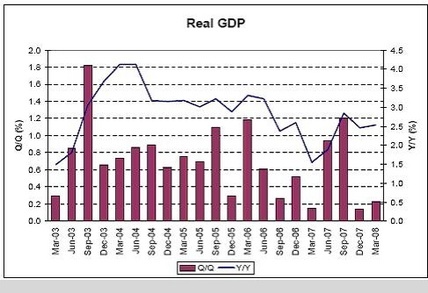
Real GDP
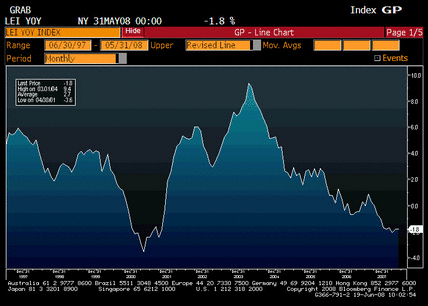
Can you find the recession? Year over year will be reasonable until last year’s large Q3 number drops out without similar sized q3 this year.
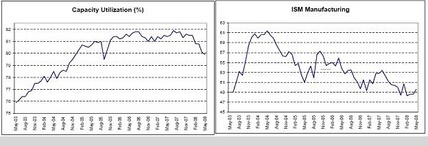
Capacity Utilization, ISM Manufacturing
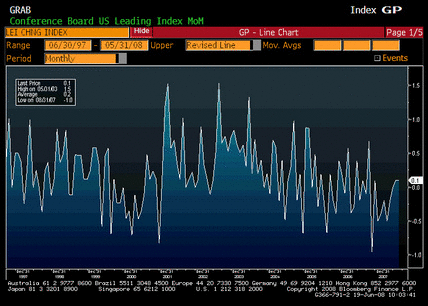
Down but not out as GDP muddles through.
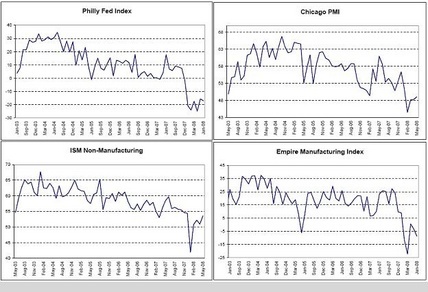
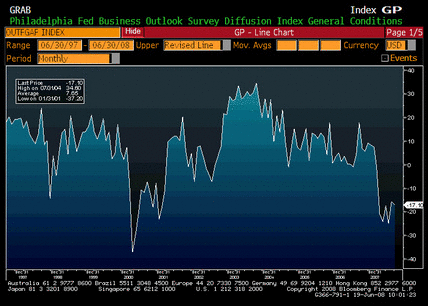
Philly Fed Index, Chicago PMI, ISM Non-Manufacturing, Empire Manufacturing Index
Limping along, but off the lows
The survey numbers seem to be depressed by inflation.
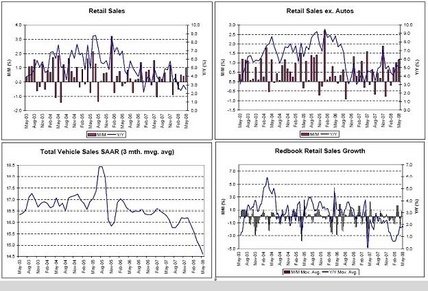
Retail Sales, Retail Sales Ex Autos, Total Vehicle Sales, Redbook Retail Sales Growth
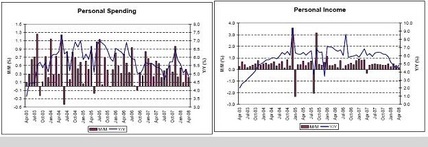
Personal Spending, Personal Income
Apart from cars and trucks, retail muddling through, and getting some support from the fiscal package.
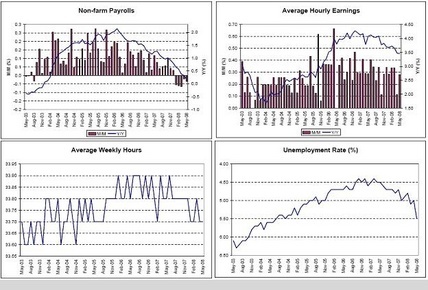
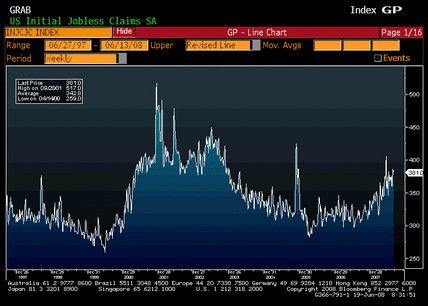
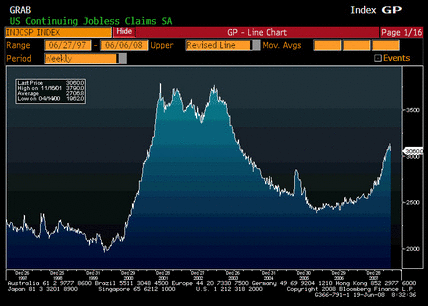
Non-farm Payrolls, Average Hourly Earnings, Average Weekly Hours, Unemployment Rate
Certainly on the soft side, but still positive year over year, earnings still increasing, and unemployment still relatively low (the last print was distorted a couple of tenths or so by technicals).
