[Skip to the end]
by Robert B. Reich
BOTH presidential candidates have been criticized for failing  at Tuesday’s debate and previously  to name any promises or plans they’re going to have to scrap because of the bailout and the failing economy. That criticism is unwarranted. The assumption that we are about to have a rerun of 1993  when Bill Clinton, newly installed as president, was forced to jettison much of his agenda because of a surging budget deficit  may well be mistaken.
No, it’s ridiculous! Cutting back is for times of excess aggregate demand – hardly the case today.
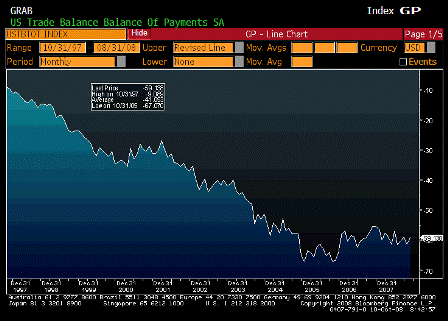
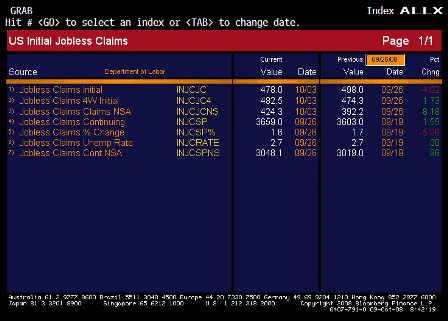
At first glance, January 2009 is starting to look a lot like January 1993. Then, the federal deficit was running at roughly $300 billion a year, or about 5 percent of gross domestic product, way too high for comfort.
Why?
By contrast, the deficit for the 2009 fiscal year is now projected to be $410 billion, or about 3.3 percent of gross domestic product. That’s not too worrying.
No number per se is worrying. It’s things like output, employment, and maybe inflation that are worrying.
But if the Treasury shovels out the full $700 billion of bailout money next year, the deficit could balloon to more than 6 percent of gross domestic product, the highest since 1983. And if the nation plunges into a deeper recession, with tax revenues dropping and domestic product shrinking, the deficit will be even larger as a proportion of the economy.
True, as a matter of accounting. But none of the above is symptomatic of excess aggregate demand.
Yet all is not what it seems. First, the $700 billion bailout is less like an additional government expense than a temporary loan or investment.
It’s an exchange of financial assets, much like the Fed does continuously, with no effect on demand.
The Treasury will take on Wall Street’s bad debts  mostly mortgage-backed securities for which there’s no market right now  and will raise the $700 billion by issuing additional government debt,
No, the government first pays for the mortgage securities and then offers Treasury securities (or now, interest-bearing reserves, which are functionally the same as Treasury securities) to support the overnight rate that the Fed’s target rate.
much of it to global lenders and foreign governments.
They exchange real goods and services for balances at the Fed because they want to. We then offer them alternative financial assets in the form of Treasury securities via an auction process that is bought at necessarily attractive levels.
As America’s housing stock regains value, as we all hope it will,
Yes, deep down we all hope for ‘inflation’…
bad debts become better debts, and the Treasury will be able to resell the securities for at least as much as it paid, if not for a profit.
And that would drain aggregate demand and be contradictionary, just like a tax.
And if there is a shortfall, the bailout bill allows the president to impose a fee on Wall Street to fill it.
Also draining aggregate demand.
Another difference is that in 1993, the nation was emerging from a recession.
Yes, because the deficit was allowed to get up to 5% of GDP.
Government deficit = Non-government accumulation of net financial assets, etc.
Although jobs were slow to return, factory orders were up and the economy was growing. This meant growing demand for private capital.
If so, loans create deposits: loanable funds went out with the gold standard.
Under these circumstances, the deficit Bill Clinton inherited threatened to overheat the economy.
I don’t recall any evidence of an overheating economy back then?
He had no choice but to trim it, a point that the Federal Reserve chairman, Alan Greenspan, was not reluctant to emphasize. Unless President Clinton cut the deficit and abandoned much of his agenda, interest rates would rise and the economic recovery would be anemic.
Interest rates would rise only if Greenspan, not market forces, raised them, which he may have threatened to do.
