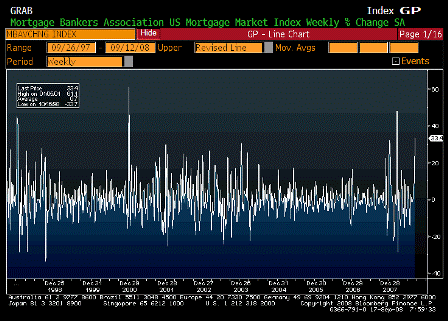
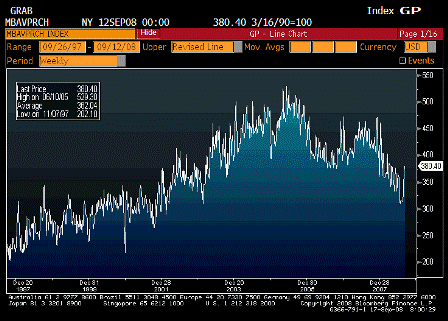
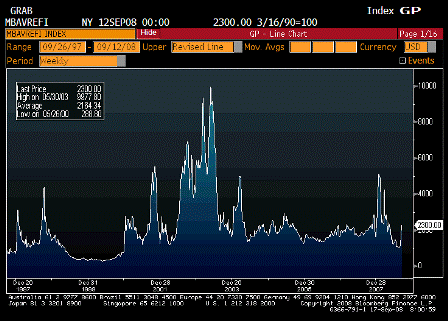
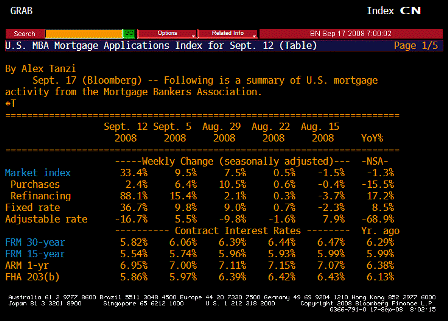
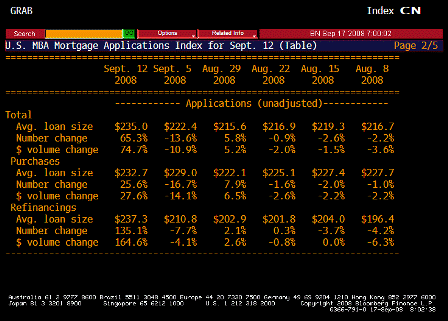
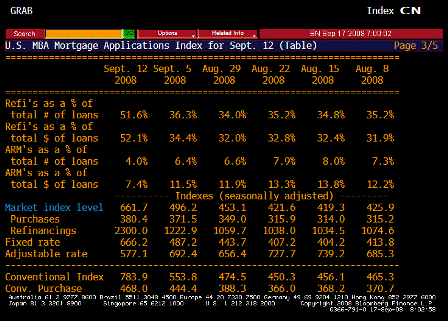
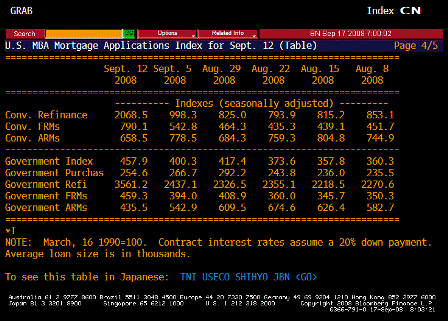
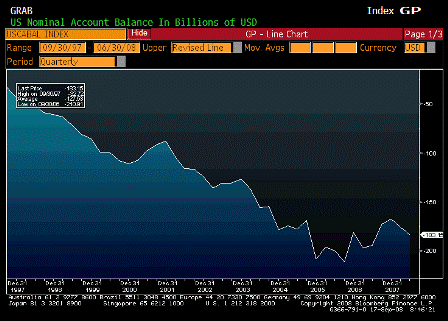
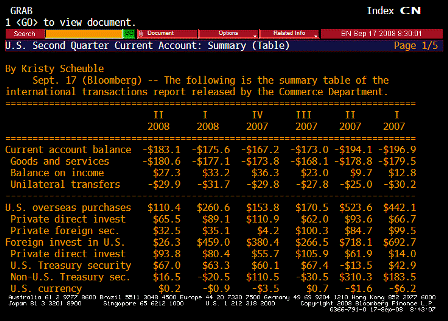
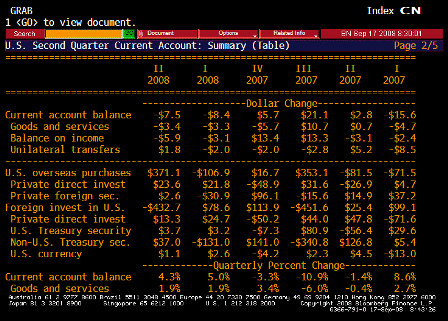
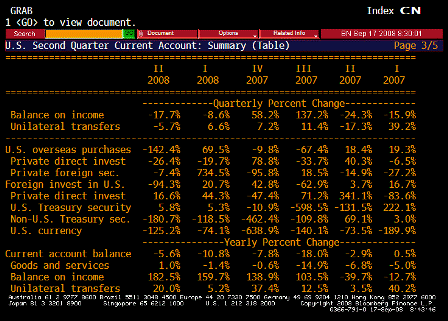
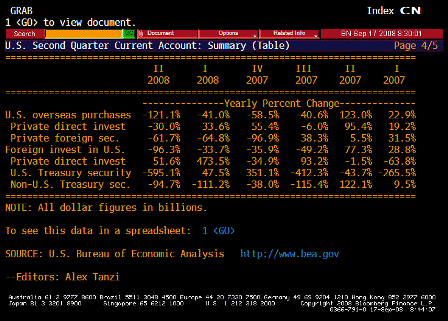
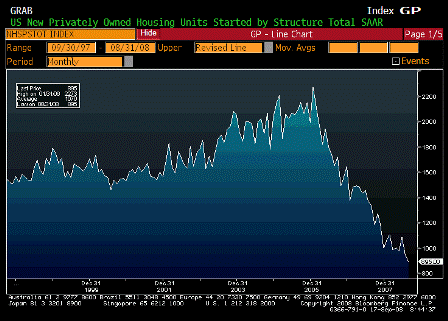
