[Skip to the end]
(email exchange)
Thanks, this is yet another example of the WSJ publishing and thereby promoting authors with no understanding of monetary operations, which means the WSJ editors don’t have any either.
Feel free to send this along the the WSJ with your own introductory comments as well!
>
> This is a well written piece, by Mr. Wood of CLSA.
>
I respectfully don’t agree.
>
> He has long maintained a bearish bias which comes through in the
> article. The points he raises I believe are cogent and logical and ones I
> have addressed as well over recent days and months.
>
It doesn’t seem you understand monetary operations either.
>
> The end of the article discussing gold I found to be particularly of
> interest.
>
By Christopher Wood
With an estimated $4 trillion in housing wealth and $9 trillion in stock-market wealth destroyed so far in the United States, there is little doubt that we are witnessing a classic debt-deflation bust at work, characterized by falling prices, frozen credit markets and plummeting asset values.
Yes, as well as fiscal automatic stabilizers working their way to the rescue as always.
Those who want to understand the mechanism might ponder Irving Fisher’s comment in 1933: When it comes to booms gone bust, “over-investment and over-speculation are often important; but they would have far less serious results were they not conducted with borrowed money.”
Irv was writing in the context of the gold standard of the time, and that did very well.
But it’s inapplicable with today’s non convertible currency and floating FX.
The growing risk of falling prices raises a challenge for one of the conventional wisdoms of the modern economics profession, and indeed modern central banking: the belief that it is impossible to have deflation in a fiat paper-money system.
You can easily have deflation if the deficit is allowed to get and remain too small.
Yet U.S. core CPI fell by 0.1% month-on-month in October, the first such decline since December 1982.
Pull back in commodity prices mainly, after a long run up, but yes, for now the moment the outlook is deflationary.
The origins of the modern conventional wisdom lies in the simplistic monetarist interpretation of the Great Depression popularized by Milton Friedman and taught to generations of economics students ever since. This argued that the Great Depression could have been avoided if the Federal Reserve had been more proactive about printing money.
On the gold standard this might have worked, though it would have meant the need to rapidly devalue the conversion rate which would have considered a government default. And this did happen.
Today it is inapplicable with non convertible currency and floating FX.
Yet the Japanese experience of the 1990s — persistent deflationary malaise unresponsive to near zero-percent interest rates — shows that it is not so easy to inflate one’s way out of a debt bust.
Doesn’t show that at all. Just shows the depth of their reluctance to use sufficient deficit spending to restore output and employment via increased domestic demand. They want to be export driven and have paid the price for a long time.
In the U.S., the Fed can only control the supply of money;
No, it only can control the term structure of risk free interest rates.
it cannot control the velocity of money or the rate at which it turns over.
True.
The dramatic collapse in securitization over the past 18 months reflects the continuing collapse in velocity as financial engineering goes into reverse.
By identity.
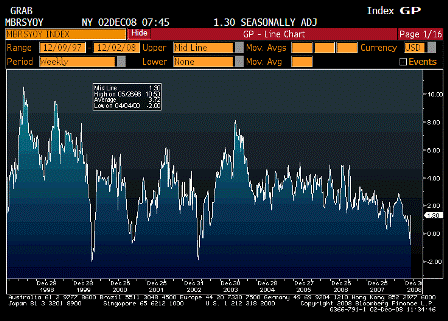
True, this will change one day. But for now, the issuance of nonagency mortgage-backed securities (MBS) in America has plunged by 98% year-on-year to a monthly average of $0.82 billion in the past four months, down from a peak of $136 billion in June 2006. There has been no new issuance in commercial MBS since July. This collapse in securitization is intensely deflationary.
Yes, though offset by increased government deficit spending, increased export revenues (for a while), and increased direct lending by banks to hold in portfolio (which is how it was all done in not so distant past cycles).
It is also true that under Chairman Ben Bernanke, the Federal Reserve balance sheet continues to expand at a frantic rate, as do commercial-bank total reserves in an effort to counter credit contraction.
In an effort to lower rates and thereby counter credit contraction.
Thus, the Federal Reserve banks’ total assets have increased by $1.28 trillion since early September to $2.19 trillion on Nov. 19. Likewise, the aggregate reserves of U.S. depository institutions have surged nearly 14-fold in the past two months to $653 billion in the week ended Nov. 19 from $47 billion at the beginning of September.
So??? Just entries on a government spread sheet with no further ramifications.
But the growth of excess reserves also reflects bank disinterest in lending the money.
So?
This suggests the banks only want to finance existing positions, such as where they have already made credit-line commitments.
Banking is necessarily pro cyclical- get over it!
Monetarist Bernanke and others blame Japan’s postbubble deflationary downturn on policy errors by the Bank of Japan.
