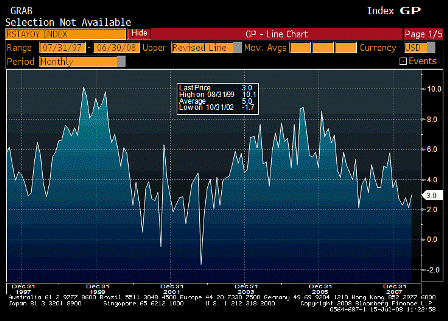A Rescue Plan for the Dollar
By Ronald McKinnon and Steve H. Hanke
The Wall Street Journal, December 27, 2007
Central banks ended the year with a spectacular injection of liquidity to lubricate the economy. On Dec. 18, the European Central Bank alone pumped $502 billion — 130% of Switzerland’s annual GDP — into the credit markets.
Misleading. It’s about price, not quantity. For all practical purposes, no net euros are involved.
I have yet to read anything by anyone in the financial press that shows a working knowledge of monetary operations and reserve accounting.
The central bankers also signaled that they will continue pumping “as long as necessary.” This delivered plenty of seasonal cheer to bankers who will be able to sweep dud loans and related impaired assets under the rug — temporarily.
Nor does this sweep anything under any rug. Banks continue to own the same assets and have the same risks of default on their loans. And, as always, the central bank, as monopoly supplier of net reserves, sets the cost of funds for the banking system.
The causation is ‘loans create deposits’, and lending is not reserve constrained. The CB sets the interest rate – the price of funding – but quantity of loans advanced grows endogenously as a function of demand at the given interest rate by credit worthy borrowers.
