Category Archives: EU
a word on the euro, US deficit doves, and Japan
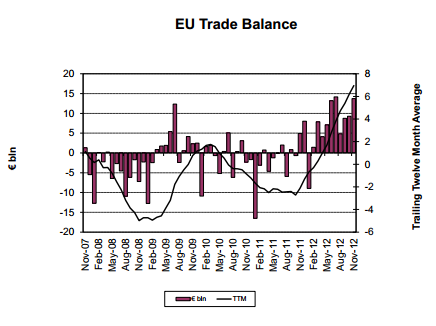
As previously discussed, the euro looks to keep going up until the trade surplus reverses. Problem is the strong euro doesn’t necessarily cause the trade surplus to reverse, at least not in the short term. But it does tend to work against earnings and growth. And there’s nothing the ECB can do about it, short of buying dollars via direct intervention, which would be counter to their core ideology, as building dollar reserves would give the appearance of the dollar backing the euro. The solvency issue has now been behind them for quite a while, and still no sign of any ‘official’ recognition that deficits need to be higher to restore output and employment.
And, also as previously discussed, while the future was looking up for the US a few months ago, the caveat of ‘austerity’ has come into play with the year end FICA and other tax hikes, and now the odds are the sequesters are allowed to come into play March 1 as well. Note this has been Japan’s policy as well- fiscal tightening at the first sign of any hope for expansion. Fed policy also looks to remain restrictive as blatantly evidenced by the recent turn over of some $90 billion of ‘profits’ to the Treasury that otherwise would have been earned by the economy.
The headline ‘deficit doves’ pushing for larger deficits with their ‘out of paradigm’ arguments are also serving to continue to support austerity. They have been arguing that the low interest rates are a signal from the markets (as if they know anything about markets) indicating the economy wants the govt to sell more bonds. This is in response to the hawk’s equally out of paradigm argument that financing deficits will eventually drive up interest rates. So now that interest rates have started going higher, the dove’s case is for higher deficits is pretty much gone, removing the resistance to ‘getting our fiscal house in order’ just as the sequester date is approaching. Whether it’s gross ignorance or intellectual dishonesty doesn’t matter all that much at this point- it’s happening. At the same time oil and gasoline prices have been creeping up, taking a few more shekels away from consumers. January and it’s strong equity inflows/allocations and releases of December’s stats ends tomorrow. February’s releases of Jan stats will bring more post FICA hike clarity.
Japan’s weak yen, pro inflation policy seems to have been all talk with only a modest fiscal expansion to do the heavy lifting. Changing targets does nothing, nor does the BOJ have any tools that do the trick as evidenced now by two decades of using all those tools to the max. And while I’ve been saying all the while that 0 rates, QE, and all that are deflationary biases that make the yen stronger, there is no sign of that understanding even being considered by policy makers, so expect more of same. What has been happening to weaken the yen is a quasi govt policy of the large pension funds and insurance companies buying euro and dollar denominated bonds, which shifts their portfolio compositions from yen to euros and dollars, thereby acting to weaken the yen. I have no idea now long this will continue, but if history is any guide, it could go on for a considerable period of time. Yes, it adds substantial fx risk to those institutions, but that kind of thing has never gotten in the way before. And should it all blow up some day, look for the govt to simply write the check and move on.
Draghi Says Conditions Considerably More Favorable Than Last Yr
As previously discussed, looking like deficits high enough for stability and even modest growth, albeit with output and employment at tragically low levels, if they don’t further tighten fiscally.
It didn’t have be this way. They could have increased deficits pro actively vs via austerity.
Also, their ‘automatic fiscal stabilizers’ are very strong and, even if all is left alone, will tend to keep any recovery muted.
EU Headlines
Draghi Says Conditions Considerably More Favorable Than Last Yr
Merkel Takes Swipe at Yen
German Business Sentiment Rose More Than Forecast in January
Ifo Business Climate Index Rises
German Cooperative Banks See Growth Exceeding Government Outlook
France needs time to overtun rampant jobless rate: minister
Monti Says Monte Paschi Bailout Hinges on Bank of Italy
Italian PM under fire over bank crisis
Spain tries to peel back business rules
Friday update
So just like Japan, as soon as the economy starts doing a bit better we hike taxes. Still too early to say how the FICA hike will impact sales and profits, but it will. And spending cuts are on the way, though they may be delayed.
Not to forget the debt ceiling thing about to be kicked 3 months down the road as it stands guard to ensure ‘meaningful’ spending cuts.

