[Skip to the end]
More on the Bernanke testimony:
Shortly after the failure of Lehman Brothers, I was in Brazil at an international meeting, and I had a meeting there with bankers, and I asked them how the Brazilian economy was doing. And they said well, it had been doing fine, but within a week after Lehman Brothers collapsed, it was like a frigid wind descended on the economy in Brazil. And there was an enormous impact almost immediately on their economy, on their ability to raise funds and make loans.
In dollars, I’m sure.
And it’s astonishing how quickly that one failure spread throughout the world, and created a very severe recession, not just in the U.S., but around the world.
The Federal Reserve, by making a large loan under very tough terms to AIG,
But allowing those funds to be used to meet margin calls on CDS and probably other related market losses. That’s perhaps the most controversial part. Those payments to creditors perhaps could have been labeled ‘loans from the Fed’ subject to AIG ultimate solvency rather than payments from the Fed.
prevented the failure of that institution, and, therefore, tried to contain the impact of the Lehman Brothers failure on the rest of the global financial system. I’ll come back and talk more about AIG, and those things later, but that was just the first step of many that we took to try to stop the crisis.
Subsequently, again, very concerned with the possibility of a global financial meltdown, we worked with Treasury and the Congress to develop a bill that would provide funding that the Fed, the Treasury and other agencies could use to stabilize the financial system, to prevent collapse of the financial system.
This immediately became relevant, because in mid-October, the crisis heated up again to the point that we thought that we were again within days or hours of a collapse of many of the largest financial firms in the world. It was a dramatic weekend. It was Oct. 10 or 11, Columbus Day weekend, when the Finance Ministers and the central bankers of seven of the largest industrial economies had a meeting here in Washington, which, of course, I attended. Usually, those meetings are very scripted and very dry. In this case, there was palpable concern among the participants that the collapse of their financial system might be just days away, and there was a great deal of discussion about how we, collectively, as the policy makers leading those countries could stop the collapse.
In the days that followed, countries all over the world, particularly the advanced industrial countries, took strong measures to prevent the collapse of the financial systems. That included putting capital into banks;
Obviously they didn’t know it was nothing more than regulatory forbearance.
it included preventing the failure of large financial firms; it included guaranteeing the debts of financial firms so they could borrow and keep themselves afloat; it included making short-term loans to firms so that they would have the short-term credit they needed to pay off lenders who were withdrawing their funding. And, again, this was the U.S. doing this, but also many of the most important industrial countries around the world simultaneously, including the U.K., Germany, France, Switzerland and others.
Again, many of those creditors ‘bailed out’ by the Fed’s liquidity provisions could have had those funds labeled ‘loans from the Fed’ rather than simply receiving payments from the Fed.
The result of this collective global effort over that week was essentially to succeed in stabilizing the global banking system, in that subsequent to that week the fears of utter collapse were largely overcome.
Now, in the following months after that, there were still many, many great difficulties in the financial markets. And the Fed, and other central banks and Treasuries around the world, worked very hard to restore the normal functioning of those markets. For example, following the Lehman failure, there was a run where ordinary investors went as quick as they could to pull their money out of money market mutual funds, which are a common investment vehicle for many Americans. It was very analogous to 100 years ago when a bank was about to fail, and the depositors would go to the bank, they would run and pull their money out as quickly as possible, and then the bank would fail. The money market mutual funds were experiencing exactly the same phenomenon.
The Fed and the Treasury working together provided short-term loans to these funds. The Treasury provided some insurance to depositors, or to investors so they would know they wouldn’t lose their money. We stopped the run on the money market mutual funds, and that was an example of how we helped stabilize the situation.
Not sure why that was critical?
There were many other steps we had to take helping individual institutions, and providing programs for backstop lending to make sure that the key markets in the financial system were functioning again, because for months after Lehman Brothers, the amount of fear and uncertainty in the financial markets was so elevated that these markets were, essentially, not functioning properly, and it took really many months until we had reached the point that these markets had begun to approach a normal state.
Doesn’t mention the dollar swap lines to foreign CB’s???