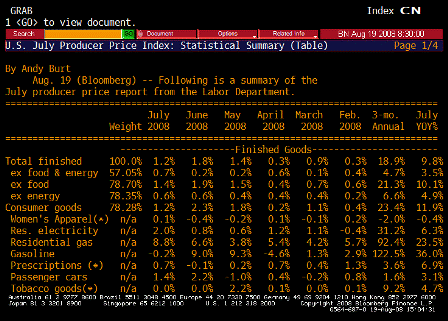
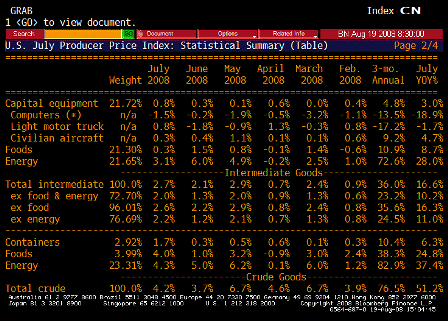
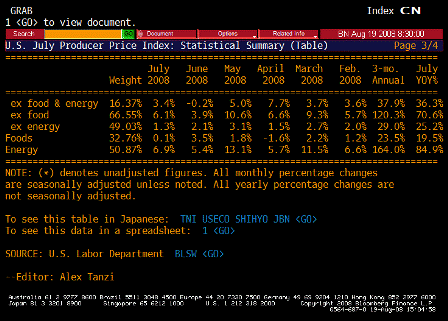
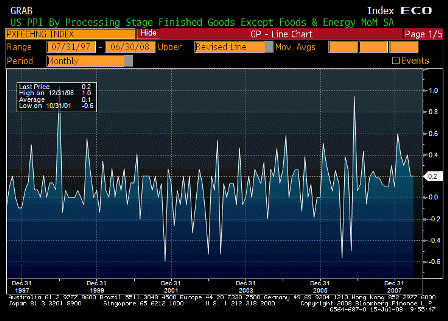
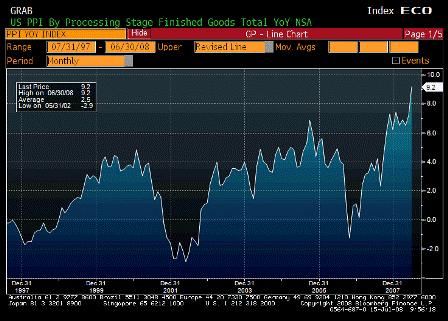
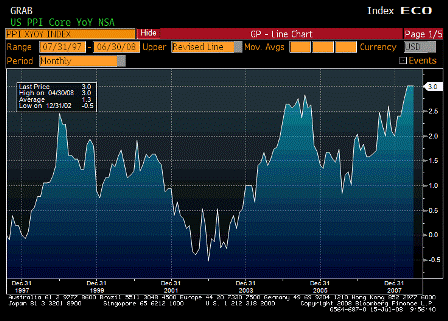
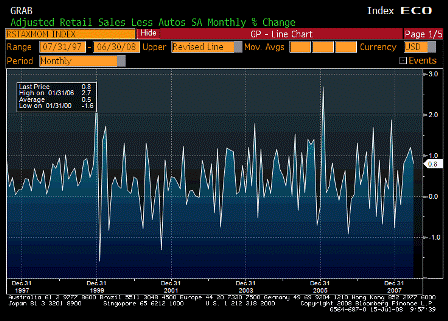
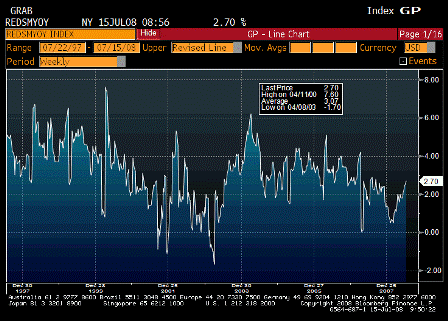
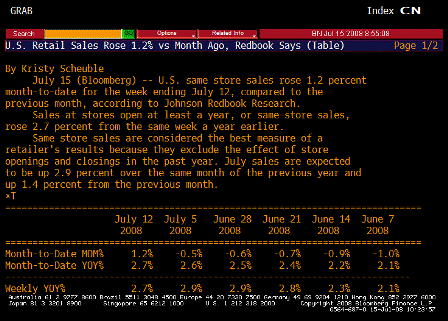
But the injection of all this liquidity coincided with a spat of troubling inflation news.
At least he didn’t say ’caused’.
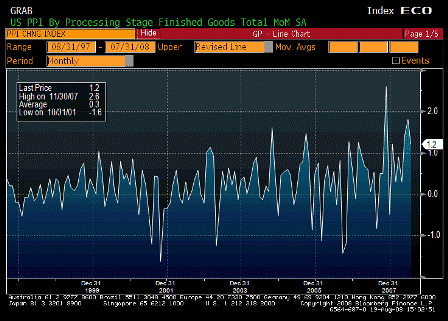
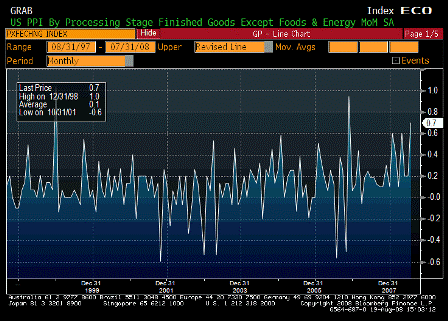
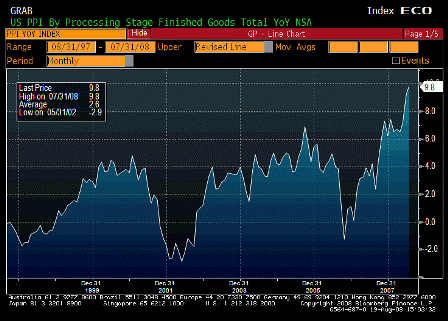
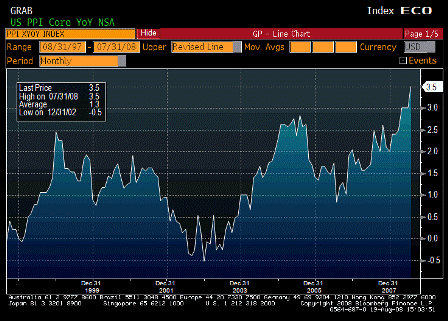
On a year-over-year basis, the consumer-price and producer-price indexes for November jumped to 4.3% and 7.2%, respectively. Even the Federal Reserve’s favorite backward-looking inflation gauge — the so-called core price index for personal consumption expenditures — has increased by 2.2% over the year, piercing the Fed’s 2% inflation ceiling.
Yes!
Contrary to what the inflation doves have been telling us, inflation and inflation expectations are not well contained. The dollar’s sinking exchange value signaled long ago that monetary policy was too loose, and that inflation would eventually rear its ugly head.
The fed either does not agree or does not care. Hard to say which.
