By Banjo Paterson
So Clancy rode to wheel them — he was racing on the wing
Where the best and boldest riders take their place,
And he raced his stock-horse past them, and he made the ranges ring
With the stockwhip, as he met them face to face.
Then they halted for a moment, while he swung the dreaded lash,
But they saw their well-loved mountain full in view,
And they charged beneath the stockwhip with a sharp and sudden dash,
And off into the mountain scrub they flew.
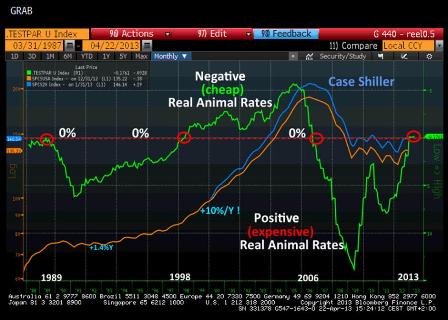
Unemployment is everywhere and always a monetary phenomenon, and necessarily a government imposed crime against humanity. The currency is a simple public monopoly.
The dollars to pay taxes, ultimately come from government spending or lending (or counterfeiting…)
Unemployment can only happen when a govt fails to spend enough to cover the tax liabilities it imposed, and any residual desire to save financial assets that are created by the tax and by other govt policy.
Said another way, for any given size government, unemployment is the evidence of over taxation.
Motivation not withstanding, David Stockman has long been aggressively promoting policy that creates and sustains unemployment.
Comments below:
By David Stockman
March 30 (NYT) — The Dow Jones and Standard & Poors 500 indexes reached record highs on Thursday, having completely erased the losses since the stock markets last peak, in 2007. But instead of cheering, we should be very afraid.
Over the last 13 years, the stock market has twice crashed and touched off a recession: American households lost $5 trillion in the 2000 dot-com bust and more than $7 trillion in the 2007 housing crash. Sooner or later within a few years, I predict this latest Wall Street bubble, inflated by an egregious flood of phony money from the Federal Reserve rather than real economic gains, will explode, too.
Phony money? What else are $US other than credit balances at the Fed or actual cash in circulation? Of course he fails to realize US treasury securities, also known as ‘securities accounts’ by Fed insiders, are likewise nothing more than dollar balances at the Fed, and that QE merely shifts dollar balances at the Fed from securities accounts to reserve accounts. It’s ‘money printing’ only under a narrow enough definition of ‘money’ to not include treasury securities as ‘money’. Additionally, of course, QE removes interest income from the economy, but that’s another story…
Since the S.&P. 500 first reached its current level, in March 2000, the mad money printers at the Federal Reserve have expanded their balance sheet sixfold (to $3.2 trillion from $500 billion).
And also debited/reduced/removed an equal amount of $US from Fed securities accounts. The net ‘dollar printing’ is 0.
Yet during that stretch, economic output has grown by an average of 1.7 percent a year (the slowest since the Civil War); real business investment has crawled forward at only 0.8 percent per year; and the payroll job count has crept up at a negligible 0.1 percent annually. Real median family income growth has dropped 8 percent, and the number of full-time middle class jobs, 6 percent. The real net worth of the bottom 90 percent has dropped by one-fourth. The number of food stamp and disability aid recipients has more than doubled, to 59 million, about one in five Americans.
Yes, and anyone who understood monetary operations knows exactly why QE did not add to sales/output/employment, as explained above.
So the Main Street economy is failing while Washington is piling a soaring debt burden on our descendants,
‘Paying off the debt’ is simply a matter of debiting securities accounts at the Fed and crediting reserve accounts at the Fed. There are no grandchildren or taxpayers involved, except maybe a few to program the computers and polish the floors and do the accounting, etc.
unable to rein in either the warfare state or the welfare state or raise the taxes needed to pay the nations bills.
The nations bills are paid via the Fed crediting member bank accounts on its books. Today’s excess capacity and unemployment means that for the size govt we have we are grossly over taxed, not under taxed.
