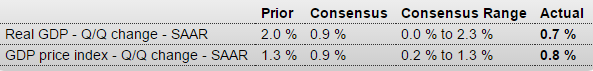
As expected, the deceleration continues, and over the next couple of years it wouldn’t surprise me if the entire year gets revised down substantially:
GDP
Highlights
Consumer spending is the central driver of the economy but is slowing, at least it was during the fourth quarter when GDP rose only at a 0.7 percent annualized rate. Final demand rose 1.2 percent, which is the weakest since first quarter last year but is still 5 tenths above GDP.
Spending on services, adding 0.9 percentage points, was a leading contributor to the quarter as was spending on goods, at plus 0.5. Residential investment, another measure of consumer health, rose very solidly once again, contributing 0.3 percentage points. Government purchases added modestly to growth.
The negatives are on the business side especially those facing foreign markets. Net exports pulled down GDP by 0.5 percentage points. Non-residential investment pulled down GDP by more than 0.2 percentage points. Reduction in inventory investment, which the FOMC warned about on Wednesday, pulled the quarter down by 0.5 percentage points.
Price data are not accelerating, at plus 0.8 percent for the GDP price index which is the lowest reading since plus 0.1 in the first quarter last year. The core price reading is only slightly higher, at plus 1.1 percent which is also the weakest reading in a year.
There are definitely points of concern in this report, especially the weakness in exports and business investment, but it’s the resilience in the consumer, despite a soft holiday season, that headlines this report and should help confirm faith in the domestic strength of the economy.
And this from JPM:
Consumer spending slowed to a 2.2% pace of advance, while business fixed investment spending contracted at a 1.8% rate, the first decline since 2012. A slowing in inventory investment subtracted 0.5%-point from growth last quarter. Even so, the pace of stockbuilding—a $69 billion annual rate—is still faster than is sustainable and poses an ongoing headwind to producers early in 2016. As such, after today’s report we see some more downside risk to our 2.0% projection for Q1 GDP growth.
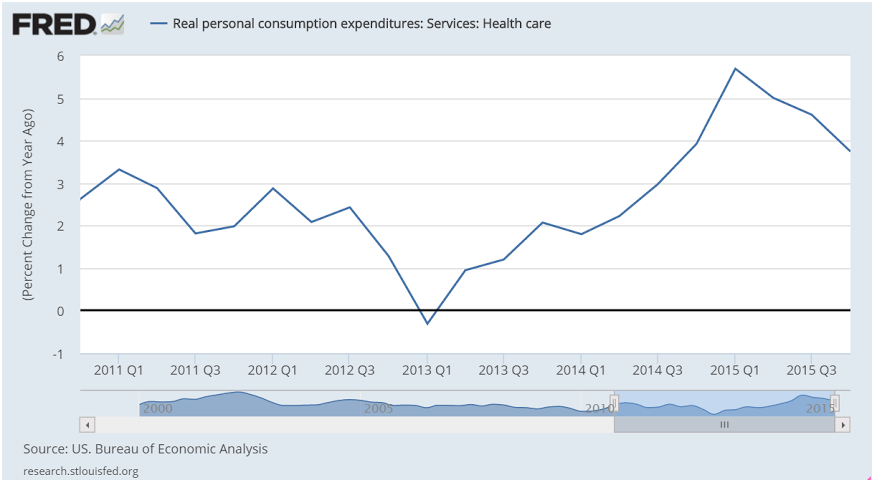
The consumer looks to be going down hill to me, and this includes increases in total health care premiums due to the newly insured under Obamacare. This chart is not adjusted for inflation, which shows the growth of nominal spending has slowed dramatically. Fortunately the ‘deflator’ indicates that with prices down real purchases have been sustained. But consumers on average tend to spend most all of their incomes, which means fortunately for them prices didn’t rise as fast or they would have bought fewer real goods and services.
