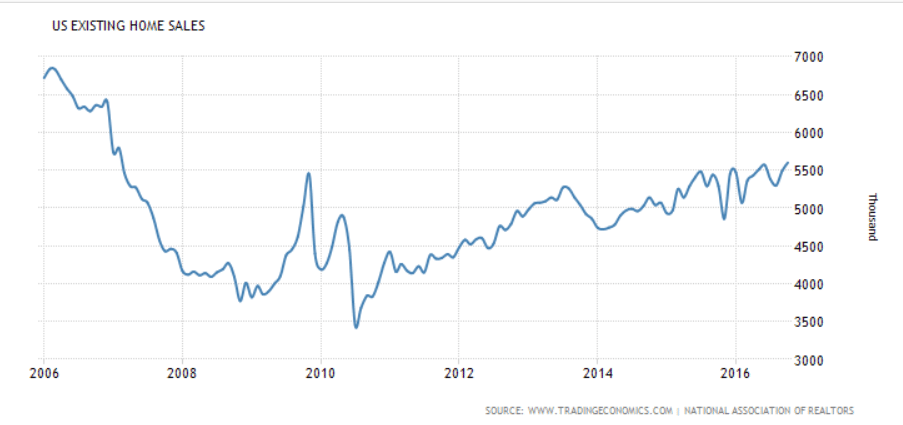
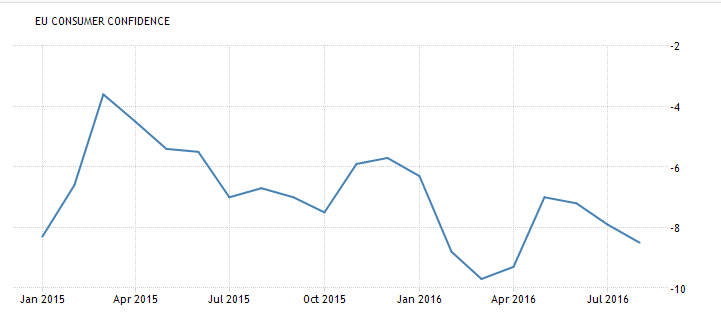
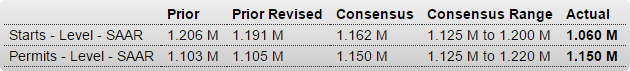
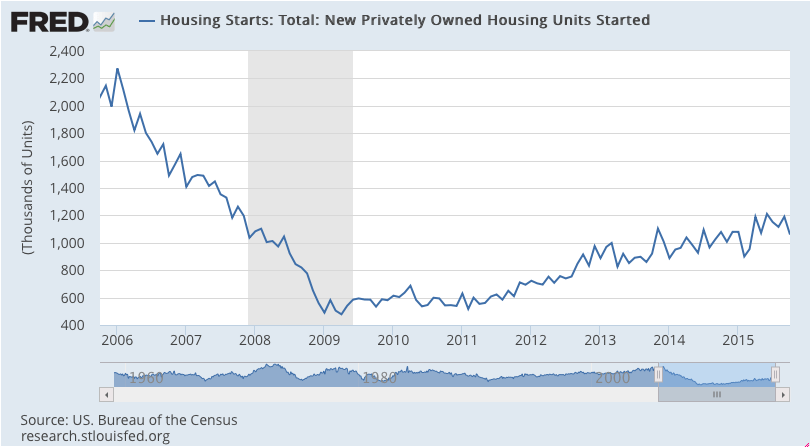
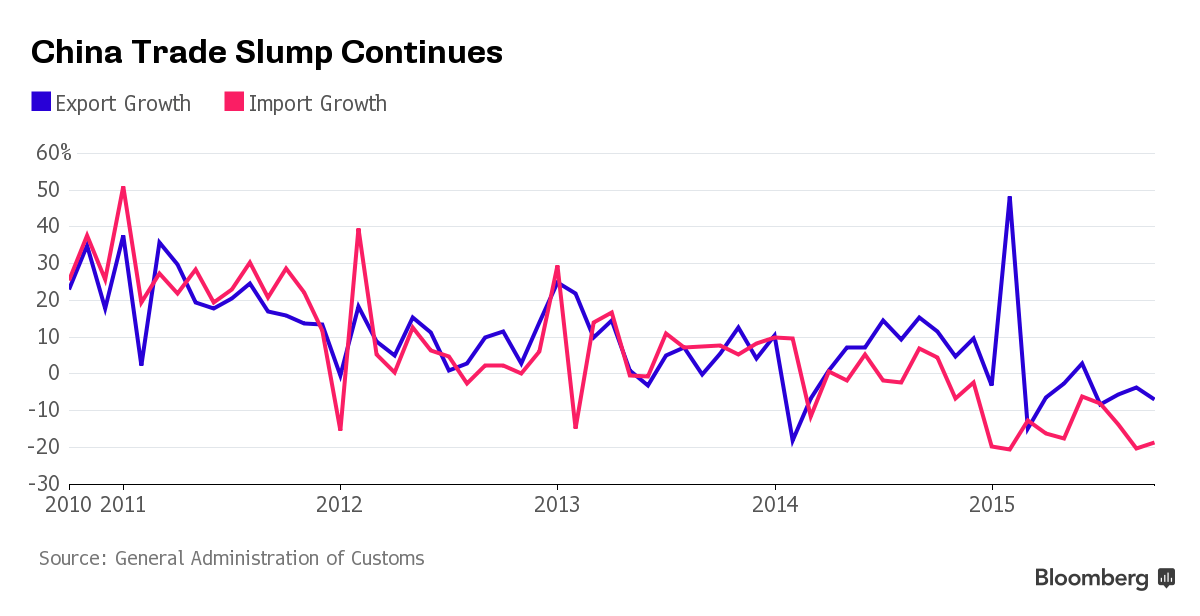
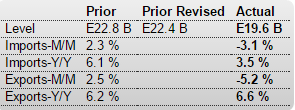
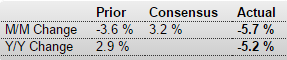
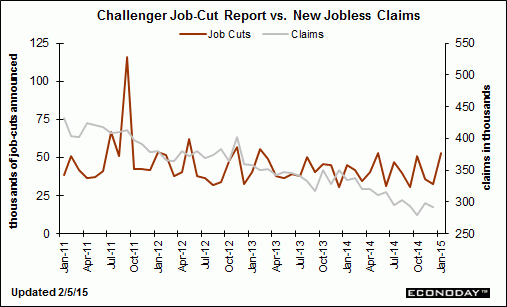
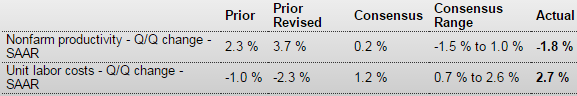
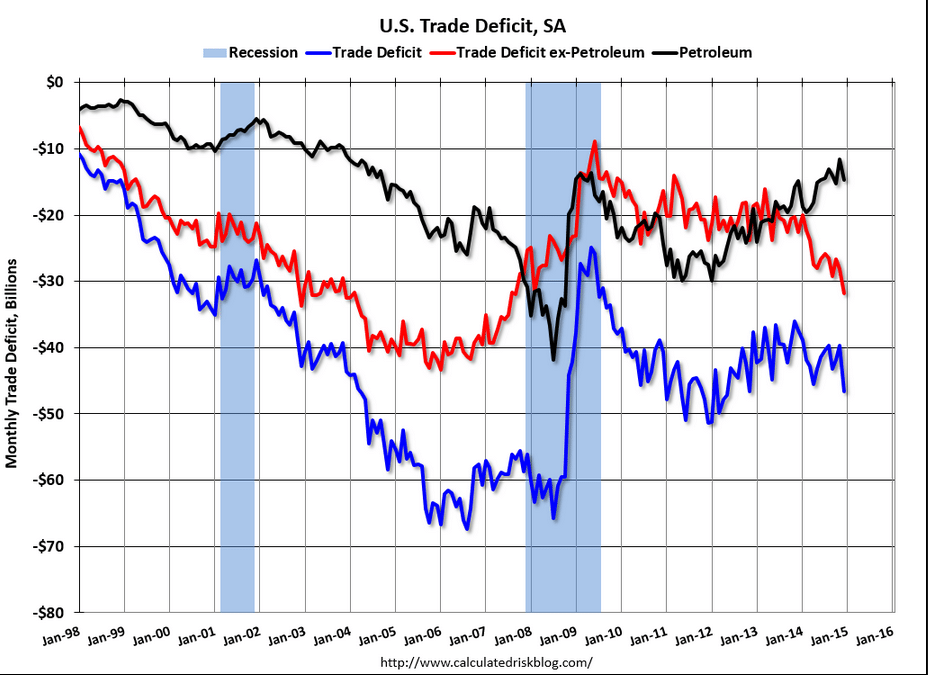
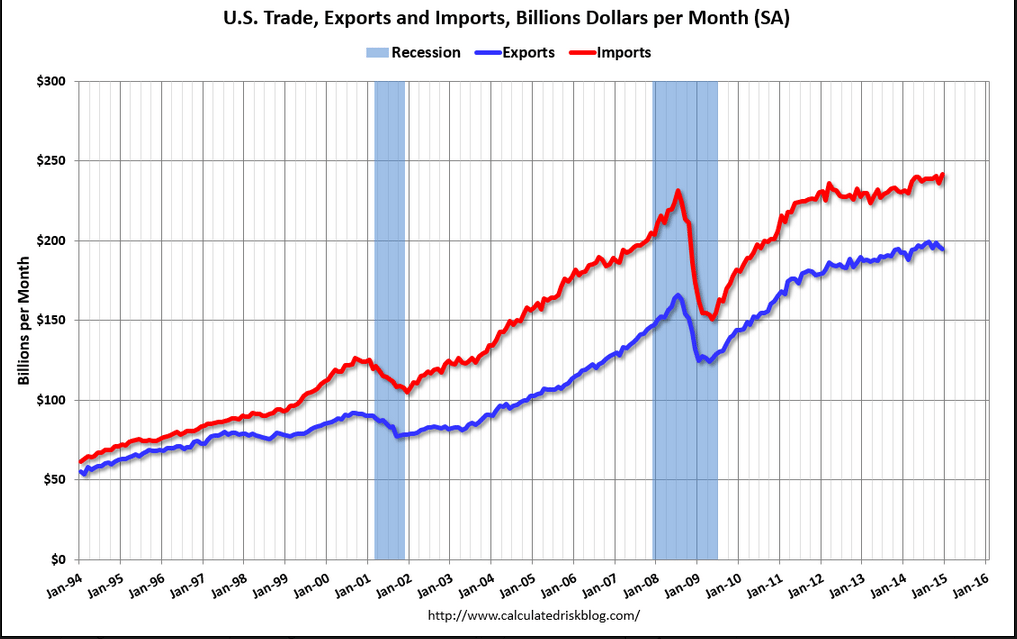
