Ed says:
Warren,
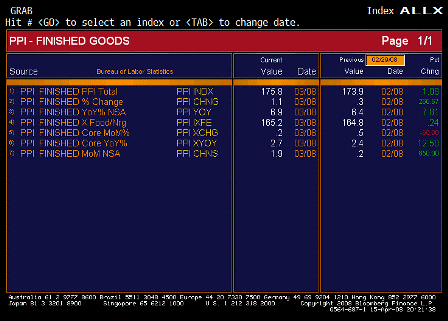
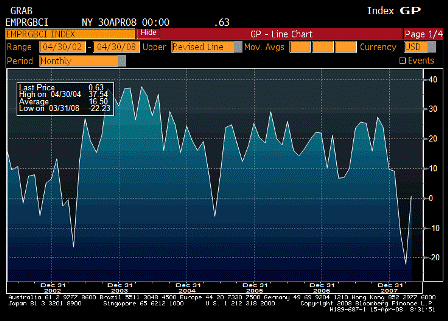
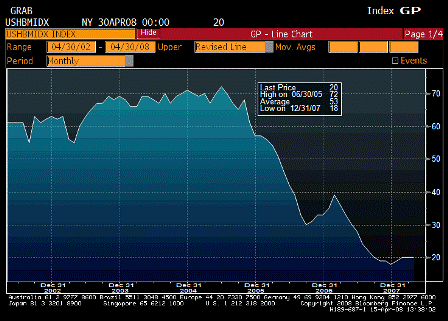
Isn’t it also true that the US export boom is less a result of the weaker dollar, so much as it is the cause? Foreigners using the trade surplus dollars they were previously content to save, are now spending them, and the shopping list is sizable. In this sense, all the dollars we have been exporting for years are coming home to roost, and that explains a good chunk of the inflation we are seeing.
Ed
I agree the cause is foreigners switching as a sector from wanting to accumulate USD to not wanting to accumulate them, and therefore spending them.
However, I see the market forces working as follows:
The first desire is ‘not to save’ which drives the USD down either until the $ is somehow low enough where they want to save it again, which doesn’t make sense to me, or until the USD is low enough for them to spend them here, which makes a bit more sense to me.
And the other force is the decreased desire to export to us which is evidenced by higher import prices.
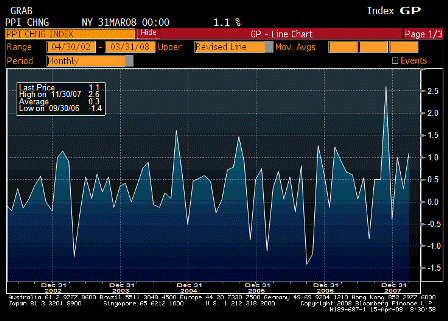
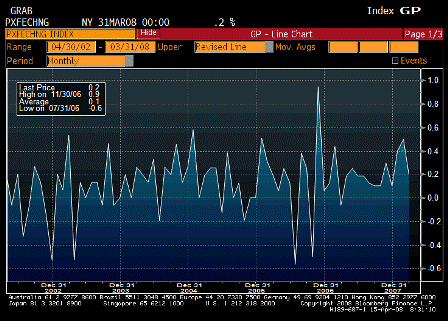
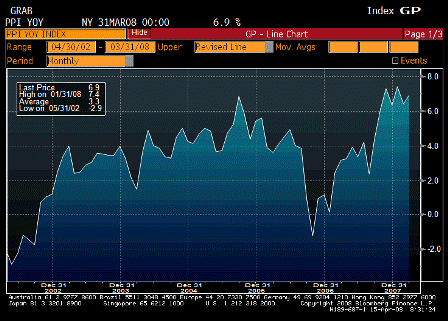
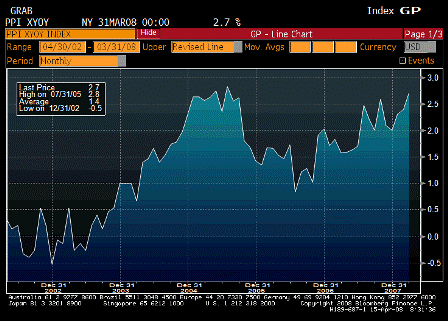
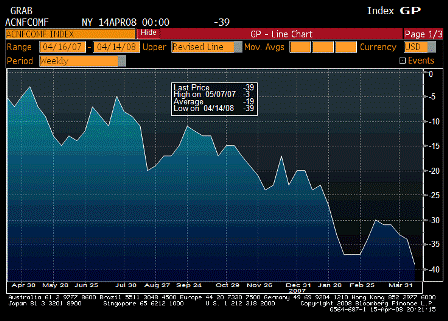
Last, this is all inflationary, and inflation is the other channel for getting rid of a trade gap.
For an extreme example, if there is sufficient inflation for the minimum wage to go to $60 billion per hour, the real trade gap is suddenly down to only an hour of labor, though still nominally at 60 billion.
The combination of rising net exports, falling imports, and inflation are all working together right now to digest the sudden shift from CBs and monetary authorities away from buying USD financial assets.
Fiscal adjustment checks start going out in a couple of weeks.
Rest of govt. spending going up as well.
GDP should muddle through and inflation continue to accelerate.
It may dawn on the Fed that the weak dollar is hurting the financial sector as the consumer is being squeezed by food/energy prices and therefore having trouble making loan payments. That’s the price of sticky wages, at least this time around.
Foreign CBs have no option regarding world currency stability but to try to put pressure on the Fed to stop cutting.