Note the inventory build:
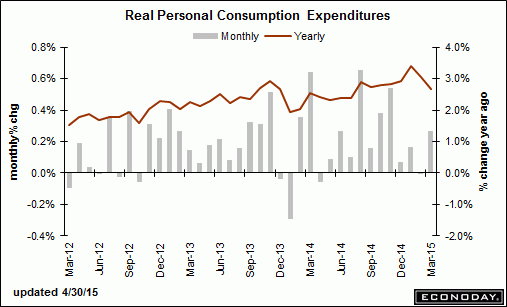
Note the ‘bending of the curve’ for nominal spending that almost never happens:
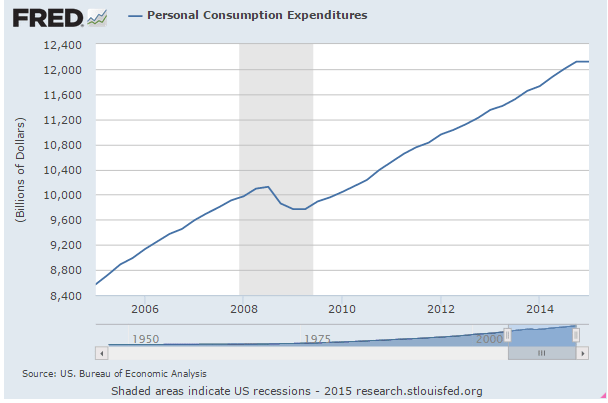
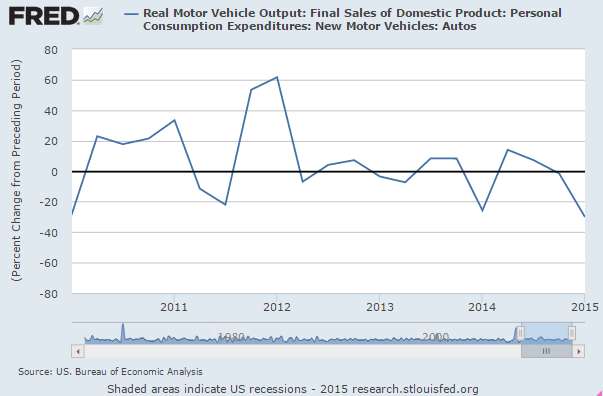
A bit of a disconnect between headline car sales and car sales’ contribution to GDP?
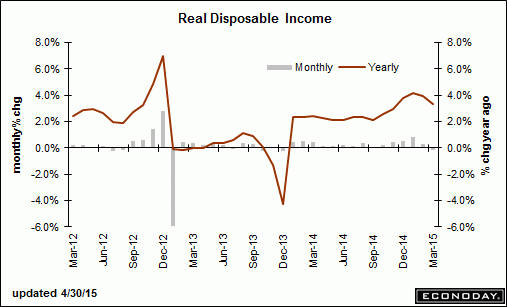
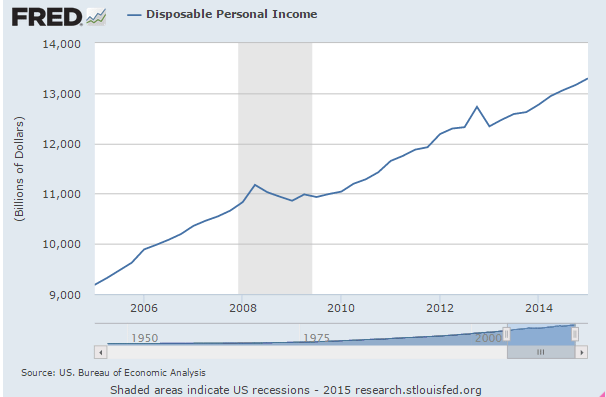
Disposable income has ratched down twice recently- once from the recession and jump in unemployment, and again with the tax hikes:
European Union : Unemployment Rate
Highlights
The Eurozone labour market made limited progress in March. Joblessness fell a further 36,000 to 18.105 million but the unemployment rate held steady at 11.3 percent, a tick above market expectations.