By default, the Fed has resorted to a radical, uncharted spree of money printing.
As above, ‘money printing’ only under a narrow definition of ‘money’.
But the flood of liquidity, instead of spurring banks to lend and corporations to spend, has stayed trapped in the canyons of Wall Street, where it is inflating yet another unsustainable bubble.
With floating exchange rates, bank liquidity, for all practical purposes, is always unlimited. Banks are constrained by capital and asset regulation, not liquidity.
When it bursts, there will be no new round of bailouts like the ones the banks got in 2008.
There is nothing to ‘burst’ as for all practical purposes liquidity is never a constraint.
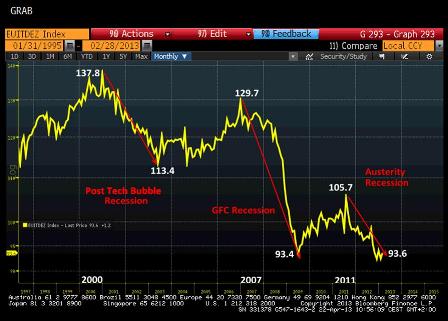
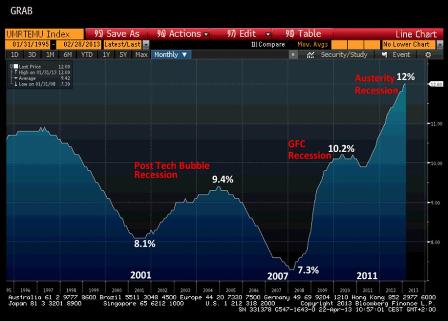
Instead, America will descend into an era of zero-sum austerity and virulent political conflict, extinguishing even todays feeble remnants of economic growth.
This dyspeptic prospect results from the fact that we are now state-wrecked. With only brief interruptions, weve had eight decades of increasingly frenetic fiscal and monetary policy activism intended to counter the cyclical bumps and grinds of the free market and its purported tendency to underproduce jobs and economic output. The toll has been heavy.
The currency itself is a simply public monopoly, and the restriction of supply by a monopolist as previously described, is, in this case the cause of unemployment and excess capacity in general.
As the federal government and its central-bank sidekick, the Fed, have groped for one goal after another smoothing out the business cycle, minimizing inflation and unemployment at the same time, rolling out a giant social insurance blanket, promoting homeownership, subsidizing medical care, propping up old industries (agriculture, automobiles) and fostering new ones (clean energy, biotechnology) and, above all, bailing out Wall Street they have now succumbed to overload, overreach and outside capture by powerful interests.
He may have something there!
The modern Keynesian state is broke,
Not applicable. Congress spends simply by having its agent, the tsy, instruct the Fed to credit a member bank’s reserve account.
paralyzed and mired in empty ritual incantations about stimulating demand, even as it fosters a mutant crony capitalism that periodically lavishes the top 1 percent with speculative windfalls.
Some truth there as well!
The culprits are bipartisan, though youd never guess that from the blather that passes for political discourse these days. The state-wreck originated in 1933, when Franklin D. Roosevelt opted for fiat money (currency not fundamentally backed by gold), economic nationalism and capitalist cartels in agriculture and industry.
Under the exigencies of World War II (which did far more to end the Depression than the New Deal did), the state got hugely bloated, but remarkably, the bloat was put into brief remission during a midcentury golden era of sound money and fiscal rectitude with Dwight D. Eisenhower in the White House and William McChesney Martin Jr. at the Fed.
Actually it was the Texas railroad commission pretty much fixing the price of oil at about $3 that did the trick, until the early 1970’s when domestic capacity fell short, and pricing power shifted to the saudis who had other ideas about ‘public purpose’ as they jacked the price up to $40 by 1980.