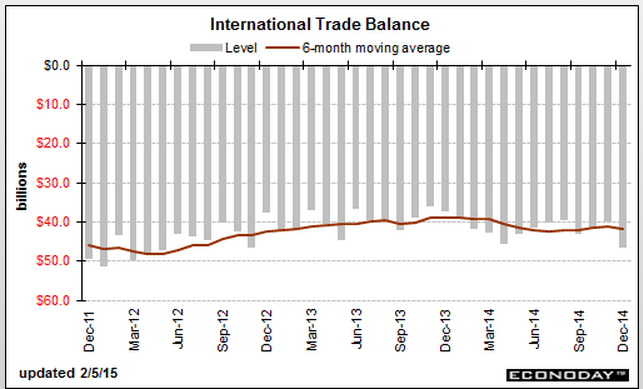
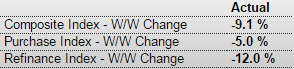
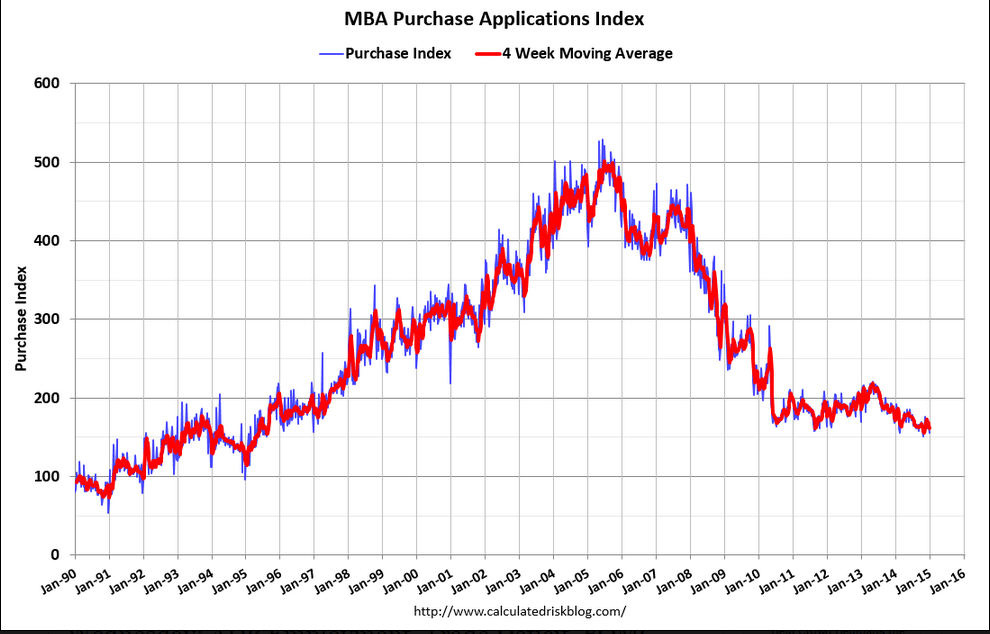
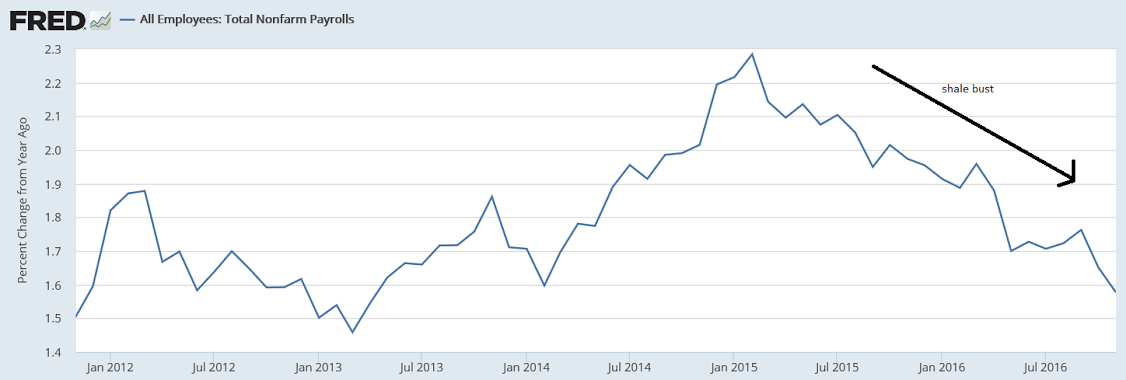
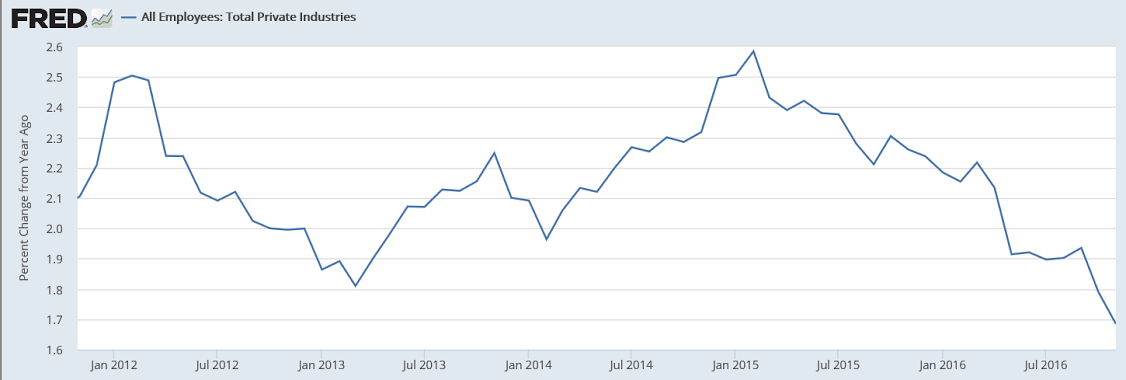
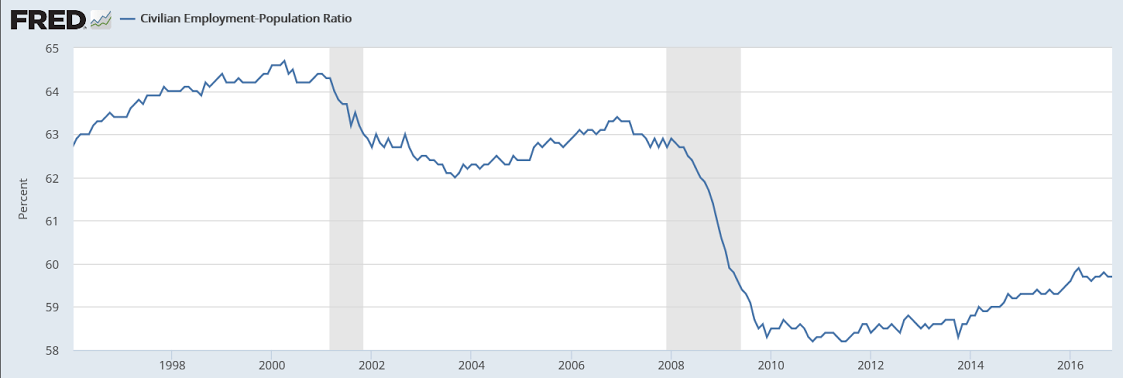
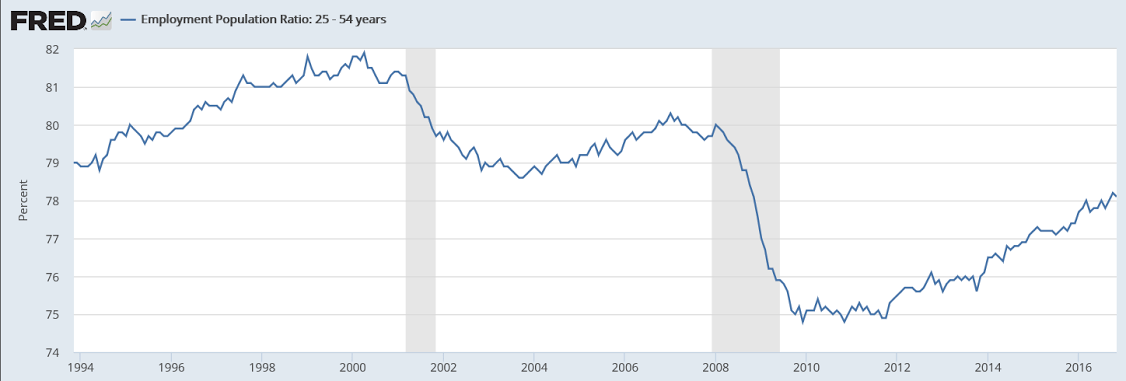
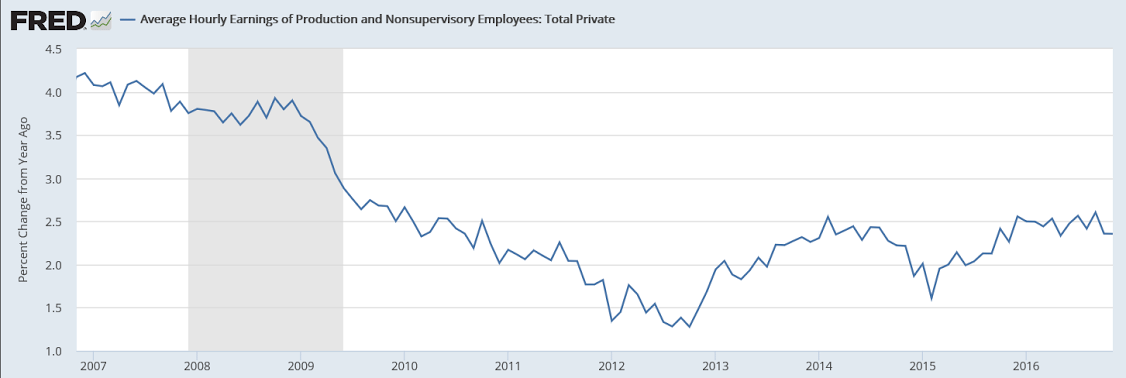
Year over year growth continues to decelerate, and wage growth remains critically low. And participation rates further evidence a massive shortage of aggregate demand, and it’s all only getting worse:

