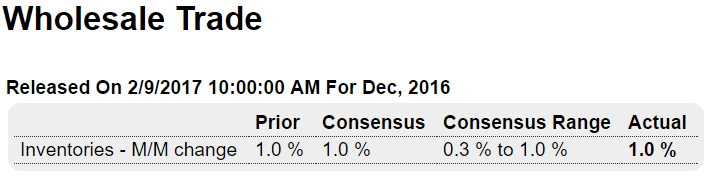
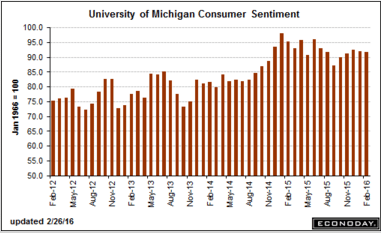
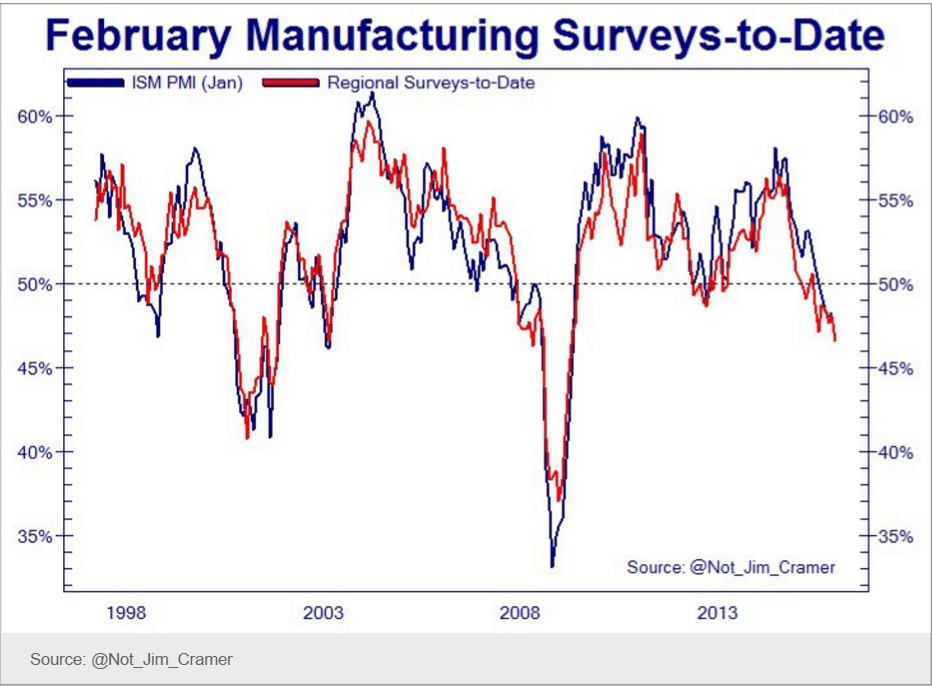
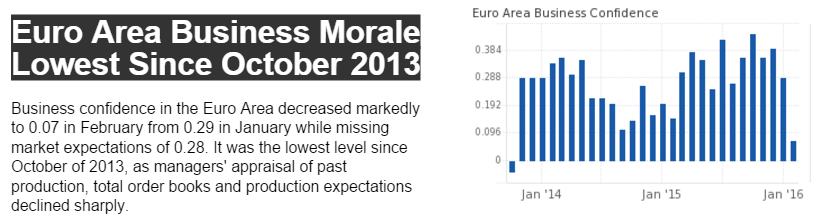
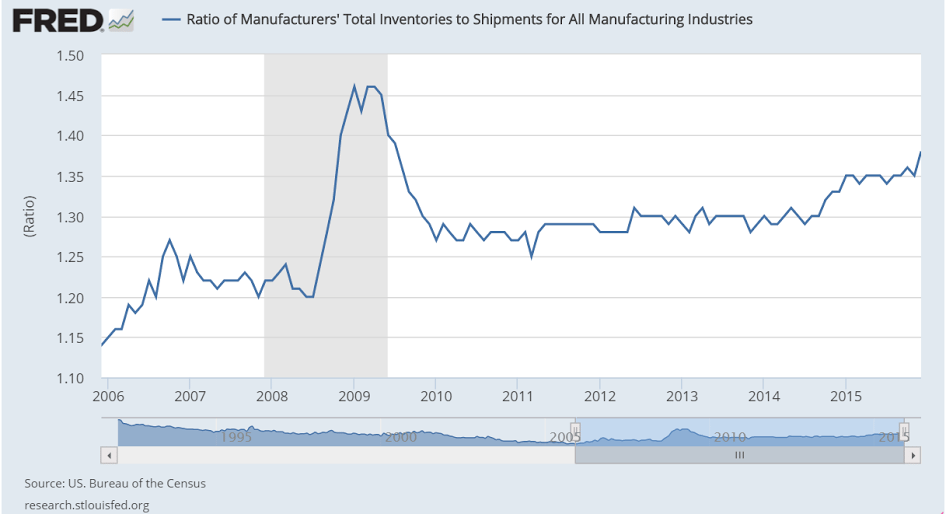
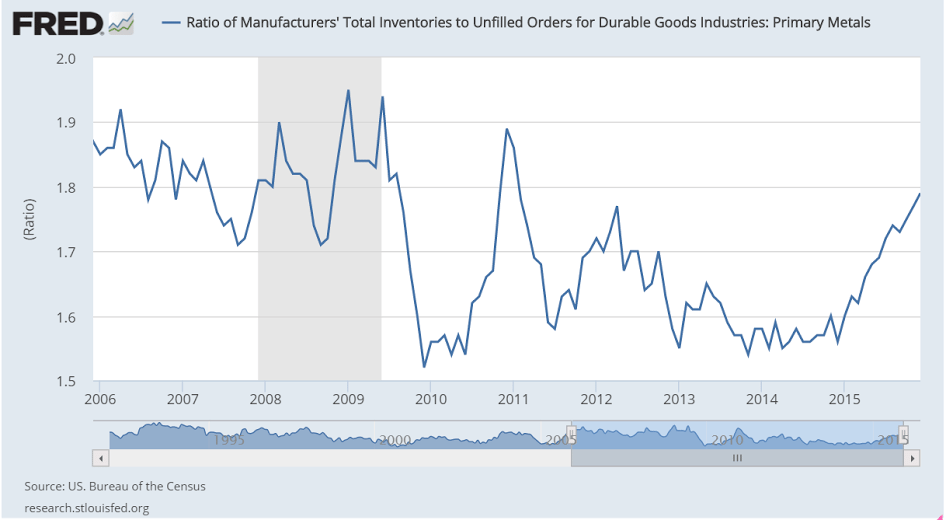