Then came Lyndon B. Johnsons guns and butter excesses, which were intensified over one perfidious weekend at Camp David, Md., in 1971, when Richard M. Nixon essentially defaulted on the nations debt obligations by finally ending the convertibility of gold to the dollar. That one act arguably a sin graver than Watergate meant the end of national financial discipline and the start of a four-decade spree during which we have lived high on the hog, running a cumulative $8 trillion current-account deficit. In effect, America underwent an internal leveraged buyout, raising our ratio of total debt (public and private) to economic output to about 3.6 from its historic level of about 1.6. Hence the $30 trillion in excess debt (more than half the total debt, $56 trillion) that hangs over the American economy today.
It also happens to equal the ‘savings’ of financial assets of the global economy, with the approximately $16 trillion of treasury securities- $US in ‘savings accounts’ at the Fed- constituting the net savings of $US financial assets of the global economy. And the current low levels of output and high unemployment tell us the ‘debt’ is far below our actual desire to save these financial assets. In other words, for the size government we have, we are grossly over taxed. The deficit needs to be larger, not smaller. We need to either increase spending and/or cut taxes, depending on one’s politics.
This explosion of borrowing was the stepchild of the floating-money contraption deposited in the Nixon White House by Milton Friedman, the supposed hero of free-market economics who in fact sowed the seed for a never-ending expansion of the money supply.
And the never ending expansion of $US global savings desires, including trillions of accumulations in pension funds, IRA’s, etc. Where there are tax advantages to save, as well as trillions in corporate reserves, foreign central bank reserves, etc. etc.
As everyone at the CBO knows, the US govt deficit = global $US net savings of financial assets, to the penny.
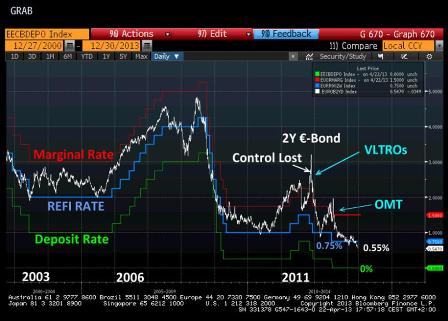
The Fed, which celebrates its centenary this year, fueled a roaring inflation in goods and commodities during the 1970s that was brought under control only by the iron resolve of Paul A. Volcker, its chairman from 1979 to 1987.
It was the Saudis hiking price, not the Fed. Note that similar ‘inflation’ hit every nation in the world, regardless of ‘monetary policy’. And it ended a few years after president Carter deregulated natural gas in 1978, which resulted in electric utilities switching out of oil to natural gas, and even OPEC’s cutting of 15 million barrels per day of production failing to stop the collapse of oil prices.
Under his successor, the lapsed hero Alan Greenspan, the Fed dropped Friedmans penurious rules for monetary expansion, keeping interest rates too low for too long and flooding Wall Street with freshly minted cash. What became known as the Greenspan put the implicit assumption that the Fed would step in if asset prices dropped, as they did after the 1987 stock-market crash was reinforced by the Feds unforgivable 1998 bailout of the hedge fund Long-Term Capital Management.
The Fed didn’t bail out LTCM. They hosted a meeting of creditors who took over the positions at prices that generated 25% types of annual returns for themselves.
That Mr. Greenspans loose monetary policies didnt set off inflation was only because domestic prices for goods and labor were crushed by the huge flow of imports from the factories of Asia.
No, because oil prices didn’t go up due to the glut from the deregulation of natural gas .
By offshoring Americas tradable-goods sector, the Fed kept the Consumer Price Index contained, but also permitted the excess liquidity to foster a roaring inflation in financial assets. Mr. Greenspans pandering incited the greatest equity boom in history, with the stock market rising fivefold between the 1987 crash and the 2000 dot-com bust.
No, it wasn’t about Greenspan, it was about the private sector and banking necessarily being pro cyclical. And the severity of the bust was a consequence of the Clinton budget surpluses ‘draining’ net financial assets from the economy, thereby removing the equity that supports the macro credit structure.
