[Skip to the end]
(an email exchange)
>
> On Wed, Aug 6, 2008 at 4:45 PM, Craig wrote:
>
> It seems that the ‘right’ price for them to set oil at is not
> necessarily the highest price possible.
>
All the 911 passports were Saudi; so, they might have other agendas.
>
> If I were them it would seem like the best policy to maximize
> the total value of their oil holdings over the life of those
> holdings. By cranking the price up ‘too high’, they incent
> substitution and potentially kill their sales in the long term.
>
Right, classic monopoly analysis.
> It would seem their goal would be to keep the price as high
> as they could w/o setting off a chain of
> substitution/invention/philosophy which would move the world
> meaningfully away from oil (or towards increased oil exploration
> or towards invading them). There is also the little matter of
> how much money do they really need (a somewhat silly question
> but this situation does create an embarrassment of riches/market
> dislocations in excess of where a rational accumulation might lie).
>
Yes, understood.
>
> It looks to me that on the highs they got everybody’s attention.
> There may still be political responses towards
> innovation/substitution/conservation at these levels, but it seems
> likely that at or above the old highs, US folks will be making their
> next car a hybrid, beating their government to get prices down
> (including pluggables/nuclear – a long term threat to Saudi
> dominance) and the like. Then there’s China’s slowdown and food
> riots. I’d have thought quietly bleeding the world would be better
> business than actually setting it on fire.
>
Yes, but again, it’s their ‘political choice.’ There is no ‘market price’.
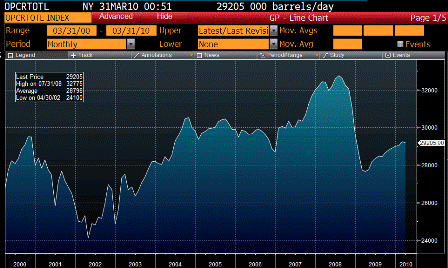
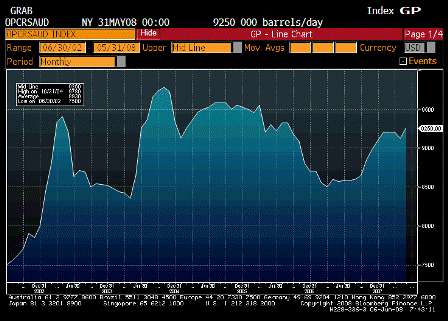
Also, with only 1.5 million bdp in total excess capacity, it might be too close to the line for them, and they might want to get prices high enough to build their excess capacity by a million or two bpd.
Otherwise they risk losing control of price on the upside, as happened a couple of years back when output briefly hit 10.5 million bpd when the funds were buying intensely enough to cause builds of physical inventory and a large contango as storage went to a premium.
>
> Of course, even if this is all true, they may be looking at it
> differently.
>
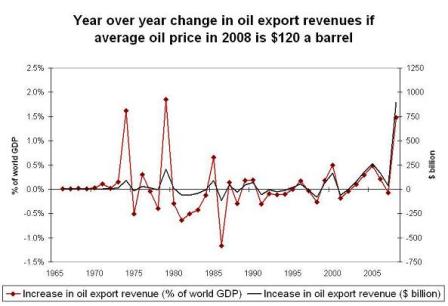
Worst case for us is they understand that they can hike all they want if they spend the extra revenues on imports of real goods and services. This keeps foreign GDPs muddling through in positive territory as they exact ever higher real terms of trade and they increasingly prosper at our expense.
And out leaders think more exports and less consumption is a good thing and are encouraging more of same.
Almost seems from the data this is exactly what they are up to?
Think they read my blog???
:)
warren
>
> Craig
>
[top]