But bank lending is still weak. The banks had a near-death experience, they are now lending in a difficult economic environment. We are strongly encouraging them to lend. We have taken a lot of steps to help them raise new capital, so they’ll have a basis on which to make new loans. And we are taking a number of steps to try to open up markets through which investors invest directly in various forms of credit, like auto loans and credit card loans. All of these steps are improving the financial situation, but particularly the banking sector, we’re still in the convalescent stage.
They only bought AAA traunches which didn’t address the credit issues. They were more worried about taking losses than restoring auto credit, but wanted to give the appearance they were doing something.
As I said, I was a professor. I never worked for Wall Street. I have no connections on Wall Street. In fact, when I first became chairman, I was criticized in some quarters for not being close enough, or knowing enough about Wall Street. So, why did I take these actions?
I didn’t take these actions, or the Federal Reserve didn’t take these actions because we were trying to help bankers, or trying to help Wall Street. What I understood, and what knowledgeable people all around the world understood, is that the financial system is essential to the functioning of any economy. And that if the financial system had collapsed to the extent to which we believed was very likely in September and October 2008, then no force on earth, no policy, could have prevented the collapse of the entire U.S. economy with long-lasting and extreme consequences for every American.
How about a proportionate fiscal response, like a payroll tax holiday and per capita revenue distributions to the States? Instead, he continues to preach ‘fiscal responsibility.’
It was because we were concerned about jobs and incomes and the economic well-being of every American that we intervened to prevent the collapse of the financial system.
Now, going forward, we have a lot to do to get the economy back to stability, get jobs created. You can talk as much as you like about the things we’re doing there, but we’re also going to have to take some very strong steps to make sure that the crisis doesn’t ever happen again.
There were, certainly, weaknesses in our financial regulatory system. There were weaknesses in the way that financial regulators supervised the banks and other financial institutions. And the financial institutions themselves made lots of mistakes in terms of their ability to measure the risks that they were taking, and to control them properly. And to make sure we don’t ever have a crisis like this again, we need to have extensive reform in the private sector, in the public sector, to eliminate these risks in the future.
You had said that the banks were convalescent still, Mr. Chairman. Can you talk to us a little bit more about what that means?
Well, the banks have been stabilized. They’ve raised a good deal of capital, so they’re in much better shape than they were. They are lending, but they are not lending enough to support a healthy recovery. One important reason for that, is that given their losses, given what they’ve been through, they’re being very conservative in the face of what is still a very weak economy; and, therefore, a sense that many borrowers are quite risky.
As bank supervisors, we have a difficult challenge. We have told the banks very clearly that we want them to make loans to credit-worthy borrowers, where there are borrowers who can repay the loans. It’s in the interest of the banks, it’s in the interest of the economy, and, of course, it’s in the interest of the borrowers for those loans to get made.
But the problem is, of course, that we got into trouble in the first place by banks making loans that couldn’t be repaid, so we don’t want banks to make bad loans. Therefore, we are trying to work with banks to make sure that they are, in fact, able to make as many good loans as possible, that they have enough capital, that they have enough short-term funding, and that the examiners and the regulators who work with the banks are not unduly restricting the loans that they make. We want to work with the banks to make sure that they balance the appropriate prudence and caution against the need to make good loans for the economy, and for their own profits.
Banks and the entire private sector is necessarily procyclical.
Only govt via fiscal policy can be countercyclical.
So, what this means is that economic policy, and financial oversight have to take into account all the international dimensions of that. So, for example, on the monetary policy side, we have worked carefully and closely with other central banks to talk about monetary policy in different parts of the world. In fact, during the heat of the crisis in October 2008, the Federal Reserve and five other major central banks cut interest rates together on the same day, as a sign of how committed we were to cooperating on monetary policy.
Doesn’t seem concerned that interest rate cuts may in fact be deflationary as he knows they remove interest income for the private sectors (Bernanke, Sacks, Reinhart, 2004 Fed paper- see ‘the fiscal channel’)
The system worked.
It did work. It was an important first step. I mean, even after we took those steps, the financial markets were in a great deal of stress, and credit at all levels was very much constrained. But it stabilized the situation, and from there, we were able to take a number of steps to – both we, and our partners in other countries – to get the key markets working again, to get the banks stabilized, and to begin the very difficult process of getting the financial system back on its feet.