Oil firm, but can still go either way. WTI converging to Brent indicates the seaway pipeline capacity increase may be enough to drain the surplus at pad 2, bringing wti up to brent, but too soon to tell for sure. And looks like the demand for saudi crude is dropping some, but not enough to dislodge them from being
swing producer/price setter.
Looks to me like the whole world is becoming ‘more competitive’ so it all cancels out. Bad for people, ok for stocks, with profits running at record highs as a % of GDP. Meaning the federal deficit has to be that much higher, all else equal, to fill the output gap.
The yen keeps going down. Looking more and more to me it’s off the radar screen intervention by the likes of insurance co’s, pension funds, and other quasi govt agencies got the note to buy fx denominated bonds in size. Not sure how far they will take it, but they have a serious herd instinct that has formed serious multi year bubbles in the past.
Europe? They fixed the solvency issue, sort of, and now just have the economy thing to deal with. Problem is the ECB grants solvency only with conditionality. Good luck to them.
quick look ahead for the euro zone
After describing since inception how the euro zone was going to get to where it is, here’s my guess on what’s coming next.
First, to recap, it took them long enough and it got bad enough before they did it, but they did decide to ‘do what it takes’ to end the solvency issues and, after the Greek PSI thing, make sure the markets stopped discounting defaults as subsequently evidenced by falling interest rates for member nation debt.
But it’s solvency with conditionality, and so while they solved the solvency and interest rate issue, the ongoing austerity requirements have served to make sure the output gap stays politically too wide. The deficits are high enough, however, for an uneasy ‘equilibrium’ of
near/just below 0% overall GDP growth and about 11% unemployment.
However, all of this is very strong euro stuff, where the euro appreciates at least until the (small) trade surplus turns to deficit. This could easily mean 1.50+ vs the dollar (and worse vs the yen) for example. This process at the same time further weakens domestic demand which supports a need for higher member govt deficits just to keep GDP near 0.
So at some point next year I can see deficits that refuse to fall resulting in more demands for austerity, while the strong euro results in demands for ‘monetary easing’ from the ECB. Of course with what they think is monetary easing actually being monetary tightening (lower rates, bond buying, everything except direct dollar buying, etc.) the fiscal and monetary just works to further support the too strong euro stronger.
All this gets me back to the idea that the path towards deficit reduction in this hopelessly out of paradigm region keep coming back to the unmentionable PSI/bond tax. Seems to me we are relentlessly approaching the point where further taxing a decimated population or cutting what remains of public services becomes a whole lot less attractive than taxing the bond holders. And the process of getting to that point, as in the case of Greece, works to cause all to agree there’s no alternative. With the far more attractive alternative of proactive increases in deficits that would restore output and employment not even making it into polite discussion, I see the walls closing in around the bond holders, along with the argument over whether the ECB writes down it’s positions back on page 1. And just the mention of PSI in polite company throws a massive wrench (spanner) into the gears. For example, if bonds go to a discount, they’ll look towards ECB supported buy backs to reduce debt, again, Greek like. And if prices don’t fall sufficiently, they’ll talk about a forced restructure of one kind or another, all the while arguing about what constitutes default, etc.
The caveats can change the numbers, but seems will just make matters worse.
The US going full cliff is highly dollar friendly, much like austerity supports the euro. In fact, the expiration of my FICA cut- the only bipartisan thing Obama has done- which apparently both sides have agreed to let happen, will alone add quite a bit of fiscal drag. This means less euro appreciation, but also lower US demand for euro zone exports. So the cliff does nothing good for the euro zone output gap.
And Japan seems to be targeting the euro zone for exports with it’s euro and dollar buying weakening the yen, as evidenced by Japan’s growing fx reserves (where else can they come from?).
The price of oil could spike, which also makes matters worse.
In general, I don’t see anything good coming out of the current global political leadership.
Please let me know if I’m missing anything!
Berlusconi comments
As if their problems end with lower borrowing costs.
No mention of needing to run much larger deficits:
Yesterday Berlusconi put it plainly and simply:
Berlusconi says Italy may be forced to leave the euro zone
Silvio Berlusconi said that Italy would be forced to leave the euro zone unless the ECB gets more powers to ensure lower borrowing costs. Berlusconi, who will again lead his People of Freedom party (PDL) in a national election, said that the ECB should become a lender of last resort for the currency bloc. “If Germany doesn’t accept that the ECB must be a real central bank, if interest rates don’t come down, we will be forced to leave the euro and return to our own currency in order to be competitive,” Berlusconi said.Berlusconi is already campaigning hard for the election with a spate of television interviews in an attempt to close the wide gap with the center-left Democratic Party which is polling at above 30 percent, some 14 points above the PDL.
