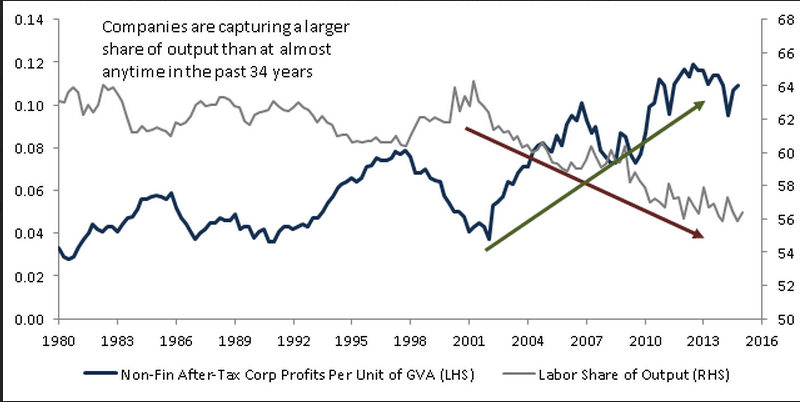
Heaps stronger than expected:
Employment Situation
Highlights
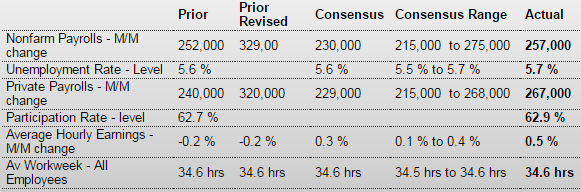
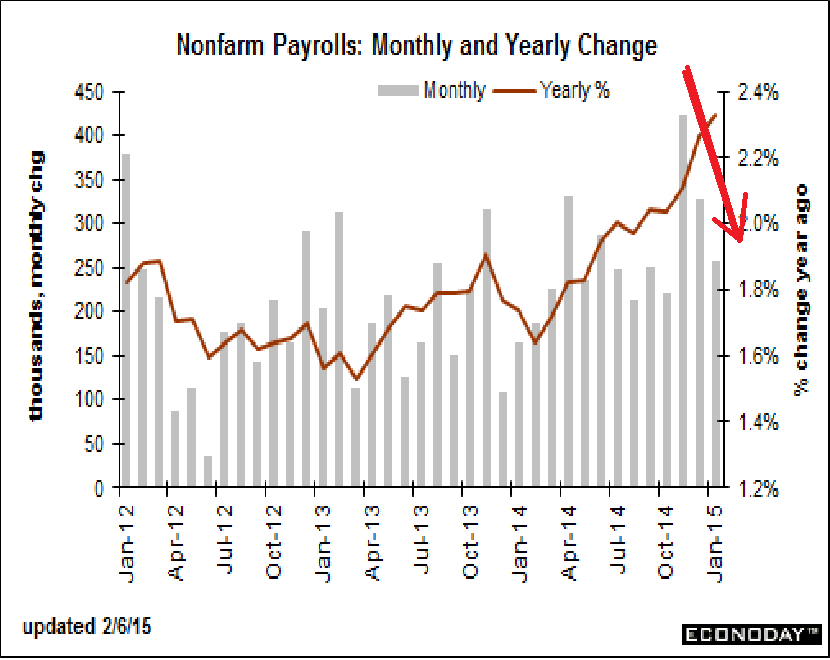
Today’s employment situation was heavily positive even though the unemployment rate edged up. Payroll jobs gained 257,000 in January after strong increases of 329,000 in December and 423,000 in November. December and November were revised up a net 86,000. With the revision, November is the strongest month since May 2010. Today’s report may tip the balance for the Fed to think about a first increase in policy rates this year rather than next-although still at a slow pace.