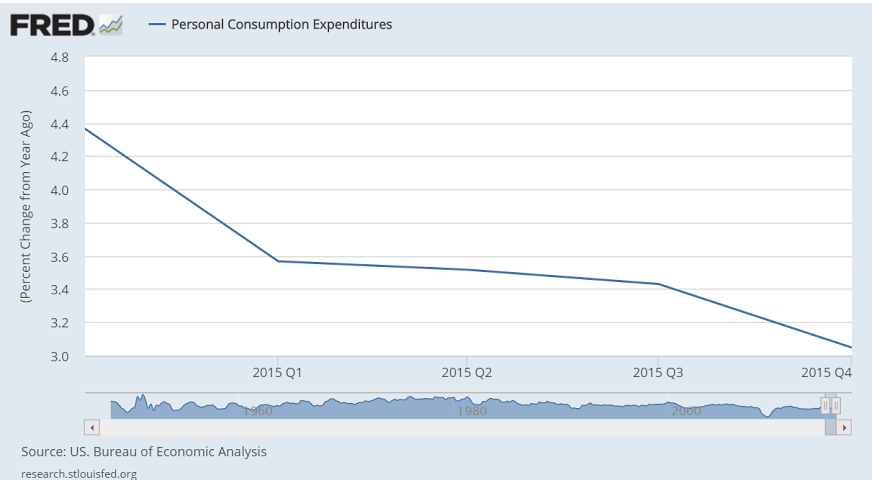
Here’s the last year of GDP year over year growth, after oil capex collapsed:
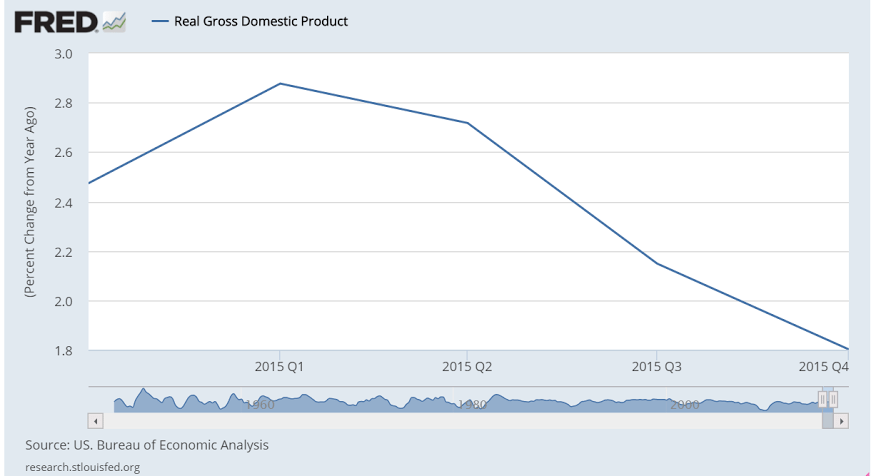
This is nominal GDP, not adjusted for inflation:
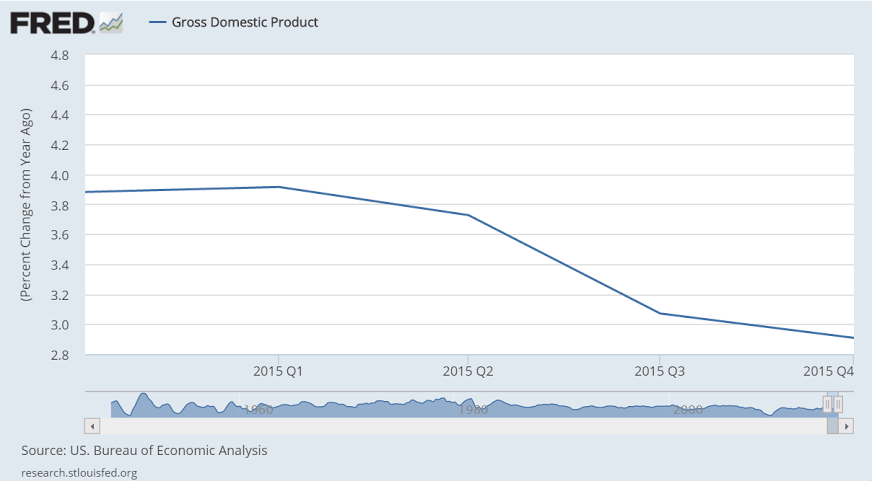
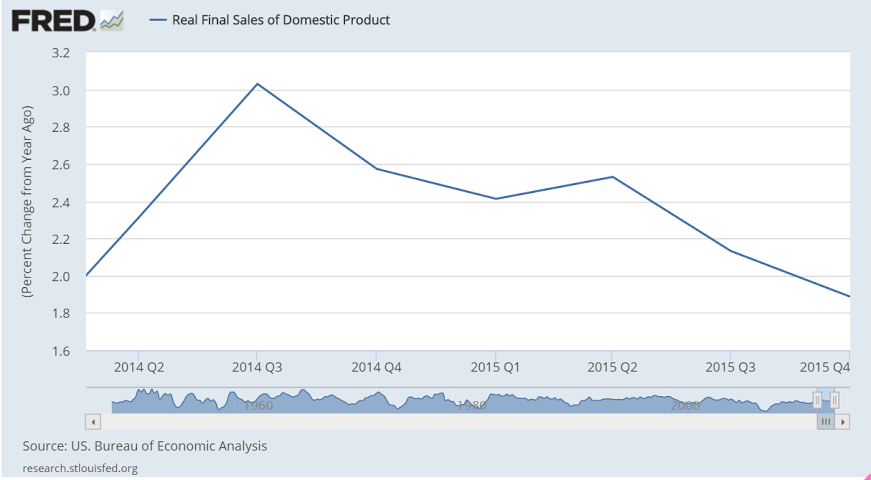