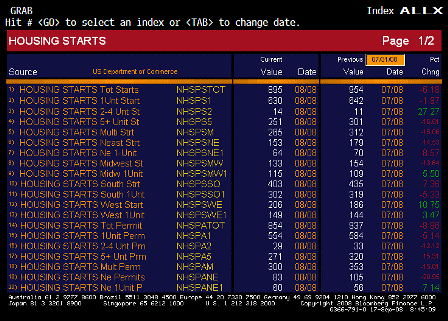
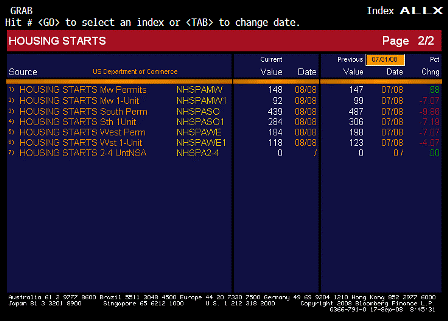
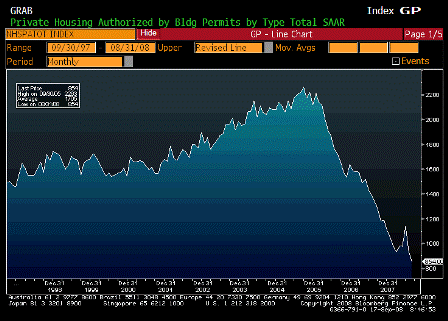
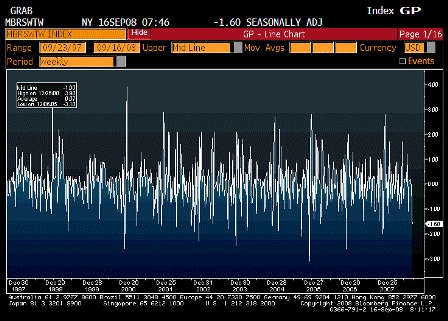
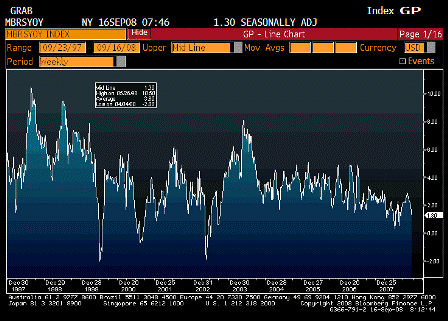
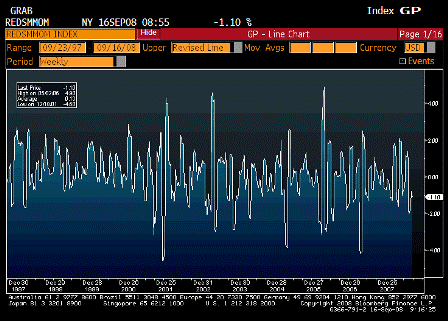
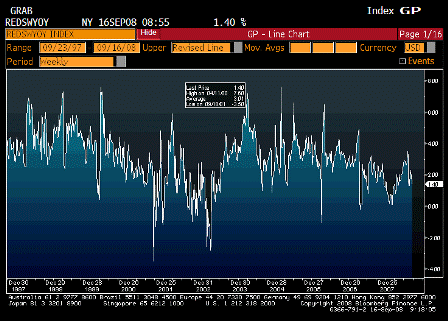
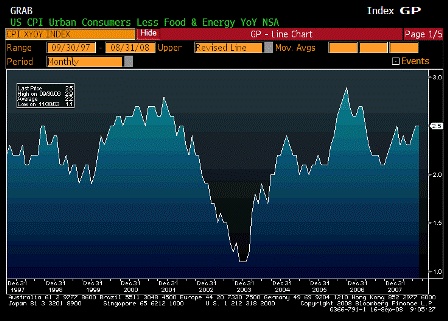
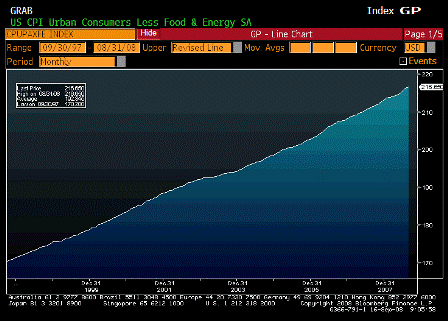
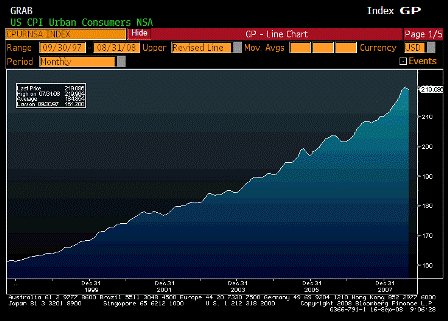
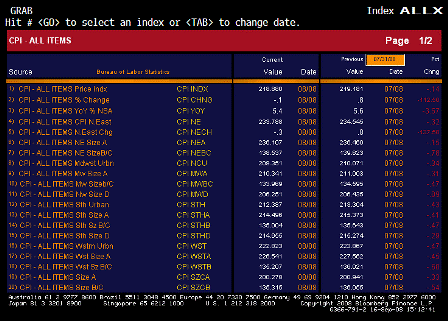
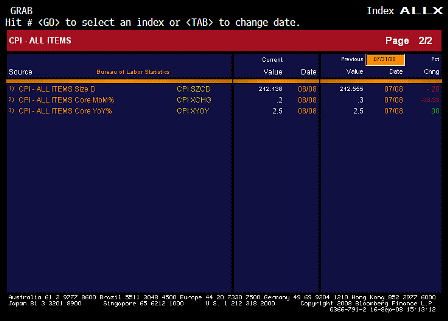