This, of course, hasn’t bothered the mercantilists in Washington, who have rejoiced as the dollar has shed almost 30% of its value against the euro over the past five years. For them, a maxi-revaluation of the Chinese renminbi against the dollar, and an unpegging of other currencies linked to the dollar, would be the ultimate prize.
Mercantilism is a fixed fx policy/notion, designed to build fx reserves. Under the gold standard it was a policy designed to accumulate gold, for example. With the current floating fx policy, it is inapplicable.
As the mercantilists see it, a decimated dollar would work wonders for the U.S. trade deficit. This is bad economics and even worse politics. In open economies, ongoing trade imbalances are all about net saving propensities,
Yes!!!
not changes in exchange rates. Large trade deficits have been around since the 1980s without being discernibly affected by fluctuations in the dollar’s exchange rate.
So what should be done? It’s time for the Bush administration to put some teeth in its “strong” dollar rhetoric by encouraging a coordinated, joint intervention by leading central banks to strengthen and put a floor under the U.S. dollar — as they have in the past during occasional bouts of undue dollar weakness. A stronger, more stable dollar will ensure that it retains its pre-eminent position as the world’s reserve, intervention and invoicing currency.
Why do we care about that?
It will also provide an anchor for inflation expectations, something the Fed is anxiously searching for.
Ah yes, the all important inflation expectations.
Mainstream models are relative value stories. The ‘price’ is only a numeraire; so, there is nothing to explain why any one particular ‘price level’ comes from or goes to, apart from expectations theory.
They don’t recognize the currency itself is a public monopoly and that ultimately the price level is a function of prices paid by the government when it spends. (See ‘Soft Currency Economics‘)
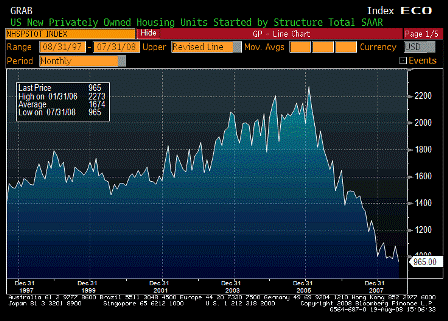
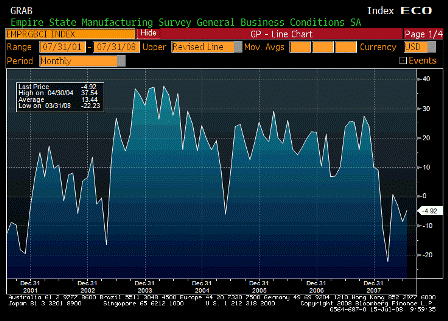
The current weakness in the dollar is cyclical. The housing downturn prompted the Fed to cut interest rates on dollar assets by a full percentage point since August — perhaps too much. Normally, the dollar would recover when growth picks up again and monetary policy tightens. But foreign-exchange markets — like those for common stocks and house prices — can suffer from irrational exuberance and bandwagon effects that lead to overshooting. This is precisely why the dollar has been under siege.
Seems to me it is portfolio shifts away from the $US. While these are limited, today’s portfolios are larger than ever and can take quite a while to run their course.
If the U.S. government truly believes that a strong stable dollar is sustainable in the long run, it should intervene in the near term to strengthen the dollar.
Borrow euros and spend them on $US??? Not my first choice!
But there’s a catch. Under the normal operation of the world dollar standard which has prevailed since 1945, the U.S. government maintains open capital markets and generally remains passive in foreign-exchange markets, while other governments intervene more or less often to influence their exchange rates.
True, though I would not call that a ‘catch’.
Today, outside of a few countries in Eastern Europe linked to the euro, countries in Asia, Latin America, and much of Africa and the Middle East use the dollar as their common intervention or “key” currency. Thus they avoid targeting their exchange rates at cross purposes and minimize political acrimony. For example, if the Korean central bank dampened its currency’s appreciation by buying yen and selling won, the higher yen would greatly upset the Japanese who are already on the cusp of deflation — and they would be even more upset if China also intervened in yen.
True.
Instead, the dollar should be kept as the common intervention currency by other countries, and it would be unwise and perhaps futile for the U.S. to intervene unilaterally against one or more foreign currencies to support the dollar. This would run counter to the accepted modus operandi of the post-World War II dollar standard, a standard that has been a great boon to the U.S. and world economies.