Note the relation between export collapses and recessions:
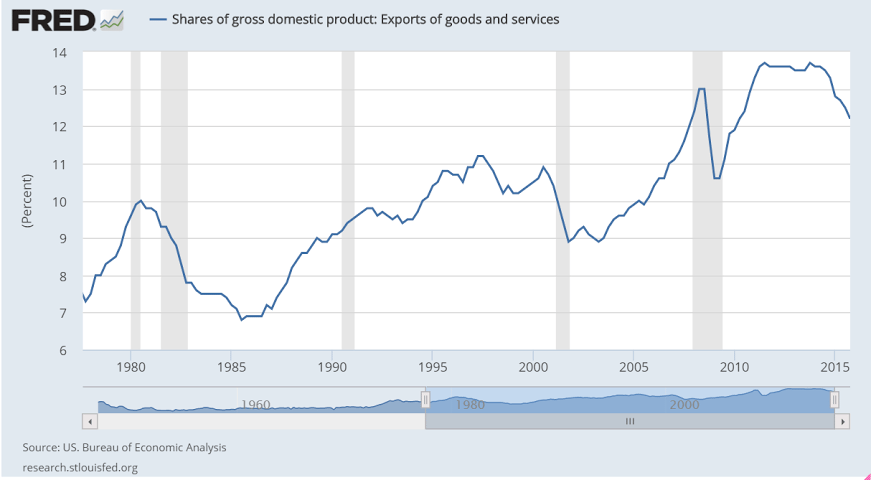
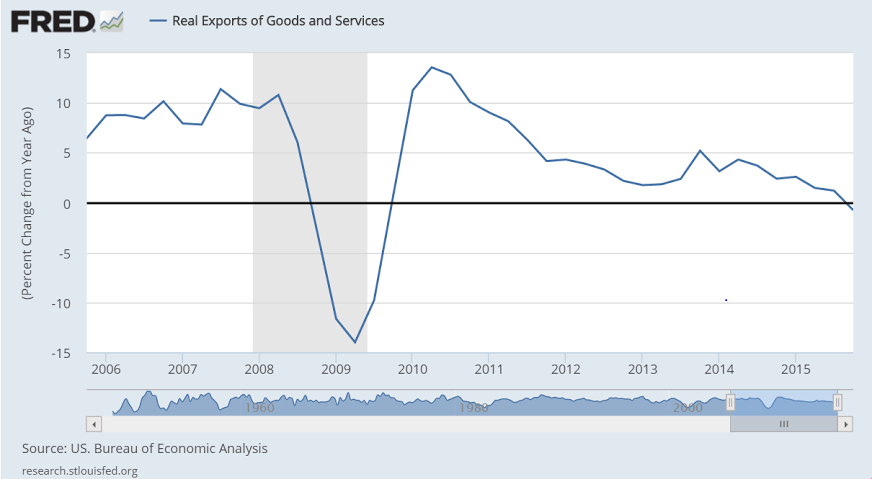
The increase in premium expenditures for the newly insured is a ‘one time’ event that offered support last year and won’t be repeated this year.