Koo on reserves time bomb – 500% inflation
So much for yet another legacy.
:(
From Richard Koo’s latest report:
But nightmare scenario awaits when private loan demand recovers. The problem is what happens when private loan demand recovers. Loan books could grow more than tenfold in the US and five fold in Japan and Europe if bank reserves remain at current levels, triggering inflation rates of 500% to over 1,000%.
To avoid this outcome, central banks will have to mop up excessive reserves by raising the statutory reserve ratio, raising the interest rate paid on reserves, and selling government bonds. All of these measures will serve to lift interest rates, sending bond yields sharply higher and triggering a possible crash in the bond markets.
A sharp increase in government bond yields could lead to fiscal collapse in countries with a large national debt. For Japan, where the national debt amounts to 240% of GDP, the results would be catastrophic.
Expanding quantitative easing because it appears to be doing no harm is grievous error. Mr. Abe and his advisors may believe that all they have to do once their anti-deflationary policies succeed and JGB yields start to rise is have the BOJ buy more bonds. However, bank reserves under quantitative easing have risen to a level capable of fueling a 500% inflation rate, in which case the BOJ would have to sell, not buy, JGBs.
Nomura | JPN
BOJ purchases of JGBs in that situation could cause the potential inflation rate to rise from 500% to 600% to 700% and trigger an economic collapse.
I do not know whether the German finance official who was opposed to reckless quantitative easing based his view on this kind of scenario. Nevertheless, it is extremely dangerous to assume that since quantitative easing does no harm in a balance sheet recession, it can be continuously expanded without concern. The real danger posed by this policy will become apparent only after private-sector balance sheets are repaired, and then it will happen suddenly.
BOJs excess reserves could become a time bomb. I would now like to bring some actual numbers into the discussion so that readers may appreciate the implications of this scenario.
Only 7.7 trillion in bank reserves are required to maintain Japans money supply. With the Japanese government now running annual fiscal deficits in excess of 40 trillion, BOJ financing of the entire deficit would require the Bank to supply reserves equal to more than five times the amount needed to maintain the money supply. Over a two-year period, it would have to supply reserves equal to more than ten times the required amount.
In other words, the purchase of one years worth of newly issued government debt by the BOJ has the potential to generate a 500% inflation rate. I suspect few Japanese are willing to accept such a trade-off.
Moreover, the BOJ has already engaged in substantial quantitative easing under heavy pressure from politicians, pushing excess reserves to 29.8 trillion. In my view this represents a time bomb.
Cliff notes
Jobless Claims Fell More Than Expected, Down by 25,000 to 370,000
I haven’t written much this week because I haven’t seen much to write about.
Still looks like both the economy and the markets are discounting the cliff. And still looks to me like ex cliff GDP would be growing at about 4% this quarter, with the Sandy-cliff related cutbacks keeping that down to maybe 2.5%. And going over the full cliff is taking off maybe 2% more, leaving GDP modestly positive.
Which is what stocks and bonds seem to be fully discounting.
As previously discussed, the housing cycle seems to have turned up, which looks to be an extended, multi year upturn with a massive ‘housing output gap’ to be filled. And employment is modestly improving as well, also with a large output gap to fill. Car sales are back over 15 million, and also with a large output gap to fill.
The way I see the politics unfolding, the full cliff will be avoided, if not in advance shortly afterwards, as fully discussed to a fault by the media. That means GDP growth head back towards 4% (and maybe more)
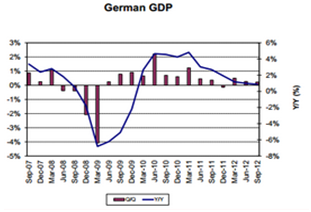
Nor do I see anything catastrophic happening in the euro zone. They continue to ‘do what it takes’ to keep everyone funded and away from default. And conditionality means continued weakness. Q3 GDP was down .1%, a modest improvement from down .2% in Q2, and a flat Q4 wouldn’t surprise me. The rising deficits from ‘automatic fiscal stabilizers’ (rising transfer payments and falling revenues) have increased deficits to the point where they can sustain what’s left of demand. And the recent report of German exports to the euro zone rising at 3.5% maybe indicating that the overall support for GDP will continue to come disproportionately from Germany. And rising net exports from the euro zone will continue to cause the euro to firm to the point of ‘rebalance’ which should mean a much firmer euro. And as part of that story, Japan may be buying euro to support it’s exports to the euro zone, as per the prior ‘Trojan Horse’ discussions, and as evidenced by the yen weakening vs the euro, also as previously discussed.