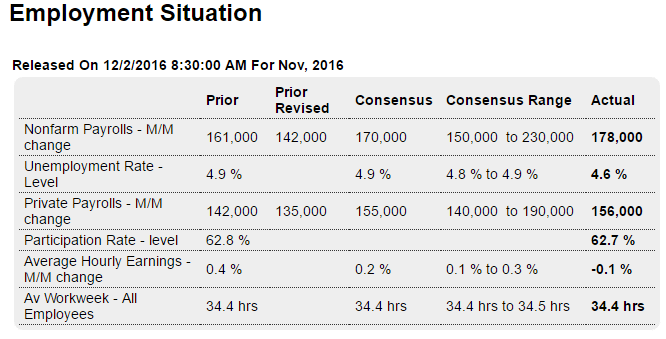
Highlights
Payroll growth is solid and the unemployment rate is down sharply, but not all the indications from the November report employment are favorable. Nonfarm payrolls rose 178,000 in November to just beat out expectations with revisions no factor, as a sharp downward revision to October, now at 142,000, is offset by a nearly as sharp upward revision to September, now at a sizable 208,000. The unemployment rate fell a very sharp 3 tenths to 4.6 percent for the lowest reading of the cycle, since August 2007.
But now the less positive news. The dip in the unemployment rate is tied, not to greater growth in employment, but to a dip in the participation rate, down 1 tenth to 62.7 percent. And a headline negative in the report is a surprise 0.1 percent decline in average hourly earnings, the first negative reading of the year and more than reversing October’s very strong 0.4 percent gain and driving down the year-on-year rate from a cycle high of 2.8 percent back down to 2.5 percent where it last was in August.
But payrolls are positive and led in November by another major gain for professional & services, up 63,000, and a 14,000 gain for the temporary help subcomponent. Gains in these readings point to demand for short-term labor in lieu of finding full-time labor. Construction is another positive, up 19,000 and reflecting strength in residential building. A negative is an 8,000 decline in retail which indicates that retailers are not gearing up much for the holidays.
For policy makers, the unemployment rate is now at their long-term target though participation is soft — and inflation is still lagging, factors that will give the doves some debate points at what is otherwise likely to be a rate-hike meeting the week after next.