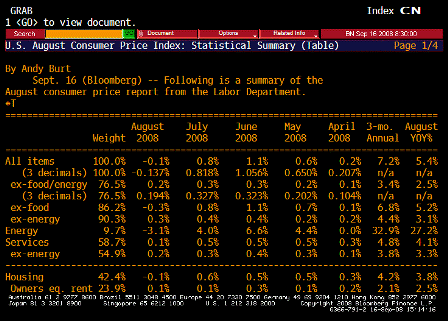
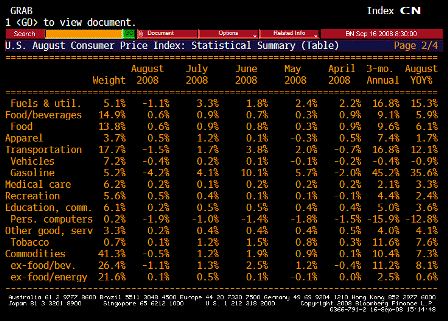
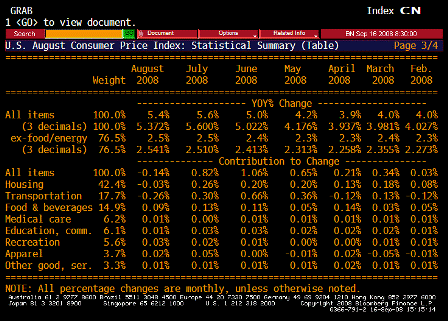
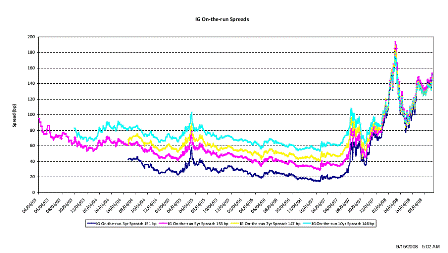
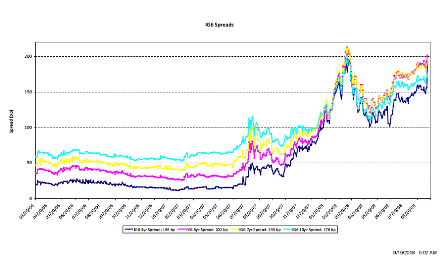
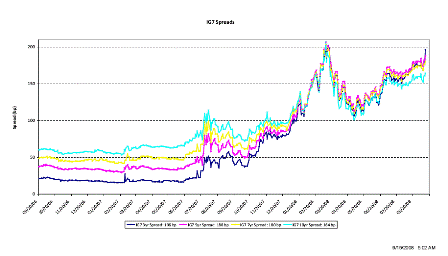
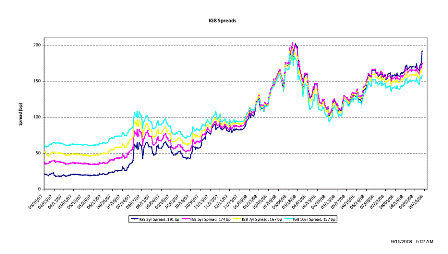
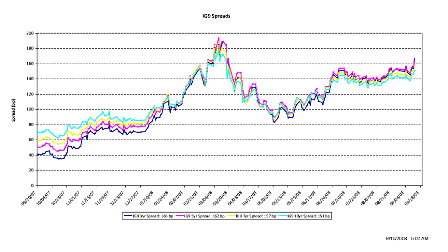
What’s happening is the world desire to net accumulate euro financial assets has increased and can only be achieved by the rest of the world net selling goods and services (or real assets) to the eurozone.