Never realizing that all the alphabet soup measures to get liquidity going missed the point that all the Fed had to do was lend fed funds to member banks without limit, as the ECB effectively did by immediately accepting any and all bank collateral, to immediately restore bank liquidity.
So, while it’s difficult to know exactly what the outcome would have been, certainly, just judging on what happened after the failure of a single firm, the collapse of the global financial system would surely have led to a far deeper recession, higher unemployment, much greater fiscal cost to the taxpayer, and to rebuild the financial system, and to get the economy moving again. And almost certainly, [we would have had] many, many years of subnormal – substandard – performance by the U.S. economy, and by other industrial economies, as well. Again, we can’t know precisely, but I think if anything, the financial crisis last fall was as severe, and as dangerous as anything we’ve ever seen, including the 1930s.
The whole point of going off the gold standard in 1934 was to be able to provide liquidity without limit to the banking system, so the fact that he did that, however belatedly, is nothing to brag about. It also allowed for unlimited fiscal responses, which he still seems to not fathom.
There is an irony here that’s literary, that here’s this man who spends his life distinguishing himself studying economic history. And then one day you wake up and realize that you’re at the center of economic history in this really unusual chapter. How do you process that personally? I mean, how does that change how you go from being the academic expert to you are in the arena?
Well, I certainly didn’t anticipate when I came to Washington in 2002, I certainly didn’t anticipate these events, or how things would evolve. No question about it. And when I became chairman in 2006, I thought that – I hoped that my main objectives would be improving the management, communication and monitoring policy.
We were certainly attentive to the risks of financial crisis. Secretary Paulson and I talk frequently to people on Wall Street, and we secured the Federal Reserve. We set up a team of staff drawn from different disciplines to try to identify problems and weaknesses in the financial sector. So, we were certainly aware of the risks of financial crisis, but one as large and as dangerous as this one, I certainly did not anticipate. I wish I had, but I didn’t.
Then when the crisis came, you know, rather unexpectedly, a different part of my training and research became relevant, which was to work on financial crises generally, and also on the Great Depression. And I believe very much that that experience, and that knowledge, was very helpful to me in many dimensions of this effort, ranging from – I think the most important lesson, there are many lessons, but I think the most important lesson was that we were not going to have a healthy stable economy with a completely dysfunctional financial system. We had to take strong measures to prevent that from happening.
And in the 1930s, the Federal Reserve was quite passive, and allowed the banks to fail, and we know the result of that. So, we were determined that that wasn’t going to happen on my watch, on our watch, so we were prepared to take very strong actions to avoid that.
That was under the gold standard. Nothing could be done without losing the nation’s gold supply. It was only after the banks reopened in 1934 with a non convertible currency could there be credible deposit insurance unlimited Fed provision of liquidity. Clearly he doesn’t understand that or a) he’d be stating it b) I don’t want to say…
You’ve been quite forthcoming, I think, in your testimony about saying, there’s a lot of things you didn’t see, there’s some things that we didn’t do. If I gave you a kind of do-over to go back as long as you want to say you know what, if we’d seen this, if we’d looked at the sub-prime mortgage crisis. I mean, how could you have handled it, and the Fed handled it better to have a different outcome?
Well, we have, based on the experience of the crisis, we – the Treasury and others – have made proposals for how the financial regulatory system ought to be reformed and restructured. I’ll say a word about that. If we had been in that forum, I think we would have avoided the crisis. So, there were some important lessons.
One was that our regulatory system was too myopic. It was too focused on individual firms, or individual markets, and there was nobody paying attention to the broad overall financial system. So, the Federal Reserve was not entrusted with looking at the whole financial system. We were – we had very specific assignments. We were supposed to look at specific institutions. Those institutions did not include many of the firms that had severe problems, like Lehman Brothers or Bear Stearns or AIG. Those were outside of our purview, and since they were outside of our purview, we didn’t look at them.