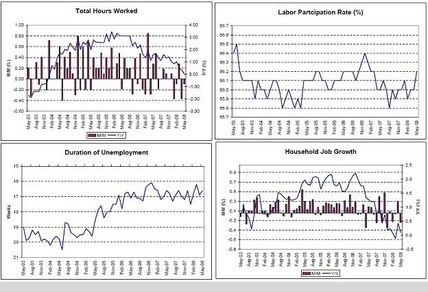
Total Hours Worked, Labor Participation Rate, Duration of Unemployment, Household Job Growth
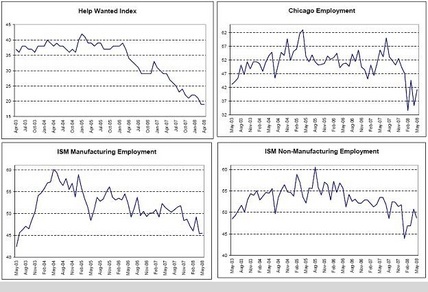
Help Wanted Index, Chicago Unemployment, ISM Manufacturing Employment, ISM Non-Manufacturing Employment
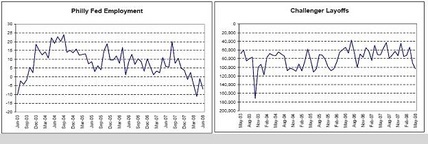
Philly Fed Employment, Challenger Layoffs
Most of the labor indicators are on the weak side, but not in a state of collapse. And GDP is picking up some from the fiscal package which should stabilize employment.
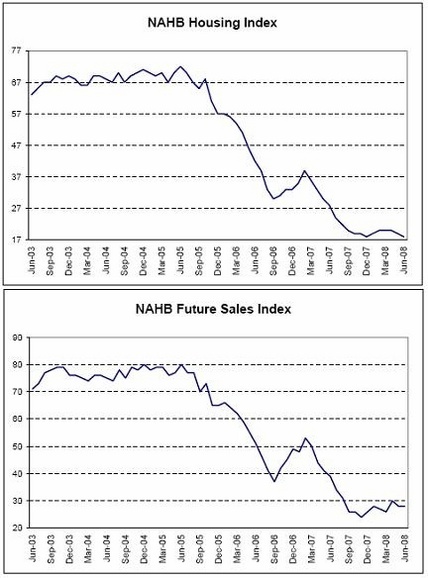
NAHB Housing Index, NAHB Future Sales Index
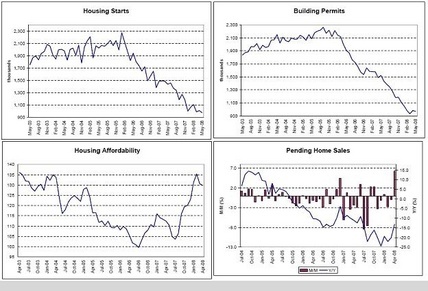
Housing Starts, Building Permits, Housing Affordability, Pending Home Sales
Leveling off to improving a touch.
Housing is still way down and could bounce 35% at any time.
And still be at relatively low levels.
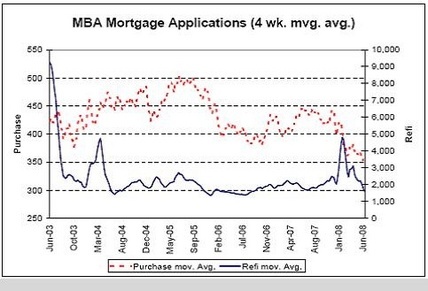
MBA Mortgage Applications
Mortgage apps are down but they are still at levels previously associated with 1.5 million starts vs today’s approx 1 million starts (annual rate).
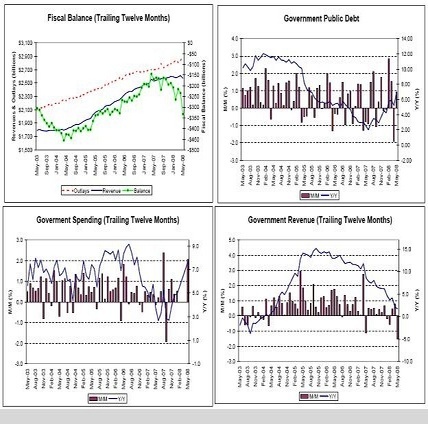
Fiscal Balance, Govt Public Debt, Govt Spending, Govt Revenue
It’s an election year, and here comes the Govt. spending which is already elevating GDP.
