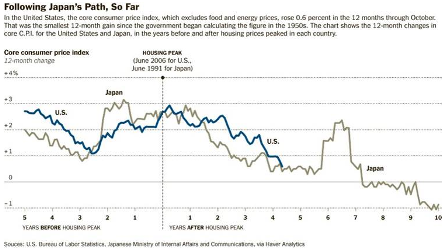
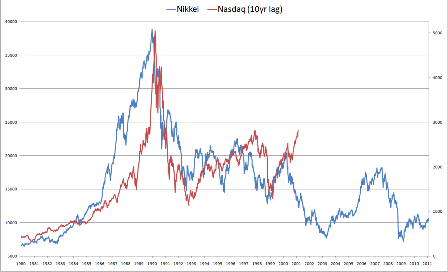
Today is year and in Japan,
which means the last few days could be mainly quarter end and year end maneuvers,
with a high probability of ‘buy the rumor sell the news’ types of unwinds coming up.
This would include the anticipation of another 200,000 new private sector jobs to be reported tomorrow am.
And the euro strength we’ve seen in front of the announced ECB rate hike next week.
There have been lots of promotional reasons to rush to get stocks on your books for year and/quarter end reporting,
as well as a bit of gold, silver, foods, and other commodities.
But fundamentally I see what’s going on below- a world heck bent on removing aggregate demand.
More noises from Japan on how they will pay for the rebuild, which looks to be a very modest appropriation tempered by fears of being at a fiscal tipping point.
UK austerity ratchets up April 1.
China still fighting inflation with further reduced spending and lending.
The euro zone demanding and getting austerity in return for funding, with signs in some members of austerity no longer bringing down deficits as revenues fall off from economic weakness. And no fiscal safety net if it does all go bad as markets have shown extreme reluctance to fund countercyclical deficits.
And food and fuel from monopoly pricing both eating into consumer demand and driving large segments of the world population into desperation.
Talk of Q1 US GDP down to maybe only +2%, housing still bumping along the bottom, and Q2 threatened by supply shortages due to the earthquake in Japan.
And the US debt ceiling showdown now possibly happing late next week as the deficit terrorists seal their congressional victory with the promised down payment on net spending cuts that won’t end there.
In fact, their army of support is now all but universal.
Everyone in DC and the mainstream media and economics profession agrees on the problem.
The only discussion is where the cuts should be, and who should pay more.
March 31, 2011
President Barack Obama
The White House
1600 Pennsylvania Avenue, NW
Washington, DC 20500
The Honorable John Boehner
Speaker of the House
1101 Longworth House Office Building
Washington, DC 20515
The Honorable Nancy Pelosi
House Minority Leader
235 Cannon House Office Building
Washington, DC 20515
The Honorable Harry Reid
Senate Majority Leader
522 Hart Senate Office Building
Washington, DC 20510
The Honorable Mitch McConnell
Senate Minority Leader
361-A Russell Senate Office Building
Washington, DC 20510
Dear President Obama, Speaker Boehner, Minority Leader Pelosi, Majority Leader Reid, and Minority Leader McConnell:
As you continue to work on our current budget situation, we are writing to let you know that we join with the 64 Senators who recently wrote that comprehensive deficit reduction measures are imperative, and to urge you to work together in support of a broad approach to solving the nation’s fiscal problems. As they said in their letter to President Obama:
“As you know, a bipartisan group of Senators has been working to craft a comprehensive deficit reduction package based upon the recommendations of the Fiscal Commission. While we may not agree with every aspect of the Commission’s recommendations, we believe that its work represents an important foundation to achieve meaningful progress on our debt. The Commission’s work also underscored the scope and breadth of our nation’s long-term fiscal challenges.
Beyond FY2011 funding decisions, we urge you to engage in a broader discussion about a comprehensive deficit reduction package. Specifically, we hope that the discussion will include discretionary spending cuts, entitlement changes and tax reform.
By approaching these negotiations comprehensively, with a strong signal of support from you, we believe that we can achieve consensus on these important fiscal issues. This would send a powerful message to Americans that Washington can work together to tackle this critical issue. Thank you for your attention to this matter.”
We agree with this letter and hope that you will work together to agree on a comprehensive, multi-year debt stabilization package.
Sincerely,
The Honorable Roger C. Altman
Former Assistant Secretary of the U.S.