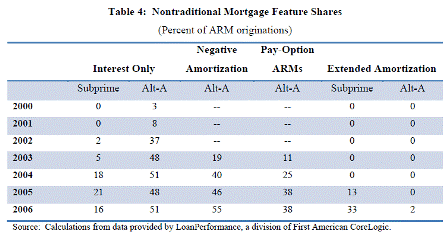
They missed one critical factor- allowing bank loan officers to work on a commission basis. Nor, did the regulators look into actual loan files to check for fraudulent appraisals and income statements promoted by loan officers working on a commission basis. Regulation is necessarily a work in progress. Mistakes will be made, including mistakes of this scale. Critical to our well being is the knowledge of how to keep these errors in the financial sector from damaging the real economy. And that requires appropriate fiscal responses to sustain aggregate demand, preferably in an equitable manner.
But there were many situations where there was really nobody who was looking carefully at what was going on, and nobody who was looking at how the parts of the system fit together. So, a very important recommendation that we have made is that there be a more systemic approach – that is, have some arrangement whereby a regulator, or a group of regulators, has responsibility to look at the system as a whole, and try to identify emerging problems, or gaps in the regulatory apparatus, or weaknesses in individual institutions, as they relate to other institutions, that threaten the integrity of the system as a whole.
Better still, most of the issues came from allowing banking activities that in fact served no further public purpose. That includes any bank participation in secondary markets, loaning against financial assets, using LIBOR as an index, and many others.
We didn’t have that. Therefore, nobody paid enough attention to AIG, nobody paid enough to attention to credit and call swaps, nobody paid enough attention to some of the activities of investment banks. You go on, and on, and on. Again, if we had had a more comprehensive overview approach that would have been helpful.
A second key element is the problem too big to fail, and how to address that. So, I just want to be very, very clear that even though the Federal Reserve was involved in rescuing Bear Stearns and AIG, we did that extremely reluctantly, and with – it was a very distasteful thing for us to do. We did not do it – we were not set up to do it. We were – it was very difficult for us to do, but we did it because there was no appropriate mechanism, there was no set of laws that would allow the government to intervene in a situation like that in a way that would allow the firm to fail, but would not have all the negative consequences for the financial system and the economy.
So, we had a situation where there were firms who were literally too big to fail, or too complex to fail, or too interconnected to fail. When they came to the edge of collapsing, we had only two very, very bad choices: we either bailed them out, put taxpayer money at risk, put the Federal Reserve at risk in terms of our lending, or we could let them collapse and have all the hugely negative consequences for the financial system and for the economy.
So, what we did not have, and what we very much need going forward, is a third option, and that option should be a legal framework which allows the government – and I think that means, in practice, the Treasury and Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation – to intervene when a large complex systemically critical firm is about to fail, and to allow the firm to fail, impose losses on the lenders, the creditors of the firm, the shareholders, fire the management, protect the taxpayer, but be able to do that in a way that protects the system, so that the financial system is protected from the immediate impact of that collapse.
I submit we already have that for the large banks, and the others as well. He just didn’t grasp how to use it. The receivership they did set up did not have to pay off all the creditors, and if there were issues, it would have been a relatively simple matter to petition congress for an ’emergency’ alteration of current law. They didn’t even try.
We did not have a system like that in place. I think if we had, we could have dealt with Lehman Brothers and AIG in a much more satisfactory way. We would have avoided many of the problems. And, most importantly, we would have not, in some sense, rewarded failure, which is what happened. In the future, it’s important that firms be allowed to fail if they, in fact, take excessive risks, and make bad gambles.
But that mechanism is not in place now.
The mechanism is not in place, and we have asked Congress to address it, and I believe that they will. But until they do, we are really still in a situation where we don’t have good options in dealing with potential collapse of a global financial firm.
It isn’t that hard to do.
Right now people are sort of looking to you, and to Congress, to kind of break the back of unemployment. And you’ve talked about how that is really our biggest challenge right now. Do you feel there is anything else that can be done, or has the Fed shot all its bullets, and has Congress shot all its bullets?
Well, the Federal Reserve has been very aggressive on the unemployment side. So, let me just first say that even though the recession may be technically over., in a sense that the economy is growing, it’s going to feel like a recession for some time, because unemployment remains very high, about 10%. And even people who have jobs, there are many people who are on short hours, that are in voluntary part-time, or maybe people who are not technically unemployed, only because they stopped looking. So, the labor market is in very weak condition, and we’re not going to see a healthy, vibrant economy again until the labor market – the job market – has recovered. So, that is really an extraordinarily important objective for policy going forward. And, certainly, our job won’t be done until the economy is growing again, and jobs are being created.