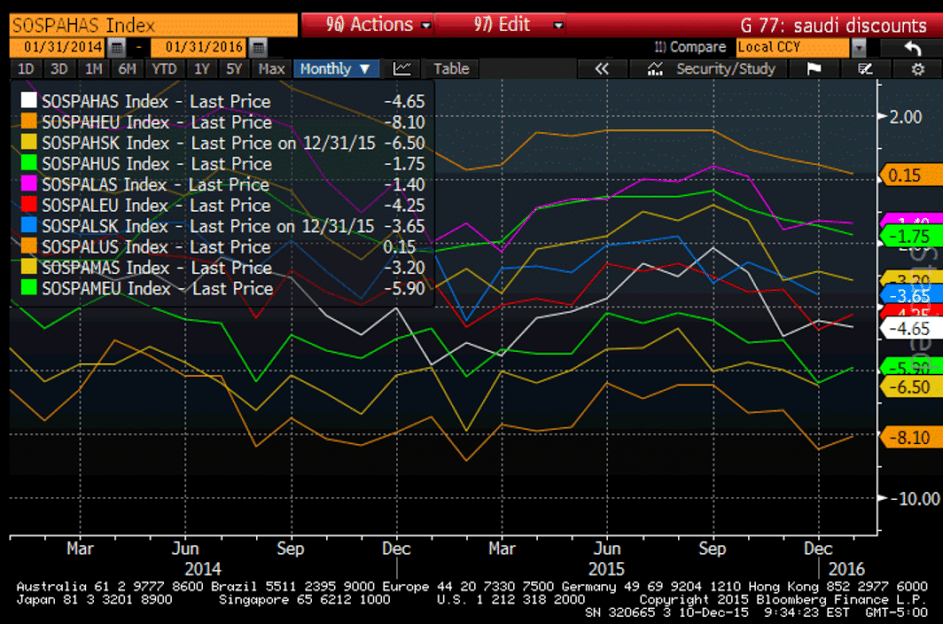
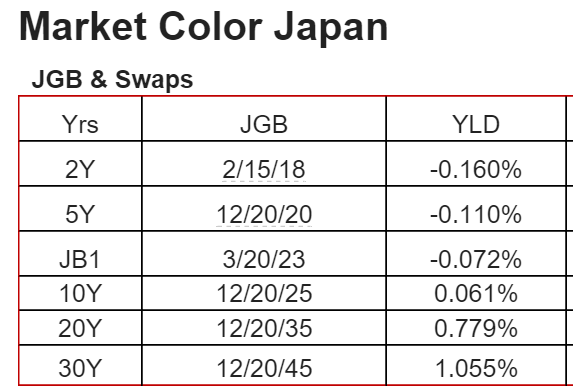
This is the yen yield curve after over 20 years of a 0 rate policy, massive QE, and now negative overnight rates. Maybe now the economy will finally respond.