Europe Trade Deficit Widens to Record on Exports, Energy Costs
by Fergal O’Brien
Sept. 17 (Bloomberg) Europe’s trade gap widened to a record in July as a cooling global economy damped exports and crude oil’s advance to a record boosted the energy deficit.
The 15-nation euro region had a seasonally adjusted deficit of 6.4 billion euros ($9.1 billion), compared with a 3.5 billion-euro trade gap in June, the European Union’s statistics office in Luxembourg said today. The July deficit is the largest since the euro was introduced in 1999.
Euro-area exports to the U.S., the second-biggest buyer of the region’s goods, have fallen the most since 2003 this year as economic expansion there has eased. At the same time, record oil prices pushed up spending on imported fuels such as gasoline and heating oil by 41 percent, further widening the trade gap.
“On the one side, you’re getting weakness in exports and that then is feeding through to weaker industrial production,” said Marco Valli, an economist at Unicredit MIB in Milan. “On the other side, there is the oil prices and in July we will see the maximum impact of that, as oil peaked in early July.”
Crude oil reached a record $147.27 a barrel on July 11 and the euro region’s energy imports soared 41 percent to 151 billion euros in the first half, according to today’s report. The detailed data are published with a one-month lag.
The soaring energy costs boosted imports from Russia, which supplies 34 percent of Europe’s imported oil and 40 percent of its imported gas. Overall imports from Russia, home of OAO Gazprom, the world’s biggest gas producer, soared 22 percent in the first half and the euro area’s trade gap with the nation soared 25 percent to 20.4 billion euros, today’s report showed.
First-Half Decline
The detailed data for the January-June period also showed exports to the U.S., the world’s largest economy, fell 4 percent from a year earlier. That is the biggest first-half decline since a 9 percent drop in 2003. Shipments to the U.K., the euro area’s biggest trading partner, rose 1 percent.
The euro reached a record above $1.60 to the dollar in July, taking its gain over the previous 12 months to 15 percent. The euro’s strength undermines the competitiveness of European goods sold abroad. The currency was at $1.4224 today, down 11 percent from its record.
A slowdown in overseas sales has curbed production at Europe’s factories and dragged the region’s economy into its first contraction in almost a decade in the second quarter. Manufacturing activity has contracted for the last three months, according to a monthly survey of purchasing managers, while export orders have fallen for five months.
`Mightily Relieved’
“Euro-zone exporters will be mightily relieved by the recent marked retreat in the euro from its July peak,” said Howard Archer, chief European economist at Global Insight in London. “However, this is being countered by slowing global growth and a very uncertain outlook.”
Some companies have tried to offset falling U.S. orders by expanding in Asia and oil-exporting countries. Asian sales at French skin-creams maker Clarins SA rose 3 percent in the second quarter as North American sales fell by the same percentage.
Volkswagen AG, Europe’s biggest carmaker, on Sept. 8 said emerging markets will provide the fastest growth in worldwide sales over the next 10 years, led by economic expansion in Asia and Russia.
Europe’s trade deficit with China, which last year overtook the U.K. to become the euro area’s biggest supplier, narrowed by 1.2 percent to 49.9 billion euros in the six months through June. Exports to Asia’s second biggest economy rose 15 percent.
Economists had expected the euro region to show a trade deficit of 3.5 million euros in July, compared with an initially reported 3 billion-euro deficit in June, according to the median of nine estimates in a Bloomberg News survey.
[top]