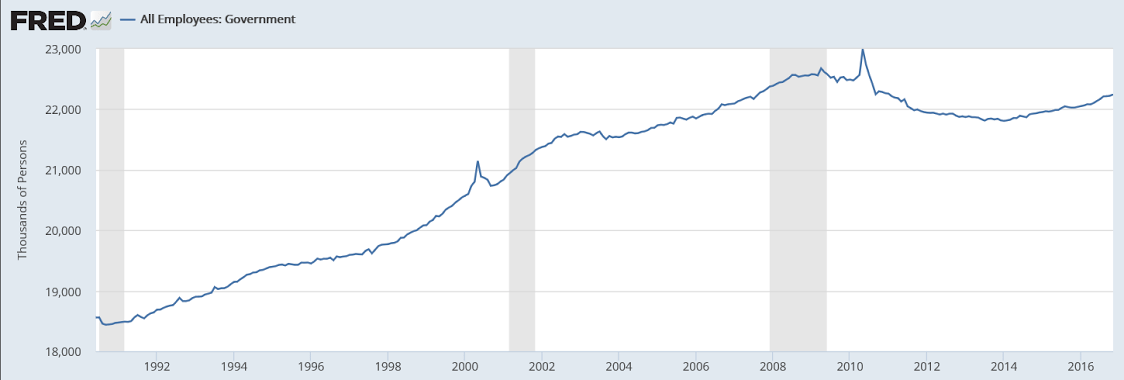
We’ll see if Trump can do the Tea Party’s bidding as well as Obama did when it comes to keeping down the size of government:
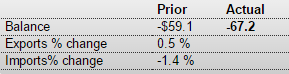
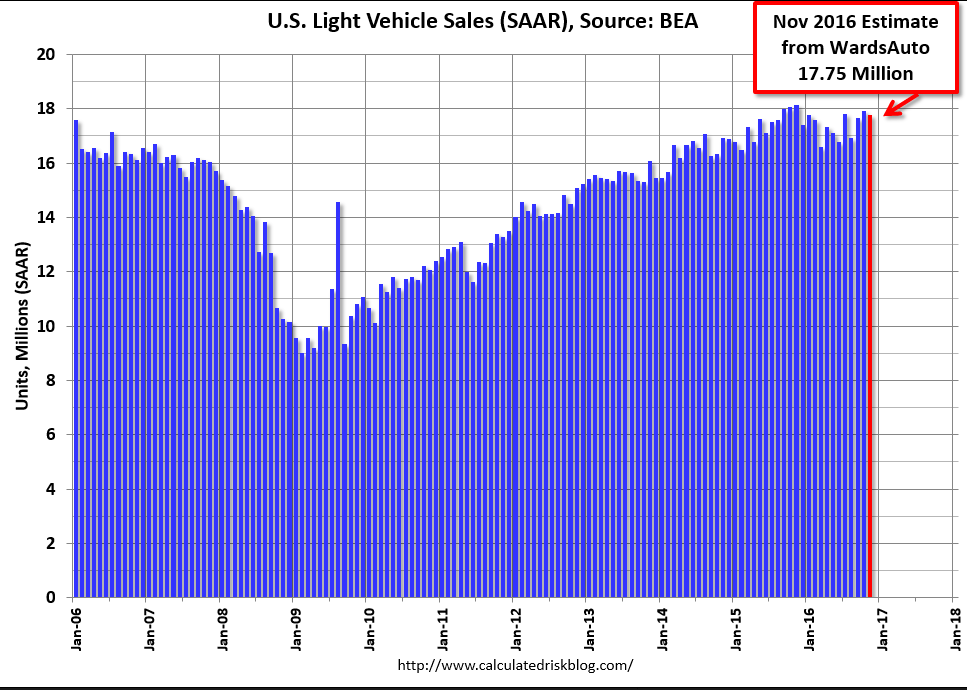
Car sales used to contribute to GDP growth. Not any more, seems:
Based on a preliminary estimate from WardsAuto, light vehicle sales were at a 17.75 million SAAR in November.
That is down about 2% from November 2015, and down 0.9% from the 17.91 million annual sales rate last month.
From John Sousanis at WardsAuto November 2016 U.S. LV Sales Thread: Light Trucks, Extra Days Boost November Volumes
With two extra selling days in November, U.S. automakers outpaced same-month year-ago sales on a volume basis, despite a 4.6% decline in the daily sales rate (DSR).
Strong light-truck sales were a key factor in November sales, as the industry delivered 1,372,402 LVs – 48,904 more than it did a year-ago, over the course of 25 selling days (vs. 23 last year).
…
Year-to-date sales for the industry reached 15.783 million units, giving the first 11 months of 2016 a lead of just 17,542 units over like-2015 heading into December – and keeping alive the prospect that 2016 will break the single-year sales record set last year.Read more at http://www.calculatedriskblog.com/#SD8fhLAodoqC8dsL.99
So much for Trump ‘deal making’ hopes:
Trump’s deal with United Technologies includes $7 million in financial incentives provided by Indiana to keep 1,100 jobs at Carrier, the company’s heating and air conditioning unit, in the state. However, Carrier still plans to move roughly 1,300 other jobs to Mexico and close another facility in Indiana.