Department of the Treasury; Founder
and Chairman, Evercore Partners
Barry Anderson
Former Acting Director, Congressional
Budget Office
Joseph Antos
Wilson H. Taylor Scholar in Health Care
and Retirement Policy, American
Enterprise Institute
The Honorable Martin Baily
Former Chairman, Council of Economic
Advisers
Robert Bixby
Executive Director, Concord Coalition
Charles Blahous
Research Fellow, Hoover Institute
Erskine Bowles
Former Co-Chair, National Commission
on Fiscal Responsibility and Reform
The Honorable Charles Bowsher
Former Comptroller General of the
United States
The Honorable John E. Chapoton
Former Assistant Secretary for Tax
Policy, U.S. Department of the Treasury
David Cote
Former Member, National Commission
on Fiscal Responsibility and Reform;
Chairman and CEO, Honeywell
International
Pete Davis
President, Davis Capital Investment
Ideas
John Endean
President, American Business
Conference
The Honorable Vic Fazio
Former Member of Congress
The Honorable Martin Feldstein
Former Chairman, Council of Economic
Advisers
The Honorable William Frenzel
Former Ranking Member, House
Budget Committee; Co-Chair,
Committee for a Responsible Federal
Budget
Ann Fudge
Former Member, National Commission
on Fiscal Responsibility and Reform;
Former CEO, Young & Rubicam Brands
William G. Gale
Senior Fellow, Brookings Institution William A. Galston
Senior Fellow and Ezra K. Zilkha Chair,
Brookings Institution
The Honorable Bill Gradison
Former Ranking Member, House
Budget Committee
The Honorable Judd Gregg
Former Chairman, Senate Budget
Committee
Ron Haskins
Senior Fellow, Brookings Institution
Kevin Hassett
Senior Fellow and Director of Economic
Policy Studies, American Enterprise
Institute
G. William Hoagland
Former Staff Director, Senate Budget
Committee
The Honorable Glenn Hubbard
Former Chairman, Council of Economic
Advisers; Dean, Columbia Business
School
David B. Kendall
Senior Fellow for Health and Fiscal
Policy, Third Way
The Honorable Bob Kerrey
Former Member of Congress
Donald F. Kettl
Dean, School of Public Policy,
University of Maryland
The Honorable Charles E.M. Kolb
President, Committee for Economic
Development
The Honorable Jim Kolbe
Former Member of Congress
Lawrence B. Lindsey
President and CEO, The Lindsey Group;
Former Director, National Economic
Council
Maya MacGuineas
President, Committee for a Responsible
Federal Budget
The Honorable N. Gregory Mankiw
Former Chairman, Council of Economic
Advisers
The Honorable Donald Marron
Director, Urban-Brookings Tax Policy
Center; Former Acting Director,
Congressional Budget Office
William Marshall
President, Progressive Policy Institute
The Honorable James T. McIntyre, Jr.
Former Director, Office of Management
and Budget
Olivia S. Mitchell
Economist
The Honorable William A. Niskanen
Chairman Emeritus and Distinguished
Senior Economist, Cato Institute; Former
Acting Chairman, Council of Economic
Advisers
The Honorable Jim Nussle
Former Director, Office of Management
and Budget; Former Chairman, House
Budget Committee; Co-Chair,
Committee for a Responsible Federal
Budget Michael E. O’Hanlon
Senior Fellow and Sydney Stein Jr.
Chair, Brookings Institution
The Honorable Paul O’Neill
Former Secretary of the U.S.
Department of the Treasury
Marne Obernauer, Jr.
Chairman, Beverage Distributors
Company
Rudolph G. Penner
Former Director, Congressional Budget
Office
The Honorable Timothy Penny
Former Member of Congress; Co-Chair,
Committee for a Responsible Federal
Budget
The Honorable Alice Rivlin
Former Director, Congressional Budget
Office; Former Director, Office of
Management and Budget; Former
Member, National Commission on
Fiscal Responsibility and Reform
The Honorable Charles Robb
Former Member of Congress
Diane Lim Rogers
Chief Economist, Concord Coalition
The Honorable Christina Romer
Former Chairwoman, Council of
Economic Advisers
The Honorable Robert E. Rubin
Former Secretary of the U.S.
Department of the Treasury
The Honorable Martin Sabo
Former Chairman, House Budget
Committee
Isabel V. Sawhill
Senior Fellow, Brookings Institution
Allen Schick
Distinguished University Professor,
University of Maryland
Sylvester J. Schieber
Former Chairman, Social Security
Advisory Board
Daniel N. Shaviro
Wayne Perry Professor of Taxation,
New York University School of Law
The Honorable George P. Shultz
Former Secretary of the U.S.
Department of the Treasury; Former
Secretary of the U.S. Department of
State; Former Secretary of the U.S.
Department of Labor
The Honorable Alan K. Simpson
Former Member of Congress; Co-Chair,
National Commission on Fiscal
Responsibility and Reform
C. Eugene Steuerle
Institute Fellow and Richard B. Fisher
Chair, Urban Institute
The Honorable Charlie Stenholm
Former Member of Congress; Co-Chair,
Committee for a Responsible Federal
Budget The Honorable Phillip Swagel
Former Assistant Secretary for
Economic Policy, U.S. Department of the
Treasury
The Honorable John Tanner
Former Member of Congress
John B. Taylor
Mary and Robert Raymond Professor of
Economics, Stanford University; George
P. Shultz Senior Fellow in Economics,
Hoover Institution
The Honorable Laura D. Tyson
Former Chairwoman, Council of
Economic Advisers; Former Director,
National Economic Council
The Honorable George Voinovich
Former Member of Congress
The Honorable Paul Volcker
Former Chairman, Federal Reserve
System
Carol Cox Wait
Former President, Committee for a
Responsible Federal Budget
The Honorable David M. Walker
Former Comptroller General of the
United States
The Honorable Murray L.
Weidenbaum
Former Chairman, Council of Economic
Advisers
The Honorable Joseph R. Wright, Jr.
Former Director, Office of Management
and Budget
Mark Zandi
Chief Economist, Moody’s Analytics