:(
(And how good can the BOJ think the economy is?)
The western educated kids/monetarists who’ve taken control don’t seem to be doing all that well, as China begins to look like the other countries they’ve taken over, like the EU, US, etc. etc. etc. What they learned is that it’s about balancing the federal budget and using monetary policy to support growth and employment as needed, allowing ‘free markets’ to ‘clear’ as per their general equilibrium models that earned them advanced degrees. Unfortunately they fail to recognize the currency itself is a (simple) public monopoly which obviates all those ‘market clearing’ assumptions in their models:
Jan 31 (CNBC) — China’s factory activity skidded to a three-year low point in January, adding to further gloom about the state of the world’s second-largest economy.
The government-compiled January manufacturing purchasing manager’s index (PMI) came in at 49.4, slightly missing Reuters consensus estimates for a 49.6 reading and ticking down from December’s 49.7 figure. It was the weakest result since 2012 and marked the sixth straight month in contraction territory.
The mood was worsened by a private survey by Caixin and Markit that showed January manufacturing activity shrinking for the eleventh straight month. Caixin’s survey, which tracks smaller firms than the official indicator, came in at 48.4, compared to December’s reading of 48.2.
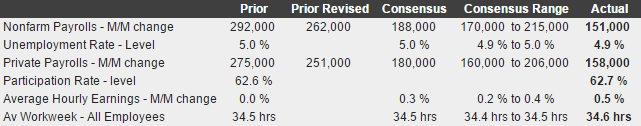
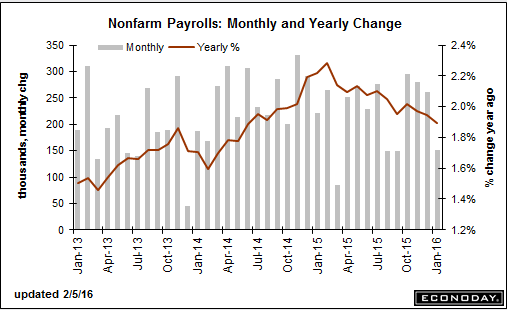
Does this read like an executive who’s organization has a $200 million per year research budget?
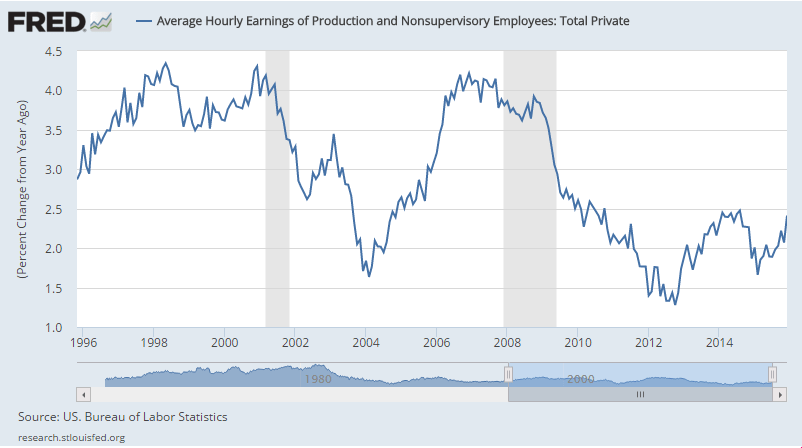
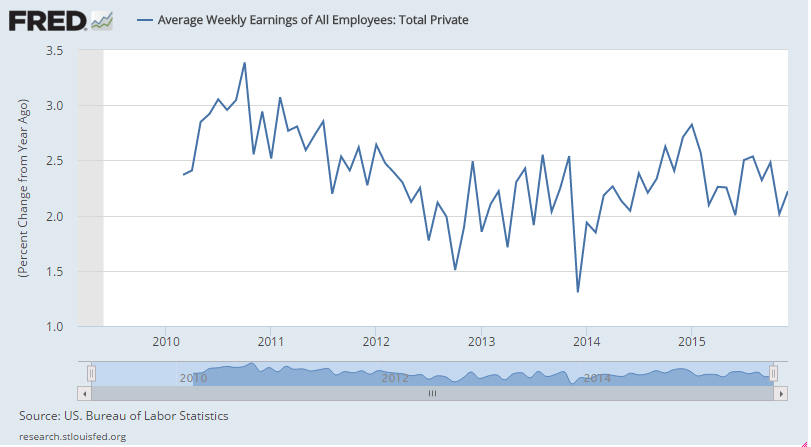
They just hiked rates in December with every chart I’ve seen having been heading south for a year or so?
