[Skip to the end]
My take is an RTC type solution only works when the government owns the institutions, so this will probably be different.
I suspect it will be more like Japan, where the government bought a new class of preferred stock in the banks to add capital.
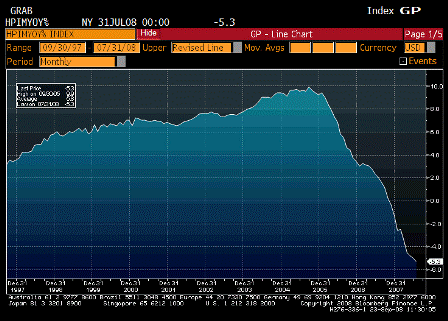
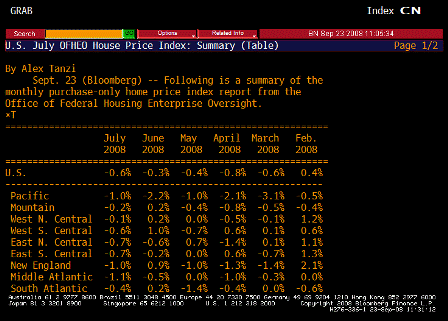
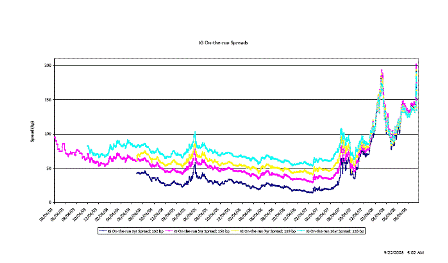
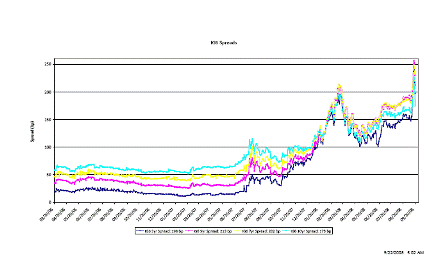
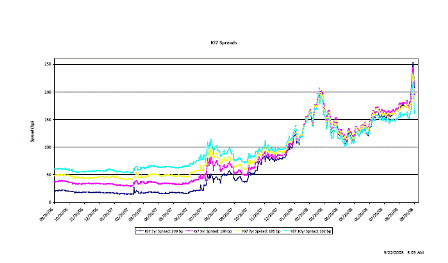
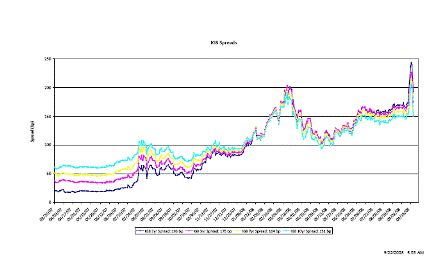
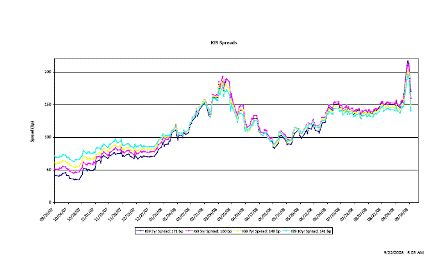
Whatever they will do will cause credit spreads to come in, which will make the assets of AIG far more valuable and probably result in a ‘profit’ for the government.
Unsold Lehman assets will also appreciate.
More comments below:
by Alison Vekshin and Dawn Kopecki
Government Options
Options that U.S. officials are considering include establishing an $800 billion fund to purchase so-called failed assets
I see this as problematic as above and as below.
and a separate $400 billion pool at the Federal Deposit Insurance Corp. to insure investors in money-market funds, said two people briefed by congressional staff. They spoke on condition of anonymity because the plans may change.
This puts money funds on par with insured bank deposits. Seems no need for both.
Instead, better to remove the $100,000 cap on bank deposit insurance to allow large investors use bank deposits safely. There is no economic reason for the low cap in any case.
Another possibility is using Fannie and Freddie, the federally chartered mortgage-finance companies seized by the government last week, to buy assets, one of the people said.
That’s already in place. They already have treasury funding to buy mortgages.
“We will try to put a bill together and do it fairly quickly,” House Financial Services Committee Chairman Barney Frank, a Massachusetts Democrat, said after the meeting. “We are not in a position to give you any specifics right now” on the proposals, he said when asked about the potential cost.
The likelihood of the government taking on yet more devalued assets, after the seizures of Fannie, Freddie and AIG and the earlier assumption by the Fed of $29 billion of Bear Stearns Cos. investments, may spur concern about its own balance sheet.
We need to get past this concern about government solvency. It’s simply not an operational issue.
Debt Concern
The Treasury has pledged to buy up to $200 billion of Fannie and Freddie stock to keep them solvent, while the Fed agreed Sept. 16 to an $85 billion bridge loan to AIG. The Treasury also plans to buy $5 billion of mortgage-backed debt this month under an emergency program.
“It sounds like there’s going to be a giant dumpster for illiquid assets,” said Mirko Mikelic, senior portfolio manager at Fifth Third Asset Management in Grand Rapids, Michigan, which oversees $22 billion in assets. “It brings up the more troubling question of whether the U.S. government is big enough to take on this whole problem, relative” to the size of the American economy, he said.
This is ridiculous and part of the problem that got us to this point.
[top]