‘Should’??? I like my reason better – borrow fx to sell more often than not sets you up for a serious blow up down the road.
The timing for joint intervention couldn’t be better. America’s most important trading partners have expressed angst over the dollar’s decline. The president of the European Central Bank (ECB), Jean Claude Trichet, has expressed concern about the “brutal” movements in the dollar-euro exchange rate.
Yes, but the ECB is categorically against buying $US, as building $US reserves would be taken as the $US ‘backing’ the euro. This is ideologically unacceptable. The euro is conceived to be a ‘stand alone’ currency to ultimately serve as the world’s currency, not the other way around.
Japan’s new Prime Minister, Yasuo Fukuda, has worried in public about the rising yen pushing Japan back into deflation.
Yes, but it is still relatively weak and in the middle of its multi-year range verses the $US.
The surge in the Canadian “petro dollar” is upsetting manufacturers in Ontario and Quebec. OPEC is studying the possibility of invoicing oil in something other than the dollar.
In a market economy, the currency you ‘invoice’ in is of no consequence. What counts are portfolio choices.
And China’s premier, Wen Jiabao, recently complained that the falling dollar was inflicting big losses on the massive credits China has extended to the U.S.
Propaganda. Its inflation that evidences real losses.
If the ECB, the Bank of Japan, the Bank of Canada, the Bank of England and so on, were to take the initiative, the U.S. would be wise to cooperate. Joint intervention on this scale would avoid intervening at cross-purposes. Also, official interventions are much more effective when all the relevant central banks are involved because markets receive a much stronger signal that national governments have made a credible commitment.
And this all assumes the fed cares about inflation. It might not. It might be a ‘beggar thy neighbor’ policy where the fed is trying to steal aggregate demand from abroad and help the financial sector inflate its way out of debt.
That is what the markets are assuming when they price in another 75 in Fed Funds cuts over the next few quarters. The January fed meeting will be telling.
While they probably do ultimately care about inflation, they have yet to take any action to show it. And markets will not believe talk, just action.
This brings us to China, and all the misplaced concern over its exchange rate. Given the need to make a strong-dollar policy credible, it is perverse to bash the one country that has done the most to prevent a dollar free fall. China’s massive interventions to buy dollars have curbed a sharp dollar depreciation against the renminbi;
Yes, as part of their plan to be the world’s slaves – they work and produce, and we consume.
they have also filled America’s savings deficiency and financed its trade deficit.
That statement has the causation backwards.
It is US domestic credit expansion that funds China’s desires to accumulate $US financial assets and thereby support their exporters.
As the renminbi’s exchange rate is the linchpin for a raft of other Asian currencies, a sharp appreciation of the renminbi would put tremendous upward pressure on all the others — including Korea, Japan, Thailand and even India. Forcing China into a major renminbi appreciation would usher in another bout of dollar weakness and further unhinge inflation expectations in the U.S. It would also send a deflationary impulse abroad and destabilize the international financial system.
Yes, that’s a possibility.
Most of the world’s government reaction functions are everything but sustaining domestic demand.
China, with its huge foreign-exchange reserves (over $1.4 trillion), has another important role to play. Once the major industrial countries with convertible currencies — led by the ECB — agree to put a floor under the dollar, emerging markets with the largest dollar holdings — China and Saudi Arabia — must agree not to “diversify” into other convertible currencies such as the euro. Absent this agreement, the required interventions by, say, the ECB would be massive, throwing the strategy into question.
Politically, this is a non starter. The ECB has ideological issues, and the largest oil producers are ideologically at war with the US.
Cooperation is a win-win situation: The gross overvaluations of European currencies would be mitigated, large holders of dollar assets would be spared capital losses, and the U.S. would escape an inflationary conflagration associated with general dollar devaluation.
Not if the Saudis/Russians continue to hike prices, with biofuels causing food to follow as well. Inflation will continue to climb until crude prices subside for a considerable period of time.
For China to agree to all of this, however, the U.S. (and EU) must support a true strong-dollar policy — by ending counterproductive China bashing.
Mr. McKinnon is professor emeritus of economics at Stanford University and a senior fellow at the Stanford Institute for Economic Policy Research. Mr. Hanke is a professor of applied economics at Johns Hopkins University and a senior fellow at the Cato Institute.
♥