And you’d think with every forecaster telling the politicians that tax hikes and spending cuts- deficit reduction- causing GDP to be revised down and unemployment up, and the reverse- tax cuts and spending hikes causing upward GDP revisions and lower unemployment- they’d finally figure this thing out and act accordingly?
Probably not…
Italian article this am
Misrepresents what I say a bit, but they do have my picture next to JFK!
;)
The IMF: sovereign currency, no longer the monopoly of the banks
Eliminate the public debt of the United States at once, and do the same with Great Britain, Italy, Germany, Japan, Greece. At the same time revive the ‘ economy, stabilize prices and oust the bankers. In a clean and painless, and faster than what you can imagine. With a magic wand? No. With a simple law, but able to replace the current system, in which to create money out of nothing are private banks. We only need a measure requiring the banks to hold a financial reserve real, 100%. To propose two economists at the International Monetary Fund, Jaromir Bene and Michael Kumhof. You, the bank, you want to make money on the loan of money? First you have to prove it really that much money. Too easy to have it by the central bank (which the factory from scratch) and then “extort” families, businesses and entire states, imposing exorbitant interest.
The study of two economists, “The Chicago Plan Revisited,” with “a revolutionary and” scandalous “‘Maria Grazia Bruzzone,” La Stampa “, emphasizes the global resonance of the dossier, that bursts like a bomb on the world capitalist system now jammed. The global debt came the exorbitant sum of 200 trillion, that is 200 trillion dollars, while the world GDP is less than 70 trillion. Translated: the world debt is 300% of gross domestic product of the entire planet. “And to hold this huge mountain of debt – which continues to grow – there are more advanced economies and developing countries,” says the Bruzzone, stressing that “the heart of the problem and the cross” is the highest “power” Japan, Europe and the United States. Hence the sortie “heretical” by Bene and Kumhof: simply write off the debt, it disappears.Sparked the debate was the last IMF report, which points the finger on austerity policies aimed at reducing thepublic debt . Policies that “could lead to recession in the economies ‘, since’ cuts and tax increases depress the ‘economy ‘.
Not only. The IMF would be really worried the crisis that is ravaging the ‘ Europe threatens to be worse than the 2008 financial. The surprise is that even the IMF now thinks that “austerity can be used to justify the privatization of public services,” with consequences “potentially disastrous”. But if the problem is the debt – public, but now “privatized” by finance – you can not delete? Solution already ventilated by the Bank of England, which holds 25% of the British sovereign debt: the Bank of England may reset it by clicking on the computer. Advantages: “You will pay much less interest, it would free up cash and you could make less harsh austerity.” The debate rages on many media, starting from the same “Financial Times”. thread which breaks now the revolutionary proposal of the two IMF economists targati: cancel the debt.
“The Chicago Plan Revisited,” writes Maria Grazia Bruzzone, raises and explores the “Chicago Plan” original, drawn up in the middle of the Great Depression of the ’30s by two other economists, Irving Fisher, Henry Simons of the University of Chicago, the cradle of liberalism . Cancel 100% of the debt? “The trick is to replace our system, where money is created by private banks – for 95-97% of the supply of money – money created by the state. It would mean return to the historical norm, before the English King Charles II put in private hands control of the money available, “back in 1666. It would mean a frontal assault on the “fractional reserve” banking, accused of seigniorage on the issue of currency speculation: if lenders are instead forced to hold 100% of its reserves to guarantee deposits and loans, “pardon the exorbitant privilege of create money out of nothing. ” As a result: “The nation regained control over the availability of money,” and also “reduces the pernicious cycles of expansion and contraction of credit.”
The authors of the first “Plan of Chicago” had thought that the cycles of expansion and contraction of credit lead to an unhealthy concentration of wealth: “They had seen in the early thirties creditors seize farmers effectively bankrupt, grab their lands or comprarsele for a piece of bread. ” Today, the authors of the new edition of this plan argue that the “trauma” of the credit cycle that expands and contracts – caused by private money creation – is a historical fact that is already outlined with Jubilees Debt ancient Mesopotamia, as well as in ancient Greece and even Rome. Sovereign control (the state or the Pope) on currency, recalls Bruzzone, Britain remained so throughout the Middle Ages, until 1666, when it began the era of the cycles of expansion and contraction. With the “bank privatization” of money, add the “Telegraph”, “opened the way for the agricultural revolution, and after the industrial revolution and the biggest leap Economic ever seen “- but it is not the case of” quibbling, “quips the newspaper.
