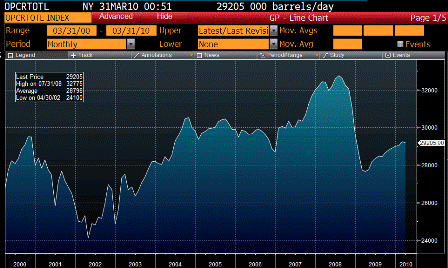
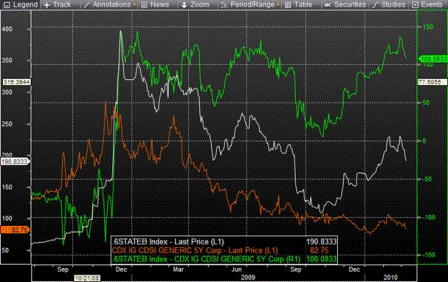
Yes, federal looking like they’ve bottomed as well.
Definitely looks like activity has bottomed.
And still feels like we are going the way of Japan, but too early to tell.
Tax Receipts Rebound as 15 Biggest States See Gain
By Dunstan McNichol
March 30 (Bloomberg) — The two-year slide in tax
collections that opened a $196 billion gap in U.S. state budgets
has stopped, easing pressure on credit ratings and giving leeway
to lawmakers as they craft spending plans for next year.
The 15 largest states by population forecast a 3.9 percent
gain in tax revenue in fiscal 2011, budget documents show. The
50 states on average may increase collections by about 3.5
percent, the first time in two years the figure is expected to
grow, said Mark Zandi, chief economist at Moody’s Economy.com,
California took in 3.9 percent more since December than
projected in January, Controller John Chiang said this month.
New York got $129 million above forecasts in its budget year
through February, according to a report from Comptroller Thomas
DiNapoli. In New Jersey, the second-wealthiest state per capita,
January sales-tax collections were 1.9 percent higher than a
year earlier, the first annual increase in 19 months,
forecasters said in a report last month.
“This time last year, we were sliding down a mountain,”
said David Rosen, chief budget officer for the New Jersey
Legislature. “I don’t think we are now; it’s stabilized.”
States collected about $79 billion less in sales, income
and corporate taxes in 2009 than in 2008, the U.S. Census Bureau
said today in a report, as the economy struggled through its
deepest slump since the Great Depression. Emergency spending
cuts and tax increases became routine during the recession that
began in December 2007.
‘Panic Mode’
The end of the collections crash will ease fiscal strains
that led New York-based Moody’s Investors Service to lower the
ratings of five states last year, after no downgrades in 2008.
It will also enable governors and legislators to draw up budgets
for fiscal 2011, which starts July 1 for most states, with more
confidence that money they plan to spend will arrive.
“As long as revenues were sliding, budgeters were in a
panic mode,” said Zandi, whose West Chester, Pennsylvania-based
company provides economic analysis to businesses, government and
investors. “It’s not as scary when revenues are rising.”
States’ combined budget gaps will still total $180 billion
in fiscal 2011 and $120 billion in fiscal 2012, the Washington-
based Center on Budget and Policy Priorities estimates.
Economic Growth
This fiscal year, the 15 largest states expect to collect
11 percent less taxes than in fiscal 2008, budget proposals
show. It won’t be until 2013 that revenue returns to 2008
levels, said New Jersey’s Rosen and Barry Boardman, the North
Carolina General Assembly’s chief economist.
Collections of personal income and sales taxes, the two
largest components of state revenue, fell by 17 percent and 7
percent, respectively, last year compared with 2008, according
to the Census Bureau. Declines were less steep in the fourth
quarter than earlier in the year, with income taxes dropping by
4.7 percent to $59.9 billion and sales taxes sliding by 2.8
percent to $71.7 billion.
Corporate taxes increased 3.4 percent to $9.1 billion in
the fourth quarter, the Census Bureau said, after declining in
seven of the previous nine quarters.
Combined state and local tax collections climbed to $360.1
billion during the final three months of 2009, the first year-
over-year gain in five quarters and an almost 1 percent boost
from the same period in 2008, according to the agency.