Amongst the larger member states the national jobless rate was unchanged in France (10.6 percent) and Germany (4.7 percent) and declined another tick to 23.0 percent in Spain. However, Italy saw its rate jump 0.3 percentage points to 13.0 percent, just a couple of ticks short of last November’s record high. Top of the pile was again Greece (25.7 percent in January) while Germany remained at the bottom.
Youth unemployment was also unchanged at 22.7 percent following a downward revision to the February rate.
The income lost due to falling oil revenues might be starting to show and the growth rate remains near stall speed:
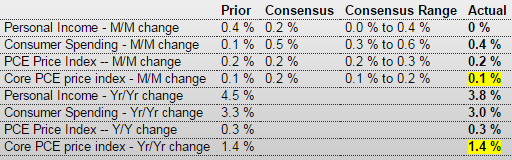
Personal Income and Outlays
Highlights
March consumer spending rebounded 0.4 percent (and was up 3.0 percent from a year ago) from a revised increase of 0.2 percent in February. But the data suggest that people remain somewhat cautious in their spending despite months of cheaper gasoline and rising confidence. Consumer spending generates more than two thirds of GDP and is a key driver of growth. Spending on services increased 0.2 percent from the prior month. Spending on goods added 1.0 percent after three consecutive monthly declines, including a 1.8 percent increase in purchases of durable goods like trucks and washing machines that are designed to last at least three years.
Personal income was flat on the month the weakest reading since December 2013. On the year, income was up 3.8 percent.
The Federal Reserve acknowledged that the economy slowed during the winter months, but they blamed the weakness on “transitory factors.” Officials said in a statement they “continue to expect that, with appropriate policy accommodation, economic activity will expand at a moderate pace.”
Personal consumption expenditures price index undershot the Fed’s 2 percent target increasing 0.3 percent in March from a year earlier, the same increase as the previous month. Excluding the volatile food and energy categories, prices climbed 1.3 percent in March from a year earlier for the fourth consecutive month.
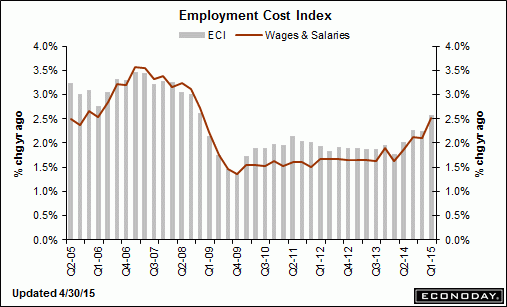
A bit higher than expected but I attribute this to hiring getting ahead of itself as reported employment gains have been outrunning growth of output:
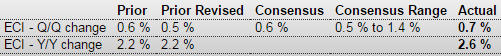
Employment Cost Index
In the 12 months through March, labor costs jumped 2.6 percent, the largest rise since the fourth quarter of 2008. That is still below the 3 percent threshold that economists say is needed to bring inflation closer to the Fed’s 2 percent target.
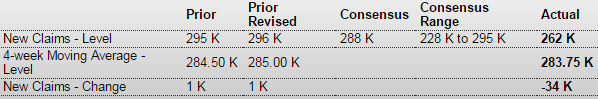
Lower than expected and the Fed knows it shows separations and not new hires, though it has correlated to hiring historically:
Jobless Claims
Highlights
The Fed is ready now to pull the trigger at anytime and today’s jobless claims data may have their finger a little itchy. Initial claims, not skewed by special factors, plunged 34,000 in the April 25 week to 262,000 which is the lowest level since all the way back to April 2000. The 4-week average is down 1,250 to a 283,750 level which is just below a month-ago and is also a 15-year low.
Bloomberg Consumer Comfort Index
Highlights
Bloomberg’s consumer confidence index declined for a third consecutive week to a six-week low of 44.7 as Americans took a less favorable view of their finances and the slowdowns at factories and oilfields soured attitudes among men. Sentiment among men showed one of the biggest decreases in the past four years, while confidence in the Midwest slumped by the most in more than a decade. While the Bloomberg comfort gauge cooled from an almost eight-year high reached earlier this month, it remains well above last year’s average of 36.7, which was the best since 2007.