According to the young economists of the IMF, is just a myth – disclosed “innocently” by Adam Smith – that the money has been developed as a medium of exchange based on gold, or related to it. Just as it is a myth, the study points out the IMF, what you learn from books: that is the Fed, the U.S. central bank, to control the creation of the dollar. “In fact, money is created by private banks to 95-97% through loans.” Private banks, in fact, do not lend as owners of cash deposits, the process is exactly the opposite. “Every time a bank makes a loan, the computer writes the loan (plus interest) and the corresponding liability in its balance sheet. But the money that pays the bank has a small part. If it does borrow from another bank, or by the central bank. And the central bank, in turn, creates out of nothing that lends the money to the bank. ”
In the current system, in fact, the bank is not required to have its own reserves – except for a tiny fraction of what it provides. Under a system of “fractional reserve”, each money created out of nothing is a debt equivalent: “Which produces an exponential increase in the debt, to the point that the system collapses on itself.” The economists of the IMF hours overturn the situation. The key is the clear distinction between the amount of money and the amount of credit between money creation and lending. If you impose banks to lend only numbers covered by actual reserves, loans would be fully funded from reserves or profits accrued. At that point, the banks can no longer create new money out of thin air. Generate profits through loans – without actually having a cash reserve – is “an extraordinary and exclusive privilege, denied to other business.”
“The banks – says Maria Grazia Bruzzone – would become what he mistakenly believed to be, pure intermediaries who have to get out their funds to be able to make loans.” In this way, the U.S. Federal Reserve “is approprierebbe for the first time the control over the availability of money, making it easier to manage inflation.” In fact, it is observed that the central bank would be nationalized, becoming a branch of the Treasury, and now the Fed is still owned by private banks. “Nationalizing” the Fed, the huge national debt would turn into a surplus, and the private banks’ should borrow reserves to offset possible liabilities. ” Already wanted to do John Fitzgerald Kennedy, who began to print – at no cost – “dollars of the Treasury,” against those “private” by the Fed, but the challenge of JFK died tragically, as we know, under the blows of the killer of Dallas , quickly stored from “amnesia” of powerful debunking.
Sovereign coin, issued directly by the government, the state would no longer be “liable”, but it would become a “creditor”, able to buy private debt, which would also be easily deleted. After decades, back on the field the ghost of Kennedy. In short: even the economists of the IMF hours espouse the theory of Warren Mosler, who are fighting for their monetary sovereignty as a trump card to go out – once and for all – from financial slavery subjecting entire populations, crushed by the crisis , the hegemonic power of a very small elite of “rentiers”, while the ‘ economic reality – with services cut and the credit granted in dribs and drabs – simply go to hell. And ‘the cardinal assumption of Modern Money Theory supported in Italy by Paul Barnard: if to emit “money created out of nothing” is the state, instead of banks, collapsing the blackmail of austerity that impoverishes all, immeasurably enriching only parasites of finance . With currency sovereign government can create jobs at low cost. That is, welfare, income and hope for millions of people, with a guaranteed recovery of consumption. Pure oxygen ‘s economy . Not surprisingly, adds Bruzzone, if already the original “Chicago Plan”, as approved by committees of the U.S. Congress, never became law, despite the fact that they were caldeggiarlo well 235 academic economists, including Milton Friedman and English liberal James Tobin, the father of the “Tobin tax”. In practice, “the plan died because of the strong resistance of the banking sector.” These are the same banks, the journalist adds the “Print”, which today recalcitrano ahead to reserve requirements a bit ‘higher (but still of the order of 4-6%) required by the Basel III rules, however, insufficient to do deterrent in the event of a newcrisis . Banks: “The same who spend billions on lobbying and campaign contributions to presidential candidates. And in front of the new “Chicago Plan” threaten havoc and that “it would mean changing the nature of western capitalism. ‘” That may be true, admits Bruzzone: “Maybe but it would be a better capitalism. And less risky. ”
Early Thought follow up… A follow up conversation with Warren Mosler
Please click here to listen to a conversation with Warren Mosler. We did an audio call with Warren in late June and he was spot on. So I thought it was a good time to circle back with him. Topics include: US stocks (they look good…deficit to GDP in US a support for market/econ), US rates, Europe and China.