Soon Americans stopped saving and consumed everything they earned and all they could borrow. The Asians, burned by their own 1997 financial crisis, were happy to oblige us. They China and Japan above all accumulated huge dollar reserves, transforming their central banks into a string of monetary roach motels where sovereign debt goes in but never comes out. Weve been living on borrowed time and spending Asians borrowed dimes.
Yes, the trade deficit is a benefit that allows us to consume more than we produce for as long as the rest of the world continues to desire to net export to us.
This dynamic reinforced the Reaganite shibboleth that deficits dont matter and the fact that nearly $5 trillion of the nations $12 trillion in publicly held debt is actually sequestered in the vaults of central banks. The destruction of fiscal rectitude under Ronald Reagan one reason I resigned as his budget chief in 1985
I wonder if he’ll ever discover how wrong he’s been, and for a very long time.
was the greatest of his many dramatic acts. It created a template for the Republicans utter abandonment of the balanced-budget policies of Calvin Coolidge and allowed George W. Bush to dive into the deep end, bankrupting the nation
Hadn’t heard about an US bankruptcy filing? Am I missing something?
through two misbegotten and unfinanced wars, a giant expansion of Medicare and a tax-cutting spree for the wealthy that turned K Street lobbyists into the de facto office of national tax policy. In effect, the G.O.P. embraced Keynesianism for the wealthy.
He’s almost convinced me deep down he’s a populist…
The explosion of the housing market, abetted by phony credit ratings, securitization shenanigans and willful malpractice by mortgage lenders, originators and brokers, has been well documented. Less known is the balance-sheet explosion among the top 10 Wall Street banks during the eight years ending in 2008. Though their tiny sliver of equity capital hardly grew, their dependence on unstable hot money soared as the regulatory harness the Glass-Steagall Act had wisely imposed during the Depression was totally dismantled.
Can’t argue with that!
Within weeks of the Lehman Brothers bankruptcy in September 2008, Washington, with Wall Streets gun to its head, propped up the remnants of this financial mess in a panic-stricken melee of bailouts and money-printing that is the single most shameful chapter in American financial history.
The shameful part was not making a fiscal adjustment when it all started falling apart. I was calling for a full ‘payroll tax holiday’ back then, for example.
There was never a remote threat of a Great Depression 2.0 or of a financial nuclear winter, contrary to the dire warnings of Ben S. Bernanke, the Fed chairman since 2006. The Great Fear manifested by the stock market plunge when the House voted down the TARP bailout before caving and passing it was purely another Wall Street concoction. Had President Bush and his Goldman Sachs adviser (a k a Treasury Secretary) Henry M. Paulson Jr. stood firm, the crisis would have burned out on its own and meted out to speculators the losses they so richly deserved. The Main Street banking system was never in serious jeopardy, ATMs were not going dark and the money market industry was not imploding.
While the actual policies implemented were far from my first choice, they did keep it from getting a lot worse. Yes, it would have ‘burned out’ as it always has, but via the automatic fiscal stabilizers working to get the deficit high enough to catch the fall. I would argue it would have gotten a lot worse by doing nothing. And, of course, a full payroll tax holiday early on would likely have sustained sales/output/employment as the near ‘normal’ levels of the year before. In other words, Wall Street didn’t have to spill over to Main Street. Wall Street Investors could have taken their lumps without causing main street unemployment to rise.
Instead, the White House, Congress and the Fed, under Mr. Bush and then President Obama, made a series of desperate, reckless maneuvers that were not only unnecessary but ruinous. The auto bailouts, for example, simply shifted jobs around particularly to the aging, electorally vital Rust Belt rather than saving them. The green energy component of Mr. Obamas stimulus was mainly a nearly $1 billion giveaway to crony capitalists, like the venture capitalist John Doerr and the self-proclaimed outer-space visionary Elon Musk, to make new toys for the affluent.
