So it looks like QE2 indeed managed to scare China out of the dollar. This is the portfolio shifting previously discussed that’s been dragging down the dollar even though, fundamentally sound, as Fed Chairman Bernanke correctly stated.
And when China (and Japan) offered to buy Spanish and other euro zone national govt debt to ‘help out’, the euro zone fell for that one, watching their currency rise against their better judgement with regards to their euro wide exports.
And maybe Fed Chairman Bernanke is aware of this, and has assured China he does favor a strong dollar as per his latest public statements, and let them know that QE3 is unlikely, and has ‘won them back’? No way to tell except by watching the market prices.
And with most everyone out of paradigm with regards to monetary operations, there’s no telling what they all might actually do next.
What is known is that world fiscal balance is tight enough to be slowing things down, and looking to keep getting tighter.
And QE/lower overall term structure of rates removes interest income from the economy, and shifts income from savers to bank net interest margins.
And if China’s growth is going to slow dramatically, its most likely to happen the second half as they tend to front load their state lending and deficit spending each year.
And all the while our own pension funds continue to allocate to passive commodity strategies, distorting those markets and sending out price signals that continue to bring out increasing levels of supply that are filling up already overflowing storage bins.
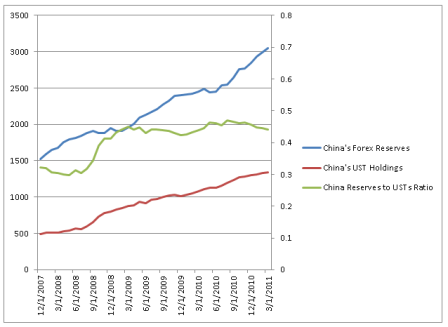

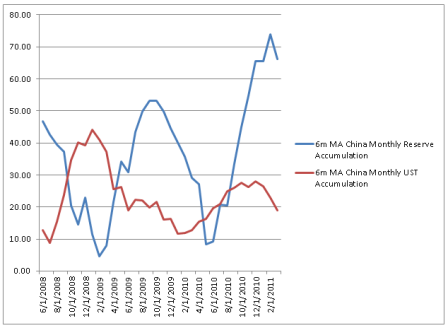
Note in particular that reserve accumulation has been high and rising recently, though UST accumulation has been moderate.


By Terence P. Jeffrey
Jun 4 (CNSNews.com) — China has dropped 97 percent of its holdings in U.S. Treasury bills, decreasing its ownership of the short-term U.S. government securities from a peak of $210.4 billion in May 2009 to $5.69 billion in March 2011, the most recent month reported by the U.S. Treasury.
Treasury bills are securities that mature in one year or less that are sold by the U.S. Treasury Department to fund the nation’s debt.
Mainland Chinese holdings of U.S. Treasury bills are reported in column 9 of the Treasury report linked here.
Until October, the Chinese were generally making up for their decreasing holdings in Treasury bills by increasing their holdings of longer-term U.S. Treasury securities. Thus, until October, China’s overall holdings of U.S. debt continued to increase.
Since October, however, China has also started to divest from longer-term U.S. Treasury securities. Thus, as reported by the Treasury Department, China’s ownership of the U.S. national debt has decreased in each of the last five months on record, including November, December, January, February and March.
Prior to the fall of 2008, acccording to Treasury Department data, Chinese ownership of short-term Treasury bills was modest, standing at only $19.8 billion in August of that year. But when President George W. Bush signed legislation to authorize a $700-billion bailout of the U.S. financial industry in October 2008 and President Barack Obama signed a $787-billion economic stimulus law in February 2009, Chinese ownership of short-term U.S. Treasury bills skyrocketed.
By December 2008, China owned $165.2 billion in U.S. Treasury bills, according to the Treasury Department. By March 2009, Chinese Treasury bill holdings were at $191.1 billion. By May 2009, Chinese holdings of Treasury bills were peaking at $210.4 billion.
However, China’s overall appetite for U.S. debt increased over a longer span than did its appetite for short-term U.S. Treasury bills.
In August 2008, before the bank bailout and the stimulus law, overall Chinese holdings of U.S. debt stood at $573.7 billion. That number continued to escalate past May 2009– when China started to reduce its holdings in short-term Treasury bills–and ultimately peaked at $1.1753 trillion last October.
As of March 2011, overall Chinese holdings of U.S. debt had decreased to 1.1449 trillion.
Most of the U.S. national debt is made up of publicly marketable securities sold by the Treasury Department and I.O.U.s called “intragovernmental” bonds that the Treasury has given to so-called government trust funds—such as the Social Security trust funds—when it has spent the trust funds’ money on other government expenses.
The publicly marketable segment of the national debt includes Treasury bills, which (as defined by the Treasury) mature in terms of one-year or less; Treasury notes, which mature in terms of 2 to 10 years; Treasury Inflation-Protected Securities (TIPS), which mature in terms of 5, 10 and 30 years; and Treasury bonds, which mature in terms of 30 years.
At the end of August 2008, before the financial bailout and the stimulus, the publicly marketable segment of the U.S. national debt was 4.88 trillion. Of that, $2.56 trillion was in the intermediate-term Treasury notes, $1.22 trillion was in short-term Treasury bills, $582.8 billion was in long-term Treasury bonds, and $521.3 billion was in TIPS.
At the end of March 2011, by which time the Chinese had dropped their Treasury bill holdings 97 percent from their peak, the publicly marketable segment of the U.S. national debt had almost doubled from August 2008, hitting $9.11 trillion. Of that $9.11 trillion, $5.8 trillion was in intermediate-term Treasury notes, $1.7 trillion was in short-term Treasury bills; $931.5 billion was in long-term Treasury bonds, and $640.7 billion was in TIPS.
Before the end of March 2012, the Treasury must redeem all of the $1.7 trillion in Treasury bills that were extant as of March 2011 and find new or old buyers who will continue to invest in U.S. debt. But, for now, the Chinese at least do not appear to be bullish customers of short-term U.S. debt.
Treasury bills carry lower interest rates than longer-term Treasury notes and bonds, but the longer term notes and bonds are exposed to a greater risk of losing their value to inflation. To the degree that the $1.7 trillion in short-term U.S. Treasury bills extant as of March must be converted into longer-term U.S. Treasury securities, the U.S. government will be forced to pay a higher annual interest rate on the national debt.
As of the close of business on Thursday, the total U.S. debt was $14.34 trillion, according to the Daily Treasury Statement. Of that, approximately $9.74 trillion was debt held by the public and approximately $4.61 trillion was “intragovernmental” debt.




