil imports to the highest since August 2008. Higher volume pushed the oil import bill higher, as the average price for imported oil fell to $106 per barrel after rising in each of the eight prior months.
U.S. exports fell for a second consecutive month to $170.9 billion, as shipments to Canada, Mexico, Brazil, Central America, France, China and Japan all declined.
