[Skip to the end]
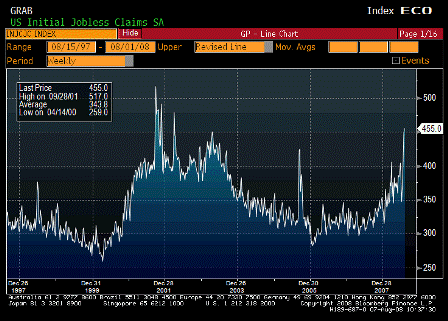


Initial Jobless Claims (Aug 2)
| Survey |
425K |
| Actual |
455K |
| Prior |
448K |
| Revised |
n/a |
Karim writes:
- Initial claims rise 7k to new cycle high of 455k with 4wk moving avg up from 393k to 420k
[top][end]
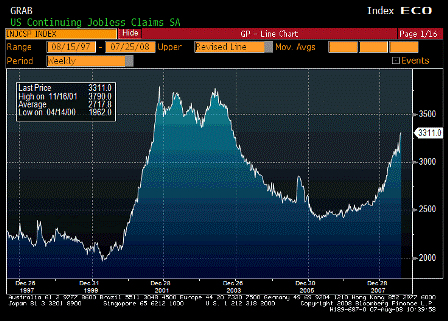


Continuing Jobless Claims (Jul 26)
| Survey |
3255K |
| Actual |
3311K |
| Prior |
3282K |
| Revised |
3280K |
Karim writes:
- Continuing claims rise from 3280k to 3311k and 4wk moving avg up from 3174k to 3201k
[top][end]
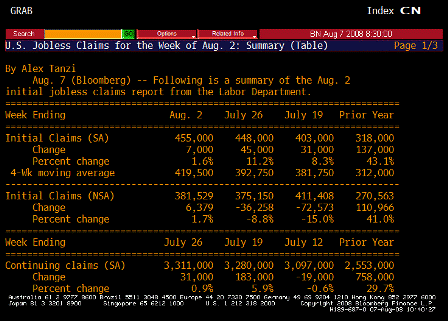


Jobless Claims TABLE 1 (Jul 26)
[top][end]
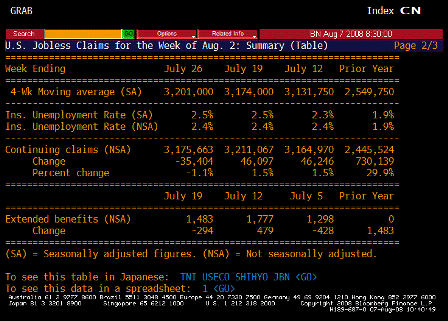


Jobless Claims TABLE 2 (Jul 26)
Cesar writes:
A year ago we were at 4.7% unemployment rate (7,137 unemployed/ 153,182 labor force)
We are currently at 5.7% unemployment rate (8,784 unemployed/ 154,603 labor force)
Seems nearly the entire jump in unemployment is due to labor force increases.
Total employed is about flat.
In that case, GDP growth is about equal to productivity growth.
Karim writes:
- Initial claims somewhat distorted by new program to extend benefits where those filing extensions are considered first time filers (double counted); this should have an effect for the first 2-3 weeks of the program before initial claims fall back to trend level (same happened back in 2001). Last week was first week of program, so numbers for next 2 weeks should reflect underlying trend (last number before extension program was 403k). Of concern would be if numbers don’t fall back much.
- This program does not effect continuing claims, which reflects ability to find a job once laid off. This is at a new cycle high.
[top][end]
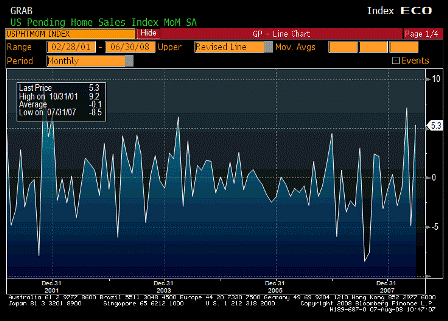


Pending Home Sales MoM (Jun)
| Survey |
-1.0% |
| Actual |
5.3% |
| Prior |
-4.7% |
| Revised |
-4.9% |
Karim writes:
- Rise 5.3% m/m, continuing recent see-saw pattern (-4.9%, +7.1% prior 2mths).
Q2 GDP for Japan and Germany are out next week. A German newspaper yesterday leaked German GDP growth likely to be -1 to -1.5%. Much of this is a giveback for a strong Q1 of +1.5% but definitely weaker than expected. Of concern to the ECB is that Spain (industrial production now down 10% y/y) and Italy already written off, so much depends on Germany. Moreover, German PMIs have gotten off to a very weak start for Q3. I imagine that was at the root of Trichet’s more dovish tone today.
Estimates for Japanese Q2 GDP are in the -1% to -3.5% range. The July Tankan and the foreign orders component of last night’s machinery orders data also don’t bode too well for Q3.
[top][end]
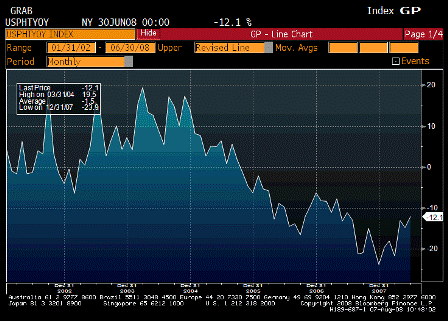