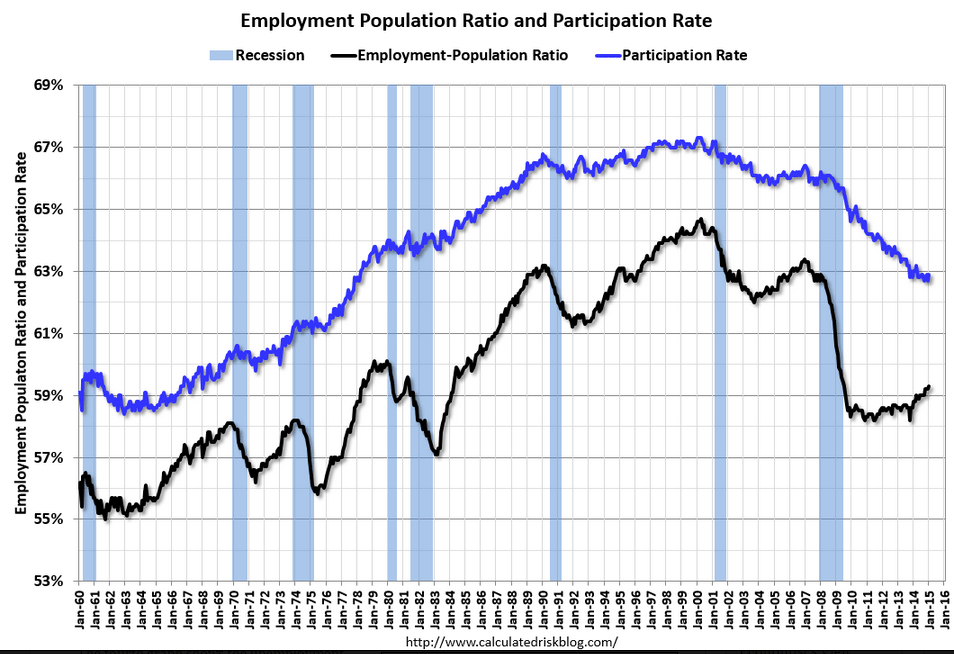
The unemployment rate nudged up to 5.7 percent from 5.6 percent in December. The rise was due to a sharp rebound in the labor force. The labor force participation rate rose to 62.9 percent from 62.7 percent in December. It appears that some discouraged workers are returning to the labor force—a positive sign for how workers view the economy.
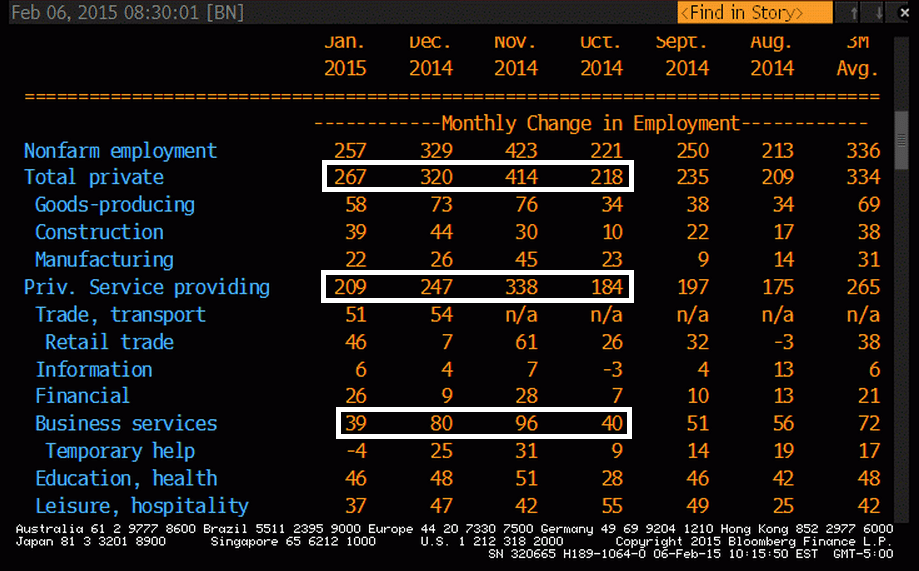
Turning back to the establishment survey, private payrolls increased 267,000 in January after a 329,000 boost the month before.
Goods-producing jobs increased 58,000 after a 73,000 boost in December. Manufacturing increased 22,000 after rising 26,000 in December. Construction jumped 39,000 in January after gaining 44,000 the month before. Mining slipped 4,000 after rising 3,000 in December. These numbers offer hope that the manufacturing and construction sectors are improving. In recent months, they have been sluggish.
Private service-providing industries posted a 209,000 increase after a gain of 247,000 in December. Government jobs declined by 10,000 in January after a rise of 9,000 the month before.
The labor force may be tightening a bit as average hourly earnings rebounded 0.5 percent, following a 0.2 percent dip in December. However, part of the boost in wages was due to increases in some states’ minimum wage. The average workweek held steady at 34.6 hours.
Overall, the latest employment situation suggests that the consumer sector is still the current backbone of the recovery. Also, the labor market has been given an upgrade with upward revisions to November and December. A caveat for the latest report is that seasonal factors for cold weather months can be volatile.
So anyone remember what that big spike in November was all about?
I don’t recall anything at the time in the news, etc. that would have indicated any kind of hiring surge was happening?
Anyway, whatever it was seems to be unwinding?
