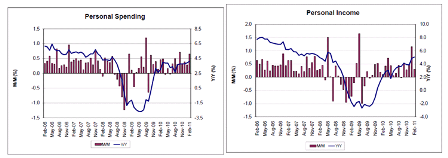
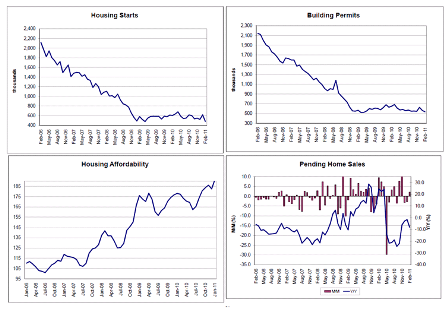
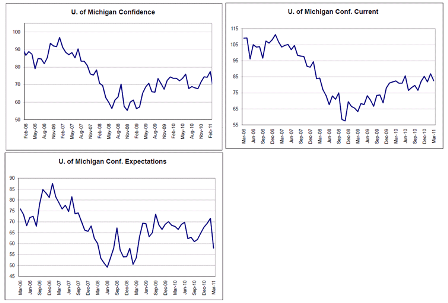
CAUTION: BE SEATED WHEN READING
COMMENTS BELOW:
By N. Gregory Mankiw
March 26 (NYT)
The following is a presidential address to the nation — to be delivered in March 2026.
My fellow Americans, I come to you today with a heavy heart. We have a crisis on our hands. It is one of our own making. And it is one that leaves us with no good choices.
For many years, our nation’s government has lived beyond its means.
A rookie, first year student mistake. Our real means are everything we can produce at full employment domestically plus whatever the rest of the world wants to net send us. The currency is the means for achieving this. Dollars are purely nominal and not the real resources.
We have promised ourselves both low taxes and a generous social safety net. But we have not faced the hard reality of budget arithmetic.
The hard reality is that for a given size government, there is a ‘right level’ of taxes that corresponds with full domestic employment, with the size of any federal deficit a reflection of net world dollar savings desires.
The seeds of this crisis were planted long ago, by previous generations. Our parents and grandparents had noble aims. They saw poverty among the elderly and created Social Security.
Yes, they decided they would like our elderly to be able to enjoy at least a minimum level of consumption of goods and services that made us all proud to be Americans.
They saw sickness and created Medicare and Medicaid. They saw Americans struggle to afford health insurance and embracedhealth care reform with subsidies for middle-class families.
Yes, they elected to make sure everyone had at least a minimum level of actual health care services.
But this expansion in government did not come cheap. Government spending has taken up an increasing share of our national income.
The real cost of this ‘expansion’ (which was more of a reorganization than an expansion of actual real resources consumed by the elderly and consumed by actual healthcare needs) may have consumed an increasing share of real GDP, but with continued productivity this would have been at most a trivial amount at current rates of expansion.
Today, most of the large baby-boom generation is retired. They are no longer working and paying taxes, but they are eligible for the many government benefits we offer the elderly.
Yes, they are consuming real goods and services produced by others. The important consideration here is the % of the population working and overall productivity which he doesn’t even begin to address.
Our efforts to control health care costs have failed. We must now acknowledge that rising costs are driven largely by technological advances in saving lives. These advances are welcome, but they are expensive nonetheless.
Still no indication of what % of real GDP he envisions going to health care and real consumption by the elderly.
If we had chosen to tax ourselves to pay for this spending, our current problems could have been avoided. But no one likes paying taxes. Taxes not only take money out of our pockets, but they also distort incentives and reduce economic growth. So, instead, we borrowed increasing amounts to pay for these programs.
At least he gives real economic growth a passing mention. However, what he seems to continuously miss is that real output is THE issue. Right now, with potential employment perhaps 20% higher than it currently is, the lost real output, which compounds continuously, plus the real costs of unemployment- deterioration of human capital, broken families and communities, deterioration of real property, foregone investment, etc. etc. etc.- are far higher than the real resources consumed by the elderly and actual health care delivery. Nor does he understand what is meant by the term Federal borrowing- that it’s nothing more than the shift of dollar balances from reserve accounts at the Fed to securities accounts at the Fed. And that repayment is nothing more than shifting dollar balances from securities accounts at the Fed to reserve accounts at the Fed. No grandchildren involved!!!
Yet debt does not avoid hard choices. It only delays them. After last week’s events in the bond market, it is clear that further delay is no longer possible. The day of reckoning is here.
This morning, the Treasury Department released a detailed report about the nature of the problem. To put it most simply, the bond market no longer trusts us.