Not me. It was the lack of sufficient deficit spending, as above.
But he and others are about to find out that monetary gymnastics are not as effective as they would like to think. So too will the Keynesians who view an aggressive fiscal policy as the best way to counter a deflationary slump. While public-works spending can blunt the downside and provide jobs, it remains the case that FDR’s New Deal did not end the Great Depression.
Mixing metaphors. The New Deal’s deficit spending was far too small to restore output and employment.
There are no easy policy answers to the current credit convulsion and intensifying financial panic — not as long as politicians and central bankers are determined not to let financial institutions fail, and so prevent the market from correcting the excesses.
Yes there is an easy answer- make a sufficiently large fiscal adjustment.
This is why this writer has a certain sympathy for Treasury Secretary Henry Paulson, even if nobody else seems to. The securitized nature of this credit cycle, combined with the nightmare levels of leverage embedded in the products dreamt up by the quantitative geeks, means this is a horribly difficult issue to solve.
Couldn’t be easier. Start with a payroll tax holiday where the treasury makes all FICA payments for employees and employers.
The spread around a few hundred billion in revenue sharing to the states for operations and infrastructure.
Crisis over.
Virtually everybody blames Mr. Paulson for the decision to let Lehman Brothers go. But this decision should be applauded for precipitating the deflationary unwind that was going to come sooner or later anyway.
The Japanese precedent also remains important because the efforts in the West to prevent the market from disciplining excesses will have, as in Japan, unintended, adverse, long-term consequences.
Doesn’t even mention output and employment.
In Japan, one legacy is the continuing existence of a large number of uncompetitive companies which have caused profit margins to fall for their more productive competitors.
Who cares?
Another consequence has been a long-term deflationary malaise, which has kept yen interest rates ridiculously low to the detriment of savers.
Interesting bit of logic!
Meanwhile, the most recent Fed survey of loan officers provides hard evidence of the intensifying credit crunch in America. A net 83.6% of domestic banks reported having tightened lending standards on commercial and industrial loans to large and midsize firms over the past three months, the highest since the data series began in 1990. A net 47% of banks also indicated that they had become less willing to make consumer installment loans over the past three months.
Banks are necessarily pro cyclical- get over it!
Consumers are also more reluctant to borrow. A net 48% of respondents indicated that they had experienced weaker demand for consumer loans of all types over the past quarter, up from 30% in the July survey. This hints at the Japanese outcome of “pushing on a string” — i.e., the banks can make credit available but cannot force people to borrow.
Good! Lower taxes for any given amount of government spending. Bring it on! Now!
The Fed Is Out of Ammunition
With a fed-funds rate at 0.5% or lower in coming months, it is fast becoming time for investors to read again Mr. Bernanke’s speeches in 2002 and 2003 on the subject of combating falling inflation. In these speeches, the Fed chairman outlined how policy could evolve once short-term interest rates get to near zero. A key focus in such an environment will be to bring down long-term interest rates, which help determine the rates of mortgages and other debt instruments. This would likely involve in practice the Fed buying longer-term Treasury bonds.
Yes. And not do a lot for output and employment until fiscal adjustment takes hold.
And do we really want to encourage an increase in private leverage? Been there done that, right?
It would seem fair to conclude that a Bernanke-led Fed will follow through on such policies in coming months if, as is likely, the U.S. economy continues to suffer and if inflationary pressures continue to collapse. Such actions will not solve the problem but will merely compound it, by adding debt to debt.
I think he’s got it right there.
In this respect the present crisis in the West will ultimately end up discrediting mechanical monetarism —
Hope so. It flies in the face of theory and reality.
and with it the fiat paper-money system in general — as the U.S. paper-dollar standard, in place since Richard Nixon broke the link with gold in 1971, finally disintegrates.
Why??? Deflation as above? Deflation is the increase in value of a currency. Disintegration is via inflation???
The catalyst will be foreign creditors fleeing the dollar for gold. That will in turn lead to global recognition of the need for a vastly more disciplined global financial system and one where gold, the “barbarous relic” scorned by most modern central bankers, may well play a part.
Fleeing the dollar for gold means inflation. He’s been preaching deflation for this whole piece. Can’t have it both ways.
Mr. Wood, equity strategist for CLSA Ltd. in Hong Kong, is the author of “The Bubble Economy: Japan’s Extraordinary Speculative Boom of the ’80s and the Dramatic Bust of the ’90s” (Solstice Publishing, 2005).
Aha! Hong Kong has a fixed FX policy, much like a gold standard. He’s applying fixed FX analysis to the us which has a floating FX policy.
The WSJ should have told him this and rejected this op-ed piece.
[top]