Some good points there. But misses the point that capitalism is about business competing for consumer dollars, with consumer choice deciding who wins and who loses. ‘Creative destruction’ is not about a collapse in aggregate demand that causes sales in general to collapse, with survival going to those with enough capital to survive, as happened in 2008 when even Toyota, who had the most desired cars, losing billions when 8 million people lost their jobs all at once and sales in general collapsed.
Less than 5 percent of the $800 billion Obama stimulus went to the truly needy for food stamps, earned-income tax credits and other forms of poverty relief. The preponderant share ended up in money dumps to state and local governments, pork-barrel infrastructure projects, business tax loopholes and indiscriminate middle-class tax cuts. The Democratic Keynesians, as intellectually bankrupt as their Republican counterparts (though less hypocritical), had no solution beyond handing out borrowed money to consumers, hoping they would buy a lawn mower, a flat-screen TV or, at least, dinner at Red Lobster.
Ok, apart from the ‘borrowed money’ part. Congressional spending is via the Fed crediting a member bank reserve account. They call it borrowing when they shift those funds from reserve accounts at the Fed to security accounts at the Fed. The word ‘borrowed’ is highly misleading, at best.
But even Mr. Obamas hopelessly glib policies could not match the audacity of the Fed, which dropped interest rates to zero and then digitally printed new money at the astounding rate of $600 million per hour.
And ‘unprinted’ securities accounts/treasury securities at exactly the same pace, to the penny.
Fast-money speculators have been purchasing giant piles of Treasury debt and mortgage-backed securities, almost entirely by using short-term overnight money borrowed at essentially zero cost, thanks to the Fed. Uncle Ben has lined their pockets.
Probably true, though quite a few ‘headline’ fund managers and speculators have apparently been going short…
If and when the Fed which now promises to get unemployment below 6.5 percent as long as inflation doesnt exceed 2.5 percent even hints at shrinking its balance sheet, it will elicit a tidal wave of sell orders, because even a modest drop in bond prices would destroy the arbitrageurs profits. Notwithstanding Mr. Bernankes assurances about eventually, gradually making a smooth exit, the Fed is domiciled in a monetary prison of its own making.
It’s about setting a policy rate. The notion of prison isn’t applicable.
While the Fed fiddles, Congress burns. Self-titled fiscal hawks like Paul D. Ryan, the chairman of the House Budget Committee, are terrified of telling the truth: that the 10-year deficit is actually $15 trillion to $20 trillion, far larger than the Congressional Budget Offices estimate of $7 trillion. Its latest forecast, which imagines 16.4 million new jobs in the next decade, compared with only 2.5 million in the last 10 years, is only one of the more extreme examples of Washingtons delusions.
And with no long term inflation problem forecast by anyone, the savings desires over that time period are at least that high.
Even a supposedly bold measure linking the cost-of-living adjustment for Social Security payments to a different kind of inflation index would save just $200 billion over a decade, amounting to hardly 1 percent of the problem.
Thank goodness, as the problem is the deficit is too low, as evidenced by unemployment.
Mr. Ryans latest budget shamelessly gives Social Security and Medicare a 10-year pass, notwithstanding that a fair portion of their nearly $19 trillion cost over that decade would go to the affluent elderly. At the same time, his proposal for draconian 30 percent cuts over a decade on the $7 trillion safety net Medicaid, food stamps and the earned-income tax credit is another front in the G.O.P.s war against the 99 percent.
Never seen him play the class warfare card like this?
Without any changes, over the next decade or so, the gross federal debt, now nearly $17 trillion, will hurtle toward $30 trillion and soar to 150 percent of gross domestic product from around 105 percent today.
Not that it will, but if it does and inflation remains low it just means savings desires are that high.
Since our constitutional stasis rules out any prospect of a grand bargain, the nations fiscal collapse will play out incrementally, like a Greek/Cypriot tragedy, in carefully choreographed crises over debt ceilings, continuing resolutions and temporary budgetary patches.
No description of what ‘fiscal collapse’ might look like. Because there is no such thing.