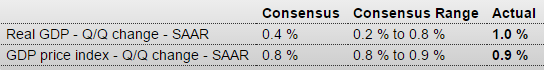
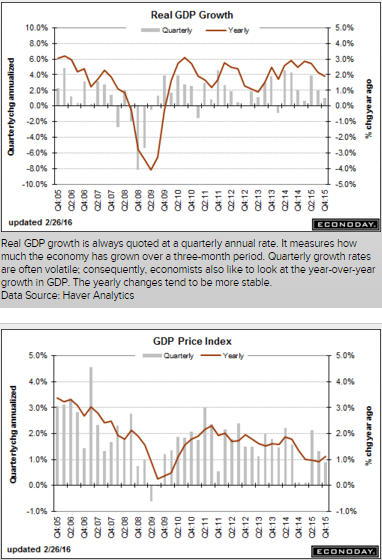
And GDP was right on forecast.
Seems to me this ‘kind of tells him’ the fundamental assumptions behind his models needs a rethink?
Jan 29 (Reuters) — “Standard monetary policy strategy says a little less inflation, maybe a little less growth … argue for just a smidgen slower process of normalizing rates,” San Francisco Fed President John Williams said. “We got a little stronger dollar, some mixed data on the economy, some weakness in Q4 GDP, all of those coming together kind of tell me that we probably need a little bit more monetary accommodation this year than I was thinking in the middle of December.” Williams said his “modal” forecast, remains fundamentally unchanged for 2016 and 2017. “The thing that has changed is that commodity prices keep coming down,” he said.
The hits keep on coming with no replacement spending in sight:
Jan 29 (WSJ) — Chevron is slashing its capital spending by more than $9 billion this year. Chevron plans to sell up to $10 billion in oil fields and other assets through 2017. A $26.6 billion spending plan detailed in December will have to be reduced given how much oil-market conditions have since deteriorated, he company said. Chevron reported a loss of $588 million, or 31 cents a share, in the fourth quarter, down from a profit of $3.47 billion, or $1.85 a share, in the year-earlier period. Revenue tumbled 37% to $29.25 billion. In Chevron’s refining division profits were cut nearly in half, falling to $496 million.
Jan 29 (WSJ) — Refined-copper supply jumped 36% to 22.5 million tons from 2005 to 2014, according to ICSG data. Over that same period, annual copper consumption increased 38% to 22.9 million tons. Total Chinese copper imports fell to 8.6 million tons in 2015, down 2.2% from the year before. Global refined supply rose 1.8% over the same period, largely because of a 4% increase in refined production from China. China imports of unfinished copper and products in December rose 26% in annual terms to 530,000 tons. More than 600,000 tons of copper supply have been taken out of the market over the past 12 months, according to Morgan Stanley.
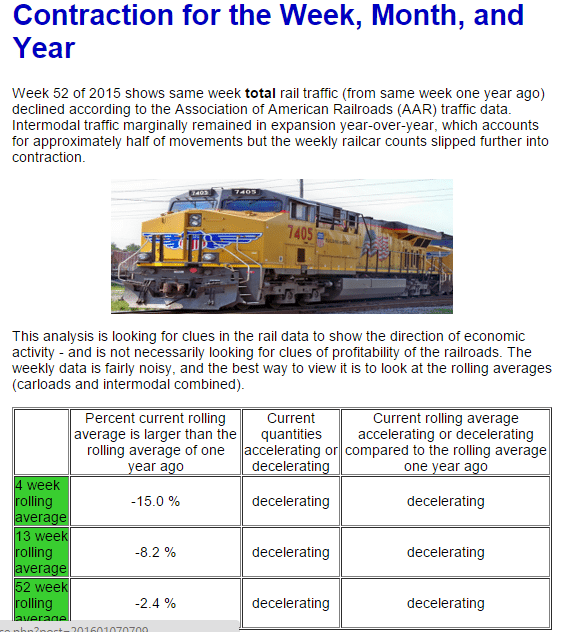
Not the worst indicator for global growth:
Jan 31 (WSJ) — Korean exports, the first shipments data released each month in Asia, slid 18.5% to $36.74 billion in January, the steepest fall since August 2009. The decline extended a run of monthly falls into a 13th month. Imports plunged 20.1% from a year earlier to $31.42 billion in January. For all of 2015, Korean shipments overseas contracted 8%—the steepest fall in six years and the first 12-month contraction in three years, the government said. The Nikkei PMI reading for January came in at 49.5, down from 50.7 in December.