The Federal Reserve’s attempts to address employment issues, we’ve done several things. Certainly, one of the things is we’re using our monetary policy. In December 2008, while the crisis was still in an intense phase, we cut the short-term interest rate that is the measure of our monetary policy almost to zero. The first time that had ever been the case, the Fed had ever done that, in order to provide the maximum amount of support to the economy, and it remains close to zero today. So, that is a very powerful measure.
Again, he gives no weight to the possibility that the interest income he removed from ‘savers’ is weighing on the economy, even though it’s in his own paper from 2004.
Having used that tool to its maximum extent, we have then turned to new and innovative tools, things that have never been done before in the Federal Reserve. I’ll give you two examples. One, we’ve purchased about $1 trillion worth of mortgages that are guaranteed by Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac, and the U.S. Treasury. And in doing those purchases, we have succeeded in reducing the national 30-year fixed-rate mortgage rate from about 6-1/2% to about 4.8%. By lowering mortgage rates that way, we have helped to stabilize the housing sector, to help stabilize the housing crisis, and allow people to refinance, to buy homes. And that, obviously, should get construction started again and house prices stabilizing, and people being able to meet their mortgages. That’s obviously going to be helpful.
The far more effective way would be to directly fund the agencies at the fixed rate the Fed wanted for mortgages and allow that funding to be prepaid without penalty if the mortgages prepaid. But that was never even a consideration.
We’ve also created a program that helps bring credit from Wall Street to support a wide variety of consumer and small-business loans. So, for example, our program allows Wall Street money to come in and support auto loans, credit card loans, student loans, small business loans, commercial real estate loans. By providing that conduit, we are supporting what the banks are doing to get credit flowing into those important sectors.
But only the AAA pieces, as previously discussed.
And I guess a third thing, an additional thing I would mention is that we serve not only as monetary policy makers, but also as bank supervisors. And there we’ve been sparing no effort, as I talked about earlier, to get the banks able and willing to lend again, to create – particularly the small businesses – to create the credit that’s needed to create new jobs and get employment back on track.
I would mention, in particular, our leadership of the stress tests. In the spring, the Federal Reserve led an effort to evaluate the balance sheets of 19 of the largest banking companies in the U.S., and our report on those balance sheets, along with the FDIC, the OCC, to other banking agencies, our reports on those balance sheets is public, greatly increased the confidence in the banking system, which meant that they were able to go out and raise new capital in the stock market, and many of them have paid back the capital to the government.
Still no clue it was only regulatory forbearance.
But by raising new capital, they increased their own capacity to lend. And, as conditions improve, they’ll be able to make new loans as well.
So, by keeping interest rates low, including both short-term rates and long-term rates, like mortgage rates, by supporting a flow of credit to small businesses, consumers and the like, that is our primary effort. Those are the tools that we have. We can always do more, if necessary, but those are the tools that we are applying trying to get job growth going again.
They have more tools but aren’t using them? Unless this is a bluff, what are they waiting for? This is an extraordinary statement.
And we have seen, obviously, the labor market is still very weak, but the last report we saw shows that we’re now coming closer to the point where we’ll stop seeing job losses and start seeing job gains.
We’ve talked about a lot of those extraordinary things you’ve done. But is that it? Like now do we have to – because there’s still really bad numbers, even your forecasts are like what, 10% [unemployment] this year, 9% going forward, I think like 8% in 2012. Do we just have to kind of now sit back and take it?
Well, the Federal Reserve will continue to see what other policy actions we can take. And we’ve really been very aggressive, thus far. And the additional steps aren’t as obvious or clear as the ones that we’ve already taken.
Right, they don’t have any actual ideas.
A lot of the scope now is on the fiscal side of the house. As you know, the government passed a major fiscal program earlier this year, and I think it was just today the President announced a number of individual – a package of programs to try to address unemployment. So, [there are] a lot of new initiatives probably coming from the fiscal side.
While he preaches fiscal responsibility. See below.
Did they ask you for your opinion of those before…
Well, our staffs confer frequently with the Treasury and other parts of the Economic Advisory Groups that advise the President. And we often give our views. Our views are solicited. But, of course, they are responsible for their policy choices.