State coffers are beginning to get a boost from an economy
that expanded at a 5.6 percent annual rate in the fourth quarter
of 2009, the most in six years. That’s stopped the drop in sales
tax collections, which generated $23 billion less last year than
in 2008, according to the Census Bureau.
Predictability a ‘Positive’
Arizona, which sold state buildings and canceled health
insurance for 47,000 children as collections this fiscal year
fell 34 percent below 2007 levels, said its January revenue was
$14.2 million above projections, the first time since March 2007
that collections exceeded forecasts.
Virginia recorded a 31.6 percent increase in corporate
taxes through February, it said on March 11. Governor Robert
McDonnell, a Republican who took office in January, increased
this year’s revenue projections by $82.5 million last month.
Improved revenues may help states replenish reserves, curb
borrowing for expenses and strengthen their debt ratings, said
Robin Prunty, credit analyst for Standard & Poor’s in New York.
“Just having predictability is a positive from a credit
standpoint,” Prunty said.
“We’ve seen the worst,” said Philip Condon, who oversees
about $9.4 billion in municipal bonds for DWS Investments in
Boston. “While it may not be great, it’s getting better.”
California Sale
DWS was among the buyers of last week’s $3.4 billion
issuance of taxable California bonds, its first such sale since
November. A scarcity of municipal debt, coupled with indications
that California’s revenue decline may have reached bottom,
attracted investors and drove down bond yields, Condon said.
“The recent uptick in revenue collections certainly didn’t
hurt us,” said Tom Dresslar, a spokesman for Treasurer Bill
Lockyer in Sacramento.
Forty-five states reduced outlays for health care, the
elderly and disabled and primary and higher education in 2008
and 2009, the Center on Budget and Policy Priorities said.
Lawmakers now may be able to restore spending or avoid
further reductions. California’s Chiang this month scrapped a
plan to delay tax refunds after revenue exceeded projections for
three months. In January, an impasse over the state’s $20
billion budget imbalance led S&P to cut its credit rating to A-,
the lowest of any state.
“The fact that revenues are performing better I think is
certainly the first bit of good news we’ve heard in a long
time,” said Amy Doppelt, a San Francisco-based managing
director at Fitch Ratings who follows California. Fitch last
year downgraded more than 200 municipal issuers, the most ever,
according to a March 25 report from the rating company.
Negative Outlook
S&P lowered its rating on California, Illinois and Arizona
last year and has a negative outlook on those and four other
states. Moody’s cut those three plus Nevada and Ohio, its first
state downgrades since Michigan in 2007. It’s negative on 15,
including five of the 10 largest: Florida, Illinois,
Pennsylvania, Ohio and Michigan.
Jobless rates in 18 states including Florida and Rhode
Island exceeded the national average of 9.7 percent in February.
Unemployment in most states is about double pre-recession
levels, according to the Labor Department.
Michigan, with the nation’s highest unemployment rate at
14.1 percent in February, is in its 10th year of job losses and
expects to end fiscal 2011 with the fewest jobs in 24 years.
“As the employment situation continues to be weak, income
tax revenues will continue to lag,” the Center on Budget and
Policy Priorities said in a Feb. 25 report.
Pension Expenses
As workers lose income, states face rising expenses for
Medicaid and other social services. Through March, they had
borrowed $37 billion from the federal government to cover
unemployment benefits, the Treasury Department said.
States face a $1 trillion gap between assets in public
pension plans and their obligations to retirees, a Feb. 18 study
by the Washington-based Pew Center on the States said. Illinois
borrowed $3.5 billion in January to finance its pension
contribution, which led Moody’s and S&P to cut their ratings to
the second-lowest of any state.
More Jobs
“You can’t exclude the expense side,” said Howard Cure,
New York-based director of municipal research for Evercore
Wealth Management LLC, which oversees $1.7 billion, half in
fixed-income municipals. “What really would alleviate that
situation is more jobs.”
States also have to prepare for the June 2011 end of help
from the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act, which will
provide them with about $140 billion of aid since its inception
in February 2009.
“States may have reached the end of the beginning of a
multiyear fiscal crisis,” the Nelson A. Rockefeller Institute
of Government in Albany, said in a January report. “The best to
be hoped for in 2010 may be the beginning of the end.”