Again, very well stated!
Thaler’s Corner
I must admit that I am at a loss for words these days. The analytical items at our disposal describe a situation so complex, given a myriad of contradictory influences, that I find it impossible to develop any sort of reasonable scenario.
I have spent a lot of time in recent weeks exchanging ideas and perceptions with academics, political officials and others in an effort to develop a coherent explanation of the events unfolding before us (Cyprus, wealth tax, etc.), but the conclusions are anything but conclusive!
Changes in financial securities will no longer be determined by purely economic factors but more and more by political decisions, such as whether or not to establish a real European banking union with all that implies in terms of cross-border budget transfer risks.
Whatever, lets take a look at the state of the real economy in the United Sates and Europe, given that it is still a bit early to draw any sort of conclusions about a third economic motor, Japan.
By the way, I strongly recommend that people check out the links in todays Macro Geeks Corner toward the end of the newsletter. It is interesting to see how two fairly divergent schools of thinking (the two first texts) end up with rather similar conclusions.
United States
In the United States, the economy is (logically) slowing as the effects of the Sequester slowly make themselves felt. Only the (increasingly discredited) partisans of Reinhold & Rogoffs constructive austerity thought it would not affect household consumption.
We had to wait for the hike in payroll taxes for the effect to be seen in retail sales figures, down 0.4% in March. Similarly, all the latest leading economic (PMI) and confidence indicators came in below expectations, which augurs for a soft patch in the US.
Moreover, the yens decline can only have a negative impact on America trade balance with Japan as it puts US exporters at a disadvantage, in particular, as they compete with their Japanese rivals on Asian markets. And the pitiful state of the European economy is not going to help this sector of the US economy either.
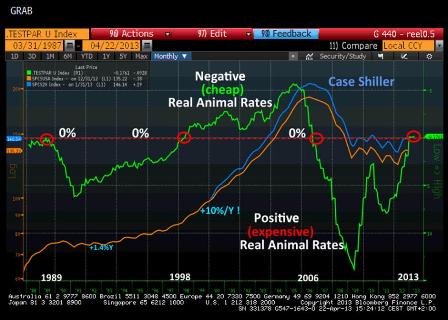
But there remains one bright spot, namely the residential real estate market, which should remain a powerful support in the quarters ahead. Check out one of my favorite graphs real animal rates.
Real animal rates in the US:
Full size image
These rates are calculated using a proprietary equation I developed, which includes, in addition to terms like mortgage interest rates, recent home price trends, the difference between the reported unemployment rate and that during periods of full employment, and the difference between the average length of unemployment and that existing in times of full employment.
With the Animal Spirits so dear to Keynes and behavioral science in mind, the goal was to factor in items more subjective than simple economic criteria (nominal borrowing rates) in the home purchase decision-making process of a household.
If experience has taught us anything, it is that the factors which most influence a potential homebuyers decision is his degree of job security and the feeling that prices can only rise.
The first point is that the only time these real animal rates dipped into negative territory (in the upper part of graph, transcribed in inverted scale) corresponds perfectly with the great real estate bubble of 1998 to 2006.
This big trend reversal occurred in 2006 when rates resurfaced above zero and thus below the graphs red line.
The only other time real animal rates became negative was in 1989, but that was abruptly reversed by the sharp hike in nominal interest rates.
In the current context, nominal interest rates are unlikely to undergo any such sharp hike in the quarters ahead, and this dip of real animal rates into negative territory should enable the real estate market to continue to recover. This all the more true, given that the yens decline will only strengthen disinflationary trends in North America, which ensure accommodative monetary policies for some time to come!
All you need to do is look at the steep decline in inflationary expectations, as expressed by the TIPS market in the US, to understand that investors seem to have finally realized that QE policies have nothing to do with the so-called dollar printing press. Notwithstanding the ZeroHedge paranoids!
That said, existing home sales in the US, out just a few minutes ago, came in weak, at -0.6% m-o-m (vs expected +0.4%, i.e. 4.92M vs 5M), which explains this afternoon shiver on stockmarket indices.
Now, as the IMF has said in recent days, the main brake on a worldwide recovery is the Eurozone, which remains paralyzed by the obsession of its northern member states on austerity and by the ECBs total and unforgivable incapacity to comply with its own mandate! In todays Macro Geeks Corner, you will find two instructive links on this matter.
Eurozone
Instead of harping on the endless stream of errors made by our beloved European monetary and governmental leaders, I prefer to comment on some far more instructive graphs.
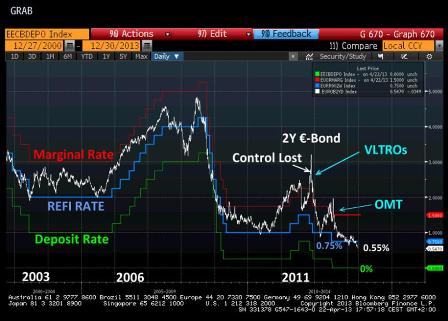
Lets start with our graph on aggregate 2-year Eurozone government bond rates, which have proven to be so useful in recent years for evaluating the ECBs reaction function.