Have you said before, or are you prepared to say now, that a second stimulus, a round of incentives, is a good idea, on the fiscal side?
So, my domain is monetary policy and financial stability. And we have done, of course, a lot of aggressive things to try to support the economy, try to support job creation. I generally leave the details of fiscal programs to the Administration and Congress. That’s really their area of authority and responsibility, and I don’t think it’s appropriate for me to second guess.
You have said that there’s a long-term deficit program that needs to be dealt with. You said health care costs ought to be cut back, so it’s not like you won’t talk at all about the fiscal situation. Regardless of the details, which I understand that you don’t want to tell them how to do it, do you think that the fiscal side ought to do something?
Well, let me say this, I think that it’s very important that whatever actions that Congress and Administration take on the fiscal side, that they begin soon, or even sooner, to develop a credible medium-term interest strategy for fiscal policy, one that will persuade the markets and the public that over the medium term, the next few years, we will – we, as government, we, as a country – will be able to bring our deficits down to a level that could be sustained over a period of time.
Yes, he’s clearly part of the problem, not part of the answer. He’s failed to realize the ramifications of lifting convertibility in 1934 (and 1971 internationally) and is one of the leading deficit terrorists.
If we can do that, which will increase the confidence of the markets in American fiscal policy, that would give us more scope to take action today, because, again, there would be confidence that we have a way out, a way back towards sustainability.
There is no sustainability issue and he should know that. But he doesn’t even fully understand monetary operations of the Fed itself.
In your testimony the other day, one Senator talked about here’s the money that the federal government takes in, here’s what we spend on entitlements. It’s basically the same. Everything else we have to borrow for. I mean, there are a lot of people saying that it’s not sustainable, as you have said. And they said one of the only solutions is some kind of tax, a sales tax, value-added tax, something other than an income tax. But would you be in favor of any of those alternatives?
So, the way I put this before Congress before is that the one law that I strongly advocate is the law of arithmetic. (Laughter.) That law of arithmetic says that if you are a low-tax person, then you have to – you are responsible for finding ways on saving on expenditure, so that you don’t have enormous imbalances between revenues and spending. And by the same law of arithmetic, if you were somebody who believes that government spending is important, and you are for bigger and more spending, and bigger programs, then it’s incumbent upon you to figure out where the revenues are going to come from to meet that spending. So, again, I think that’s, again, Congress’ main responsibility.
I have spoken about deficit, and I think deficits are important, because they address broad economic and financial stability. We need to talk about that. But in terms of the specifics about how to get to fiscal balance, that’s the elected officials’ responsibility.
He sees spending as revenue constrained where that concept is entirely inapplicable to non convertible currency and floating fx policy.
Do you think Congress is fiscally illiterate? Economically illiterate?
No, of course not. But what they have to deal with is not just a question of understanding. It’s a question of making very, very tough choices, and in a political environment, where people understandably are resistant to cuts in programs or benefits, or increases of taxes. So, there needs to be tough choices made, there needs to be leadership. And I don’t envy Congress those choices, because they’re very difficult ones to make.
Are you saying that time for fiscal and monetary stimulus is over? And, if so, what’s the downside of pushing even harder?
There are not easy solutions. It’s an enormous problem. I think the Federal Reserve – one direction that we can go is to continue to encourage the extension of credit, small businesses, in particular, create a lot of jobs, particularly during economic recoveries. And we have lots and lots of evidence and anecdotes suggesting that small businesses are particularly harmed by the tightness of the bank lending standards and unavailability of credit. So, everything we can do, and that the Administration and Congress can do, to support credit extension to all business, but primarily small business, would be a very powerful.
You don’t think it’s a liquidity problem?
Well, I mean, interest rates are very low, so I think it’s going to be a question, first of all, of getting credit flowing again. And the Federal Reserve has got a role to play there. And then, Congress and the Administration will consider possible programs and fiscal policies.
You’re definitely not okay with long-term profligacy, but are you okay with them doing something in the short-term?
I think if they do that, it’s critically important they clarify the longer-term plan for establishing sustainable fiscal [policy].
Again ducking the question. But it’s clear he is not a supporter of using fiscal adjustments to sustain aggregate demand.