For years, the United States government borrowed on good terms. Investors both at home and abroad were confident that we would honor our debts. They were sure that when the time came, we would do the right thing and bring spending and taxes into line.
But over the last several years, as the ratio of our debt to gross domestic product reached ever-higher levels, investors started getting nervous. They demanded higher interest rates to compensate for the perceived risk.
This is all entirely inapplicable. It applies only to fixed exchange rate regimes, such as a gold standard, and not to non convertible currency/floating exchange rate regimes. This is nothing more than another rookie blunder.
Higher interest rates increased the cost of servicing our debt, adding to the upward pressure on spending. We found ourselves in a vicious circle of rising budget deficits and falling investor confidence.
With our non convertible dollar and a floating exchange rate, the Fed currently sets short term interest rates by voice vote, and the term structure of interest rates for the most part anticipates the Fed’s reaction function and future Fed votes. Nor is there any operational imperative for the US Government to offer longer term liabilities, such as 5 year, 7 year, 10 year, and 30 year US Treasury securities for sale, which serve to drive up long rates at levels higher than otherwise. That too is a practice left over from gold standard days that’s no longer applicable.
As economists often remind us, crises take longer to arrive than you think, but then they happen much faster than you could have imagined. Last week, when the Treasury tried to auction its most recent issue of government bonds, almost no one was buying. The private market will lend us no more. Our national credit card has been rejected.
As above, the US Government is under no operational imperative to issue Treasury securities. US Government spending is not, operationally, constrained by revenues. At the point of all US govt spending, all that happens is the Fed, which is controlled by Congress, credits a member bank reserve account on its own books. All US Government spending is simply a matter of data entry on the US Governments own books. Any restrictions on the US government’s ability to make timely payment of dollars are necessarily self imposed, and in no case external.
So where do we go from here?
WE DON’T GET ‘HERE’- THERE IS NO SUCH PLACE!!!
Yesterday, I returned from a meeting at the International Monetary Fund in its new headquarters in Beijing. I am pleased to report some good news. I have managed to secure from the I.M.F. a temporary line of credit to help us through this crisis.
This loan comes with some conditions. As your president, I have to be frank: I don’t like them, and neither will you. But, under the circumstances, accepting these conditions is our only choice.
Mankiw’s display of ignorance and absurdities continues to compound geometrically.
We have to cut Social Security immediately, especially for higher-income beneficiaries. Social Security will still keep the elderly out of poverty, but just barely.
We have to limit Medicare and Medicaid. These programs will still provide basic health care, but they will no longer cover many expensive treatments. Individuals will have to pay for these treatments on their own or, sadly, do without.
We have to cut health insurance subsidies to middle-income families. Health insurance will be less a right of citizenship and more a personal responsibility.
We have to eliminate inessential government functions, like subsidies for farming, ethanol production, public broadcasting, energy conservation and trade promotion.
The only reason we would ever be ‘forced’ to make those cuts would be real resource constraints- actual shortages of land, housing, food, drugs, labor, clothing, energy, etc. etc. And yes, that could indeed happen. Those are the real issues facing us. But Mankiw is so lost in his errant understanding of actual monetary operations he doesn’t even begin to get to where he should have started.
We will raise taxes on all but the poorest Americans. We will do this primarily by broadening the tax base, eliminating deductions for mortgage interest and state and local taxes. Employer-provided health insurance will hereafter be taxable compensation.
He fails to recognize that federal taxes function to regulate aggregate demand, and not to raise revenue per se, again showing a complete lack of understanding of current monetary arrangements.
We will increase the gasoline tax by $2 a gallon. This will not only increase revenue, but will also address various social ills, from global climate change to local traffic congestion.
Ok, finally, apart from the revenue error, he’s got the rest of it sort of right, except he left out the part about that tax being highly regressive.
As I have said, these changes are repellant to me. When you elected me, I promised to preserve the social safety net. I assured you that the budget deficit could be fixed by eliminating waste, fraud and abuse, and by increasing taxes on only the richest Americans. But now we have little choice in the matter.
Due entirely to ignorance of actual monetary operations.
If only we had faced up to this problem a generation ago. The choices then would not have been easy, but they would have been less draconian than the sudden, nonnegotiable demands we now face. Americans would have come to rely less on government and more on themselves, and so would be better prepared today.
What I wouldn’t give for a chance to go back and change the past. But what is done is done. Americans have faced hardship and adversity before, and we have triumphed. Working together, we can make the sacrifices it takes so our children and grandchildren will enjoy a more prosperous future.
N. Gregory Mankiw is a professor of economics at Harvard.
And no small part of the real problem we face as a nation!
Feel free to repost and distribute