In fact, no one on the FOMC has called for QE3, so it’s highly unlikely with anything short of actual negative growth.
So the question is, why the unamimous consensus?
I’d say it varies from member to member, with each concerned for his own reason, for better or for worse.
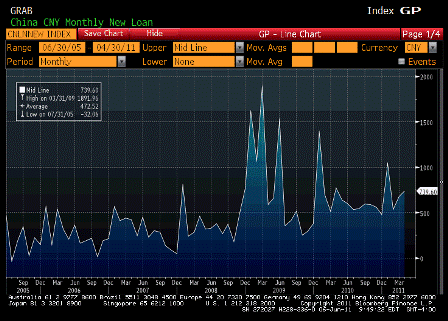
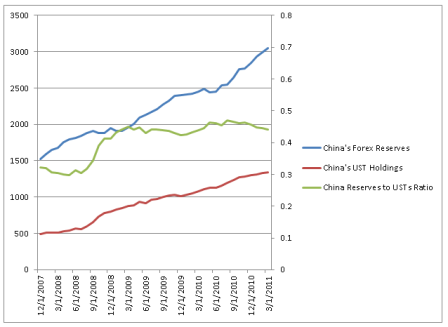
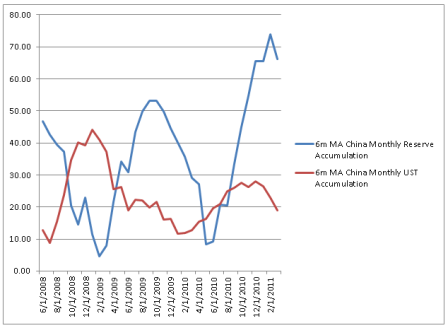
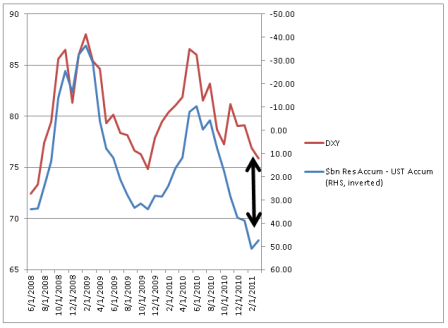
And I do think the odds of their being an understanding with China are high, particularly with China having let their T bill portfolio run off, while directing additions to reserves to currencies other than the $US, as well as evidence of a multitude of other portfolio managers doing much the same thing. This includes buying gold and other commodities, all in response to (misguided notions of) QE2 and monetary and fiscal policy in general. So the Fed may be hoping to reverse the (mistaken) notion that they are ‘printing money and creating inflation’ by making it clear that there are no plans for further QE.
Hence the ‘new’ strong dollar rhetoric: no more ‘monetary stimulus’ and lots of talk about keeping the dollar strong fundamentally via low inflation and pro growth policy. And the tough talk about the long term deficit plays to this theme as well, even as the Chairman recognizes the downside risks to immediate budget cuts, as he continues to see the risks as asymetric. The Fed believes it can deal with inflation, should that happen, but that it’s come to the end of the tool box, for all practical purposes, in their fight against deflation, even as they fail to meet either of their dual mandates of full employment and price stability to their satisfaction.
They also see downside risk to US GDP from China, Japan, and Europe for all the well publicized reasons.
And, with regard to statements warning against immediate budget cuts, I have some reason to believe at least one Fed official has read my book and is aware of MMT in general.
Bernanke Admits Economy Slowing; No Hint of New Stimulus
June 7 (Reuters) — Federal Reserve Chairman Ben Bernanke Tuesday acknowledged a slowdown in the U.S. economy but offered no suggestion the central bank is considering any further monetary stimulus to support growth.
He also issued a stern warning to lawmakers in Washington who are considering aggressive budget cuts, saying they have the potential to derail the economic recovery if cuts in government spending take hold too soon.
A recent spate of weak economic data, capped by a report Friday showing U.S. employers expanded payrolls by a meager 54,000 workers last month, has renewed investor speculation the economy could need more help from the Fed.
“U.S. economic growth so far this year looks to have been somewhat slower than expected,” Bernanke told a banking conference. “A number of indicators also suggest some loss in momentum in labor markets in recent weeks.”
He said the recovery was still weak enough to warrant keeping in place the Fed’s strong monetary support, saying the economy was still growing well below its full potential.
At the same time, Bernanke argued that the latest bout of weakness would likely not last very long, and should give way to stronger growth in the second half of the year. He said a recent spike in U.S. inflation, while worrisome, should be similarly transitory. Weak growth in wages and stable inflation expectations suggest few lasting inflation pressures, Bernanke said.
On the budget, Bernanke repeated his call for a long-term plan for a sustainable fiscal path, but warned politicians against massive short-term reductions in spending.
“A sharp fiscal consolidation focused on the very near term could be self-defeating if it were to undercut the still-fragile recovery,” Bernanke said.
“By taking decisions today that lead to fiscal consolidation over a longer horizon, policymakers can avoid a sudden fiscal contraction that could put the recovery at risk,” he said.
All Tapped Out?
The central bank has already slashed overnight interest rates to zero and purchased more than $2 trillion in government bonds in an effort to pull the economy from a deep recession and spur a stronger recovery.
With the central bank’s balance sheet already bloated, officials have made clear the bar is high for any further easing of monetary policy. The Fed’s current $600 billion round of government bond buying, known as QE2, runs its course later this month.
Sharp criticism in the wake of QE2 is one factor likely to make policymakers reluctant to push the limits of unconventional policy. They also may have concerns that more stimulus would face diminishing economic returns, while potentially complicating their effort to return policy to a more normal footing.
But a further worsening of economic conditions, particularly one that is accompanied by a reversal of recent upward pressure on inflation, could change that outlook.
The government’s jobs report Friday was almost uniformly bleak. The pace of hiring was just over a third of what economists had expected and the unemployment rate rose to 9.1 percent, defying predictions for a slight drop.
In a Reuters poll of U.S. primary dealer banks conducted after the employment data, analysts saw only a 10 percent chance for another round of government bond purchases by the central bank over the next two years. Dealers also pushed back the timing of an eventual rate hike further into 2012.
The weakening in the U.S. recovery comes against a backdrop of uncertainty over the course of fiscal policy and bickering over the U.S. debt limit in Congress, with Republicans pushing hard for deep budget cuts.
Fragility is Global
Hurdles to better economic health have emerged from overseas as well. Europe is struggling with a debt crisis, while Japan is still reeling from the effects of a traumatic earthquake and tsunami.
In emerging markets, China is trying to rein in its red-hot growth to prevent inflation.
Fed policymakers have admitted to being surprised by how weak the economy appears, but none have yet called for more stimulus.
In an interview with the Wall Street Journal, Chicago Federal Reserve Bank President Charles Evans, a noted policy dove, said he was not yet ready to support a third round of so-called quantitative easing. His counterpart in Atlanta, Dennis Lockhart, also said the economy was not weak enough to warrant further support.
While Boston Fed President Eric Rosengren told CNBC Monday the economy’s weakness might delay the timing of an eventual monetary tightening, the head of the Dallas Federal Reserve Bank, Richard Fisher, said the Fed may have already done too much.
Evans and Fisher have a policy vote on the Fed this year while Rosengren and Lockhart do not.