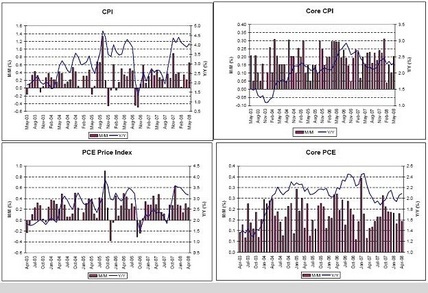
CPI, Core CPI, PCE Price Index, Core PCE
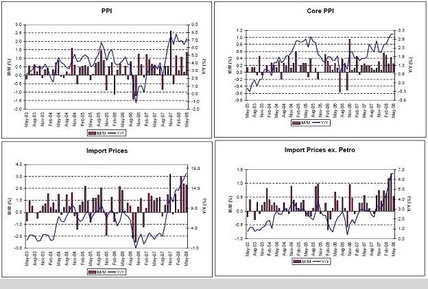
PPI, Core PPI, Import Prices, Import Prices Ex Petro
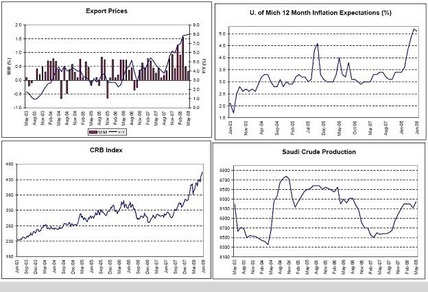
Export Prices, U of Michigan Inflation Expectations, CRB Index, Saudi Oil Production
The ‘inflation’ is only going to work its way higher as it pours through the import and export channels.
And with Saudi production completely demand driven, there’s no sign of a fall off of world demand for crude at current prices.
Yes, the world’s growing numbers of newly rich are outbidding America’s lower income consumers for gasoline, as US demand falls off and rest of world demand increases.
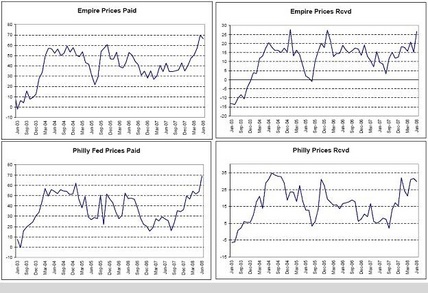
Empire Prices Paid, Empire Prices Received, Philly Fed Prices Paid, Philly Prices Received
All the price surveys are pretty much the same as ‘inflation’ pours in.
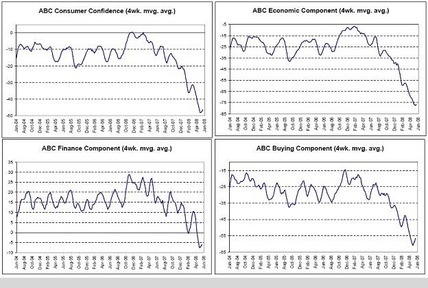
ABC Consumer Confidence, ABC Econ Component, ABC Finance Component, ABC Buying Component
And all the surveys look pretty much the same as ‘inflation’ eats into confidence
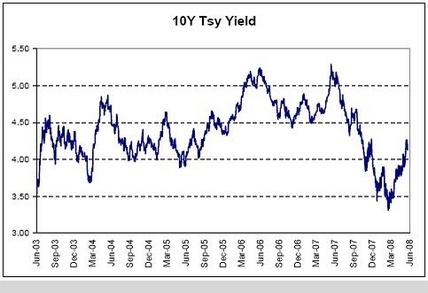
10Y Tsy Yield
And with all the weakness rates have generally moved higher as it seems inflation is doing more harm than ultra low interest rates are helping, perhaps causing the Fed to reverse course.
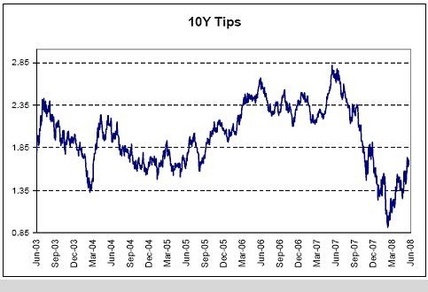
10Y Tips
The TIPS market has been discounting higher ‘real’ rates from the Fed.
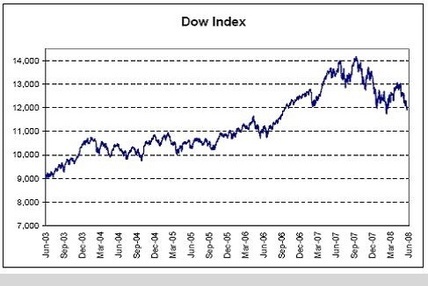
Dow Index
Even as stocks look to test the lows
[top]