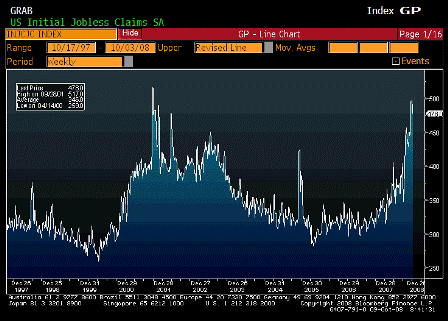
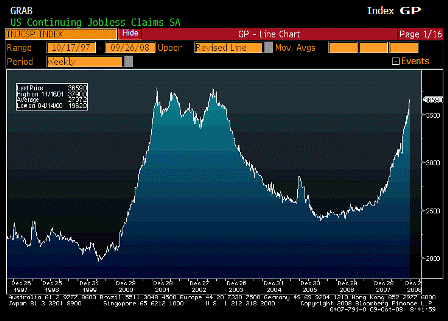
Next year, however, is likely to be quite different. All economic indicators are now pointing toward a deepening recession. Unemployment is already high, and the trend is not encouraging. Factory orders are down. Worried about their jobs and rising costs of fuel, food and health insurance, middle-class Americans are unable or unwilling to spend on much other than necessities.
Under these circumstances, deficit spending is not unwelcome. Indeed, as spender of last resort, the government will probably have to run deficits to keep the economy going anywhere near capacity, a lesson the nation learned when mobilization for World War II finally lifted us out of the Great Depression.
Agreed!!!
Finally, not all deficits are equal. As every family knows, going into debt in order to send a child to college is fundamentally different from going into debt to take an ocean cruise. Deficits that finance investments in the nation’s future are not the same as deficits that maintain the current standard of living.
Agreed!
Here again, there’s marked difference between 1993 and 2009. Then, some of our highways, bridges, levees and transit systems needed repair. Today, they are crumbling. In 1993, some of our children were in classrooms too crowded to learn in, and some districts were shutting preschool and after-school programs. Today, such inadequacies are endemic.
Yes, trillions of USD could be spent on infrastructure. But the key to ‘affordability’ at the macro level is unemployment and excess capital in general.
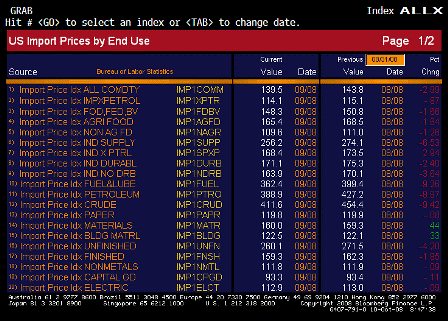
In 1993, some 35 million Americans had no health insurance and millions more were barely able to afford it. Today, 50 million are without insurance, and a large swath of the middle class is barely holding on.
Insurance is an entirely different issue than whether people are getting health care or not. He should make that point and then address the real issue (distribution of health care and other real goods and services) and not miss the financial for the real issues.
In 1993, climate change was a problem. Now, it’s an emergency.
Moreover, without adequate public investment, the vast majority of Americans will be condemned to a lower standard of living for themselves and their children. The top 1 percent now takes home about 20 percent of total national income. As recently as 1980, it took home 8 percent. Although the economy has grown considerably since 1980, the middle class’s share has shrunk. That’s a problem not just because it strikes so many as being unfair, but also because it’s starting to limit the capacity of most Americans to buy the goods and services we produce without going deep into debt.
That’s because incomes are too low, the largest taxes are the regressive payroll deductions, and the deficit is too small.
Time for a payroll tax holiday.
The last time the top 1 percent took home 20 percent of national income, not incidentally, was 1928.
Good statistic!
Perhaps it should not be surprising, then, that the Wall Street bailout has generated so much anger among middle-class Americans. Let’s not compound the problem by needlessly letting it prevent the government from spending what it must to lift the prospects of Main Street.
Agreed, but not by writing this type of thing.
Feel free to distribute.
Robert B. Reich, a secretary of labor under President Bill Clinton and a professor at the University of California, Berkeley, is the author of “Supercapitalism.”
[top]