This rate, currently at a record low 0.55%, is now well below the 0.75% set for the refi. This stems from two factors.
First, in view of the state of the economy and the latest comments by certain ECB board members, investors expect that the refi rate will very soon (May or June) be cut to 0.50%.
Second, certainty that short-term interest rates, like the Eonia, which have been stuck between 5 bps and 12 bps for the past 9 months, are not going to rise anytime soon is pushing investors to seek yields wherever they can still find them, like in Spain and Italy where 2-year bonds still fetch between 1.95% and 1.25%, now that they are assured that, henceforth, in case of insolvency, bank depositors will be forced to pay the bill without pushing sovereign issuers into default, as happened in Greece!
Aggregated Eurozone government 2-year rate:
Full size image
However, we have reason to be concerned that the ECB, if it does lower the refi to 0.50%, will be satisfied with what it already deems a low rate and highly accommodative monetary policy. Such is far from being the case, even if we go by the ECBs own obsolete aggregates, like M3, as money velocity continues to skid to a halt, following Cyprus.
And all this has an impact on the real economy, as you can see in the following graphs.
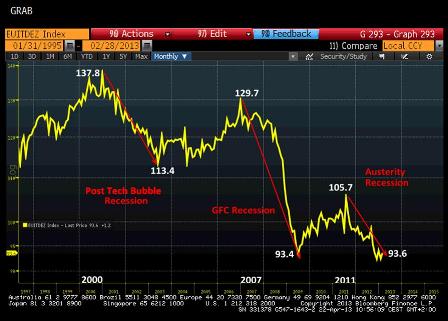
Eurozone Industrial Production
Full size image
The least we can say is that this graph is particularly distressing. Of course, it does not account for the economys industrial aspect, which some call the old economy. But it provides a whole lot of jobs and no economic area can afford to neglect it.
And the impact of Mr Sarkozys renowned Walk of Canossa, following his summons by Ms Merkel in July 2011 to Berlin where the unfortunate decision to create the first sovereign default of a developed country was endorsed (Greek PSI), is very clear on this graph. Together with a hardening of austerity policies and the nefarious consequences of the ECBs hikes of benchmark interest rates in the spring of 2011, this decision torpedoed already distressed economies, with the consequences we all know today.
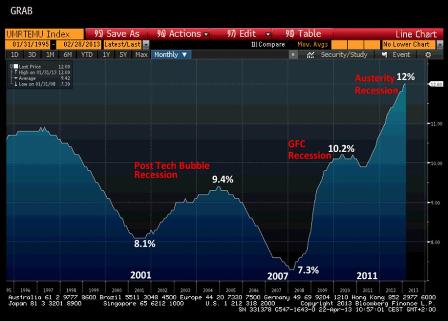
But if there is one depressing economic indicator, which reflects even more cruelly how austerity affected the Eurozone, it is surely the unemployment curve.
Eurozone Unemployment
Full size image
Here again, no comment is needed. I included earlier in this newsletter the graph comparing the US and Eurozone curves, but even that is no longer all that relevant. If people are happy to underperform the United States, who cares? If the Eurozone wants to try liquidationist economic policies to help drive home the morality message, it has every right to do so, just as its citizens merit the leadership they elect.
But to go from there to creating a situation of hysteria, leading to an increasingly large segment of the active population being ejected from the labor market, is a big step that must never be taken.
In some countries, the figures are just horrifying, with nearly 30% general unemployment and over 50% for those under 25 years of age. It is incredible that some continue to boast the merits of such policies for countries like Ireland while ignoring the daily siphoning of the population due to massive immigration to seek jobs elsewhere!!
I wonder if those responsible for such policies have forgotten the consequences of such an approach in Europe and the breakdown in the social fabric during the Great Depression, especially now, with so many leaders spicing their speeches with anti-German references?
This pathetic situation, reflecting month after month of economic policies based on no worthwhile or credible foundations, be it on a theoretical or empirical basis, explains why I am having a hard time re-establishing a decent pace of publication.
This is especially so in that the conflict between this depressive macro situation and the strong efforts undertaken by the Fed and the BoJ (among others) to reignite economic activity leave no space for laying out clear asset allocation biases.
We continue to enable our clients to take advantage of opportunities on option markets which make it possible during these troubled times to make bets on the cheap but without any real conviction.
Has our asset allocation strategy, dating from 2007 (a bit early, I know), of favoring government debt came to maturity with German 10-year rates at 1.23%, i.e. more than 30 bps below those of the United States?
Will European stock markets continue to suffer from our big fear, the Japanese syndrome? Or will popular pressure push the ECB and the Austrian School proponents to realize that they have a modern currency at their disposal and that reversing their entire intellectual edifice is possible?
Despite all my efforts, studies, reading and discussion, I am totally incapable of responding to these questions, which a great lesson in humility. Sorry for the consequences in terms of this newsletters clarity and frequency of publication, but if anyone has any ideas, I am all ears!
The Macro Geeks Corner:
Dear Northern Europeans Monetary easing is not a bailout
A factual rebuttal of remarks of ECB chief Jrg Asmussen, made at the Bank of America/Merrill Lynch Investor conference
Breaking bad inflation expectations