Adair Turner, the chief British [financial services] regulator, said that we’ve learned that much of what the financial services sector did in the past 10 years has no economic or social value. Do you agree? Did the financial services sector just get too big, and should it be smaller?
Okay. Well, a strong financial system is very important. It allocates capital to new businesses and new industries. It allows for people to invest in a wide range of activities, so it’s critically important to have a good financial system. And the evidence for that is that when the financial system breaks down, the system just doesn’t function.
That is not evidence for that. Seems a breakdown of logic???
You see what the impact has had on the economy. With that being said, the financial system is unique to the extent, first, that it is so critical to the economy, and, secondly, to the very, very old tendency to succumb to booms and busts.
Again, this is too confused to not be an insight into his basic sense of logic.
And, therefore, we do need to have an effective comprehensive financial regulatory system that will essentially allow us to tame the beast so that it provides the benefits, the growth and development without creating these kinds of crisis.
And then this says it all regarding his understanding of monetary operations:
Okay. When the Federal Reserve buys mortgages, it pays for them by creating reserves the banks hold in Federal Reserve. So, as we purchase $1 trillion of mortgages, we’ve created roughly $1 trillion of reserves that banks hold at the Federal Reserve. The banks, at this point, are just willing to hold those reserves with the Fed, and not do anything with them.
Banks don’t ‘do anything’ with reserves.
Ultimately, if the economy normalized, and the Fed took no action, the banks would take those reserves, try to lend them out, and they would begin to circulate, and the money supply would start to grow.
Banks don’t ‘lend out’ reserves.
And then, ultimately, that would create an inflationary risk.
This is not how it works.
So, therefore, as the economy begins to recover, and as we move away from this very weak economic environment, the Federal Reserve is going to have to pull those reserves out of the system.
We have a number of means for doing that, which we have explained to the markets, and the public, and everyone is confident we can do that. And we will do that over time, in order to make sure that as we come out of this crisis, we don’t generate inflation at the end.
Reserve management has nothing to do with inflation with a non convertible currency and floating fx. This is ancient gold standard rhetoric.
So, the reserves can be pulled out through various mechanisms or can mobilize. And we don’t have to do that yet, but when the time comes, we have tools to do that.
And are there lurking dangers in those mortgages that you purchased that we don’t even know about now?
Well, the mortgages are guaranteed. The credit, even if they go bad, Fannie and Freddie with the backing of the U.S. Treasury will pay them off, so the Fed is not taking any credit risk by holding these mortgages.
It’s comforting for you, but not for the taxpayers. Right?
Well, on the other hand, what’s happening is that we earn the interest from those mortgages, and then we remit that interest back to the Treasury, so the money finds its way back to the taxpayer.
That’s exactly how the Fed’s portfolio removes interest income from the private sectors.
And, indeed, the Federal Reserve will be paying the Treasury a good bit more money the next few years than it has in the past, because of the interest we’re earning on these mortgages we acquired.
On that note, this week we did learn the TARP is going to pay back nearly all of what it was required to from the taxpayer. Looking back a year later, are surprised by that?
Well, we said at the beginning that the TARP money was an investment. It was going to acquire assets, and that most or all might come back to the taxpayer. Right now, if you look at all these repayments from banks, and the fact that the government is sitting on capital gains, as well as other investments, I think it’s a reasonable probability that the TARP money invested in financial institutions, that the great majority of it will come back to the taxpayer. So, in the end, we will have stabilized the financial system and avoided this global crisis at not a small amount of money, but relative to the alternative, a quite small amount of money.
Were there days where you woke up and you thought, what am I not thinking of that we could be doing?
We had a philosophy right here, which was what we called blue-sky thinking. And what blue-sky thinking was, was we have a problem, I want everybody to give me just three associations. What can you think of? How can we approach this, what can we do? And we’ll worry about getting rid of the silly answers later. So, there’s been a lot of creativity here, and I give credit to terrific staff . I think one of the lessons of the depression, and this is something that Franklin Roosevelt demonstrated, was that when orthodoxy fails, then you need to try new things. And he was very willing to try unorthodox approaches when the orthodox approach had shown that it was not adequate.
[top]