The future is bleak. The greatest construction boom in recorded history Chinas money dump on infrastructure over the last 15 years is slowing. Brazil, India, Russia, Turkey, South Africa and all the other growing middle-income nations cannot make up for the shortfall in demand.
Agreed.
The American machinery of monetary and fiscal stimulus has reached its limits.
Do not agree. In fact, there are no numerical limits.
Japan is sinking into old-age bankruptcy and Europe into welfare-state senescence. The new rulers enthroned in Beijing last year know that after two decades of wild lending, speculation and building, even they will face a day of reckoning, too.
The state-wreck ahead is a far cry from the Great Moderation proclaimed in 2004 by Mr. Bernanke, who predicted that prosperity would be everlasting because the Fed had tamed the business cycle and, as late as March 2007, testified that the impact of the subprime meltdown seems likely to be contained. Instead of moderation, whats at hand is a Great Deformation, arising from a rogue central bank that has abetted the Wall Street casino, crucified savers on a cross of zero interest rates and fueled a global commodity bubble that erodes Main Street living standards through rising food and energy prices a form of inflation that the Fed fecklessly disregards in calculating inflation.
It’s not at all disregarded. And the Fed has only done ‘pretend money printing’ since they ‘unprint’ treasury securities as they ‘print’ reserve balances.
These policies have brought America to an end-stage metastasis. The way out would be so radical it cant happen.
How about a full payroll tax holiday? Too radical to happen???
It would necessitate a sweeping divorce of the state and the market economy. It would require a renunciation of crony capitalism and its first cousin: Keynesian economics in all its forms. The state would need to get out of the business of imperial hubris, economic uplift and social insurance and shift its focus to managing and financing an effective, affordable, means-tested safety net.
These are the conclusions of his way out of paradigm conceptualizing.
All this would require drastic deflation of the realm of politics and the abolition of incumbency itself, because the machinery of the state and the machinery of re-election have become conterminous. Prying them apart would entail sweeping constitutional surgery: amendments to give the president and members of Congress a single six-year term, with no re-election; providing 100 percent public financing for candidates; strictly limiting the duration of campaigns (say, to eight weeks); and prohibiting, for life, lobbying by anyone who has been on a legislative or executive payroll. It would also require overturning Citizens United and mandating that Congress pass a balanced budget, or face an automatic sequester of spending.
Whatever…
It would also require purging the corrosive financialization that has turned the economy into a giant casino since the 1970s. This would mean putting the great Wall Street banks out in the cold to compete as at-risk free enterprises, without access to cheap Fed loans or deposit insurance. Banks would be able to take deposits and make commercial loans, but be banned from trading, underwriting and money management in all its forms.
I happen to fully agree with narrow banking, as per my proposals.
It would require, finally, benching the Feds central planners, and restoring the central banks original mission: to provide liquidity in times of crisis but never to buy government debt or try to micromanage the economy. Getting the Fed out of the financial markets is the only way to put free markets and genuine wealth creation back into capitalism.
Rhetoric that shows his total lack of understanding of monetary operations.
That, of course, will never happen because there are trillions of dollars of assets, from Shanghai skyscrapers to Fortune 1000 stocks to the latest housing market recovery, artificially propped up by the Feds interest-rate repression.
No govt policy necessarily supports rates. Without the issuance of treasury securities, paying interest on reserves, and other ‘interest rate support’ policy rates fall to 0%. He’s got the repression thing backwards.
The United States is broke fiscally, morally, intellectually and the Fed has incited a global currency war (Japan just signed up, the Brazilians and Chinese are angry, and the German-dominated euro zone is crumbling) that will soon overwhelm it. When the latest bubble pops, there will be nothing to stop the collapse.
How about a full payroll tax holiday???
If this sounds like advice to get out of the markets and hide out in cash, it is.
I tend to agree but for the opposite reason.
The deficit may have gotten too small with the latest tax hikes and spending cuts.
(feel free to distribute)