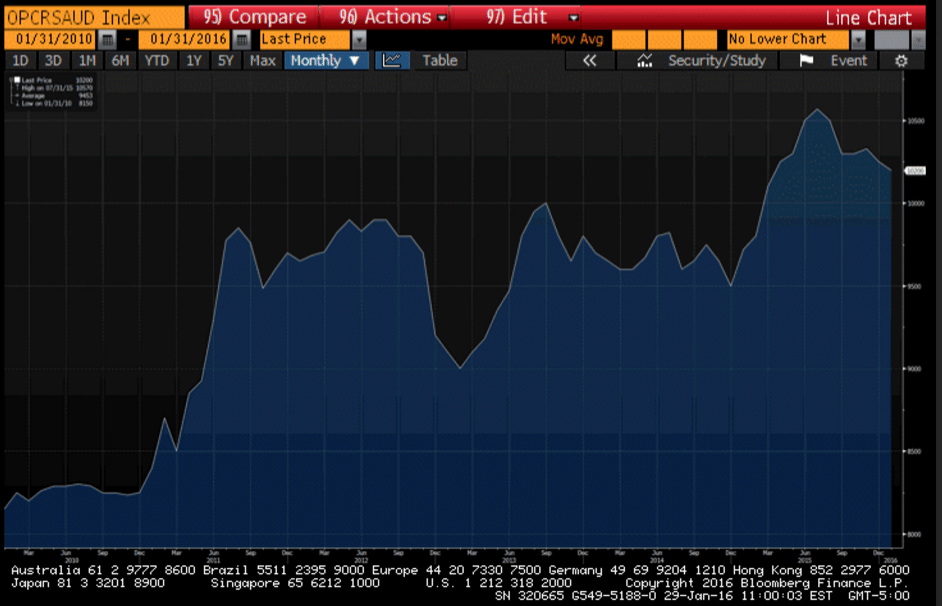
Interesting how even at the dramatically lowered prices due to increased discounts the Saudis appear to be selling less oil. Patiently waiting for March pricing to be released:
Yet another bad one:
Kansas City Fed Manufacturing Index
Highlights
Kansas City manufacturing, along with that of Dallas, are suffering the worst of any regions in the nation’s factory contraction. Kansas City came in at minus 9 for the ninth contraction in 10 months.
Minus signs sweep nearly all readings including new orders and backlogs which are in extremely deep contraction, at minus 27 and minus 36 respectively. Production is at minus 8 with shipments at minus 7. Employment is at minus 7 with price readings moving deeper into contraction, at minus 14 for raw materials and, ominously for inflation expectations, at minus 15 for finished products.
One of the few pluses in the report, ironically, is the index for new export orders which came in at a very modest plus 1. But it’s not only exports that have been pulling down the factory sector but also energy equipment, the latter which is especially sinking the nation’s energy patch.
Chicago PMI: Jan Chicago Business Barometer Jumps 12.7 Points to 55.6
The Chicago Business Barometer bounced back sharply in January, increasing 12.7 points to 55.6 from 42.9 in December, the highest pace of growth in a year.
Chief Economist of MNI Indicators Philip Uglow said, “While the surge in activity in January marks a positive start to the year, it follows significant weakness in the previous two months, with the latest rise not sufficient to offset the previous falls in output and orders. Previously, surges of such magnitude have not been maintained so we would expect to see some easing in February. Still, even if activity does moderate somewhat next month, the latest increase supports the view that GDP will bounce back in Q1 following the expected slowdown in Q4.”
“At current prices U.S. shale producers are losing more than $2 billion a week, according to consulting firm AlixPartners LLP.”
” Italian gross domestic product per capita has hardly changed in 20 years.”
And all they needed was a fiscal adjustment sufficient to get aggregate demand to appropriate levels:
Amari’s fall leaves Abenomics in lurch
Jan 29 (Nikkei) — “I bear responsibility for appointing him,” a visibly pained Abe told reporters Thursday following the resignation of Akira Amari, who also served as his right-hand man in the Trans-Pacific Partnership trade negotiations. Amari devised the basis for Abenomics. He helped alter LDP economic policy’s traditional bias toward public works, shifting the emphasis to a pro-growth strategy of making Japanese companies more competitive and innovative. After Abe led the LDP back to power in 2012, he put Amari in charge of the government’s new industrial competitiveness council and the reconstituted Council on Economic and Fiscal Policy.
Nor will this work, negative rates are just another tax:
BOJ adopts negative interest rates
Jan 29 (Nikkei) — The Bank of Japan decided to adopt negative interest rates at its policy meeting on Friday, voting 5-4 to apply an interest rate of -0.1 percent on current accounts that financial institutions hold at the central bank. At the same time, the BOJ revised its inflation forecast for fiscal 2016 down to 0.8% from a previous level of 1.4%. In a statement, the BOJ said it adopted the negative interest rate policy in order to achieve its price stability target of 2% at the earliest possible time, and signalled that it will “cut the interest rate further into negative territory if judged necessary.”
This might have had something to do with their decision:
Japan’s industrial output falls 1.4% in December, down for 2nd month
Jan 29 (Kyodo) — Japan’s industrial output in December fell a seasonally adjusted 1.4 percent from the previous month, in sharp contrast with a rise of 0.9 percent the government had projected based on hearings with manufacturers last month. The government said the trend of output is fluctuating without clear direction, maintaining its basic assessment of production from the previous month. For 2015, the industrial output index fell 0.8 percent from the previous year. The production index increased 2.1 percent in 2014. Polled manufacturers said they expect output to rise 7.6 percent in January and then fall by 4.1 percent in February.