Currency wars, deflation fights, and with all the guns shooting backwards. As the carpenter said, ‘no matter how much I cut off it’s still too short.’
History will not be kind to these people…
Currency war a worry ahead of G-20 finance gathering (Nikkei) With a number of countries loosening monetary policy, avoiding competitive currency devaluation has emerged as a key issue for the meeting of Group of 20 finance ministers and central bankers that kicks off Monday in Istanbul. The communique released after the September G-20 meeting in Cairns, Australia, included language that in effect tacitly condoned monetary easing aimed at economic improvement. “Monetary policy in advanced economies … should address, in a timely manner, deflationary pressures where needed,” it read in part. The IMF, in January, projected growth of 1.2% in the eurozone, down 0.2 point from the October 2014 edition. The IMF cut its outlook for emerging markets by 0.6 point as well.
Fed’s Rosengren: Weak inflation is key challenge for central banks (WSJ) “The problem of significantly undershooting inflation—a dynamic which could well keep interest rates at the zero lower bound—is likely to be a key challenge to central bankers in the first two decades of the 21st century,” Federal Reserve Bank of Boston President Eric Rosengren said. “As with the oil shock in the 1970s, the current shock has served to accentuate a potential monetary policy pitfall—in this case, the failure to quickly and vigorously address a significant undershooting of inflation targets,” the central banker said. “We still are a long way from normalizing either short-term interest rates or our balance sheet,” the official said.
Benefits of aggressive Fed policy still to peak (WSJ) “The net stimulus to real activity and inflation was limited by the gradual nature of the changes in policy expectations and term premium effects, as well as by a persistent belief on the part of the public that the pace of recovery would be much faster than proved to be the case,” according to a new Fed board paper. “The peak unemployment effect—subtracting 1¼ percentage points from the unemployment rate relative to what would have occurred in the absence of the unconventional policy actions—does not occur until early 2015, while the peak inflation effect—adding ½ percentage point to the inflation rate—is not anticipated until early 2016,” write the authors.
Denmark Cuts Rates Again to Protect Currency Peg (WSJ) Denmark’s central bank scrambled to defend its under-pressure currency peg Thursday, cutting its benchmark interest rate for the fourth time in less than three weeks. The decision to cut the interest rate on deposits—to -0.75% from -0.5%–marks the latest effort to maintain the peg. Last week, the central bank, known as Nationalbanken, announced the surprise suspension of government bond auctions, and the bank said Tuesday it sold record amounts of kroner in January to weaken its currency. Nationalbanken Governor Lars Rohde tried to calm any fears about the future of the policy cornerstone. The central bank “has the necessary instruments to defend the fixed exchange rate policy for as long as it takes,” he said in a statement.
China cuts bank reserve requirement to spur growth (Reuters) China’s central bank made a system-wide cut to bank reserve requirements on Wednesday, the first time it has done so in over two years, to unleash a fresh flood of liquidity to fight off economic slowdown and looming deflation.
Greek leadership assures policy is good for its banks, while real economy and real people are devastated:
Greek central bank says ‘absolutely no problem’ with banks (Reuters) Greek central bank governor Yannis Stournaras said on Thursday that Greek banks were solid and under control. “Deposits and liquidity are absolutely safe,” Stournaras, who is also a member of the European Central Bank’s Governing Council, told reporters. “There is absolutely no problem with the banks. We are under control. It was a calm day today,” he said referring to bank deposits. Greek Prime Minister Alexis Tsipras and Finance Minister Yanis Varoufakis have been seeking support for a new deal with Greece’s international lenders that would allow an end to years of imposed austerity. “The ECB’s decision can be taken back if there is a deal from the Greek government (and its EU partners),” he said.
Not a good sign:
Baltic Dry Freight Index Plummets Amid Commodities Slump (WSJ) The Baltic Dry Index fell to 577 this week, a far cry from its peak of 11,793 in 2008. The size of the world’s fleet of dry-bulk ships far exceeds demand for the vessels which carry commodities, with over capacity estimated at around 20% above demand over the past few years. Many ships ordered at a time of booming global trade before the 2008 financial crisis have come into service as economic growth has spluttered in the years since. Rui Guo, a freight analyst at ICAP Shipping, said the tonnage in the water of dry-bulk vessels has gone up 85% since 2008, even as demand has fallen. Mr. Guo said daily freight rates for a 150,000-ton freight vessel are now around $5,500, with the break-even point around $7,500.
The Korea International Trade Association reported that exports of general machinery to China declined 7.1% in the January-November period of 2014, in contrast to a 2.0% increase in 2013.