Pending Home Sales YoY (Jun)
| Survey |
n/a |
| Actual |
-12.1% |
| Prior |
-14.8% |
| Revised |
n/a |
Looks like it has bottomed and moving up as prices have adjusted and GDP has improved.
Housing my no longer be subtracting from GDP.
[top][end]
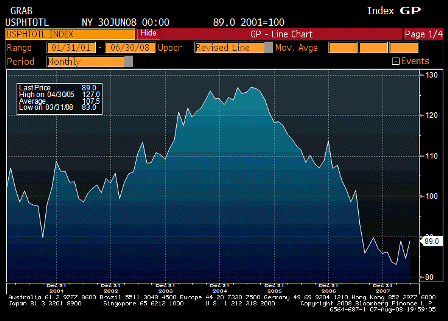


Pending Home Sales Total SA (Jun)
| Survey |
n/a |
| Actual |
89.0 |
| Prior |
84.5 |
| Revised |
n/a |
Looks to have found support and probably bottomed albeit at very low levels.
[top][end]
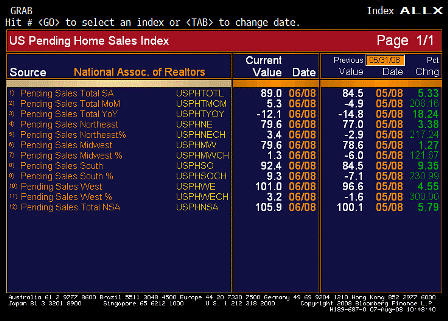


Pending Home Sales ALLX (Jun)
[top][end]
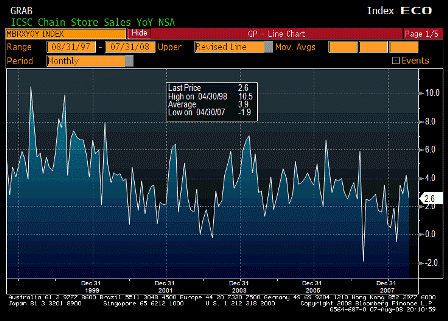


ICSC Chain Store Sales YoY (Jul)
| Survey |
3.4% |
| Actual |
2.6% |
| Prior |
4.3% |
| Revised |
4.2% |
Less then expected but not bad.
[top][end]
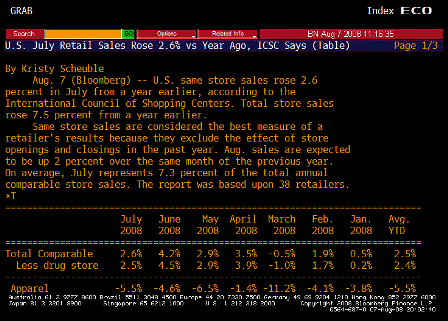


ICSC TABLE 1 (Jul)
[top][end]
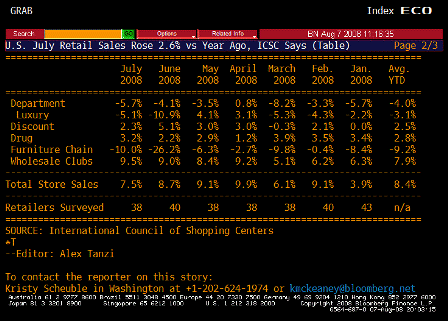


ICSC TABLE 2 (Jul)
[top][end]
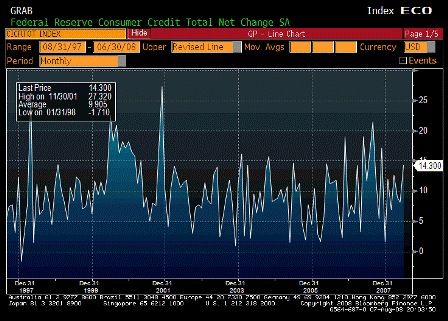


Consumer Credit (Jun)
| Survey |
$6.3B |
| Actual |
$14.3B |
| Prior |
$7.8B |
| Revised |
$8.1B |
Volatile series. Moving up some to support higher levels of spending.
[top][end]
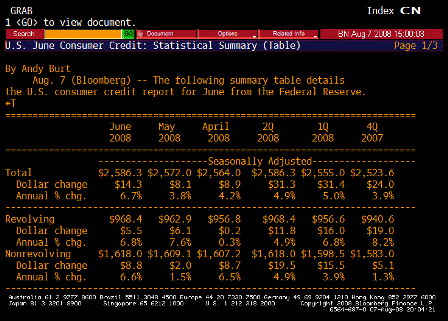


Consumer Credit TABLE 1 (Jun)
[top][end]


Consumer Credit TABLE 2 (Jun)
Note from the graph the improving position of the domestic sector as the government deficit and net exports rise and support domestic ‘savings’ and spending. The US budget deficit is expected to exceed 3% this year and exports should remain firm even with slowing foreign economies. In fact, that’s one of the primary reasons those economies are slowing.
by Shobhana Chandra
(Bloomberg) U.S. consumers borrowed more than twice as much as economists forecast in June as the slump in real-estate prices prevented American homeowners from tapping into home-equity lines of credit.
Consumer credit rose by $14.3 billion, the most since November, to $2.59 trillion, the Federal Reserve said today in Washington. In May, credit rose by $8.1 billion, previously reported as an increase of $7.8 billion. The Fed’s report doesn’t cover borrowing secured by real estate.
Consumers are using credit cards and loans to cover expenses as falling home values cause banks to restrict access to home- equity lines. The Bush administration sent out tax rebate checks in the past three months to help support spending, which accounts for more than two-thirds of the economy.
“Consumers are stressed, and some who are short of cash are relying more on credit cards,” Joseph Brusuelas, chief economist at Merk Investments LLC in Palo Alto, California, said before the report.
[top]