The President’s proposal is now looking anemic at best.
Like I think Woody Allen once said, the food was bad and the portions were small.
This will cost the Dems even more seats in November.
Fortunately the federal deficit is already large enough to support a bit of modest growth.
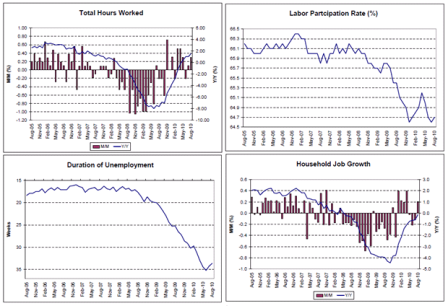
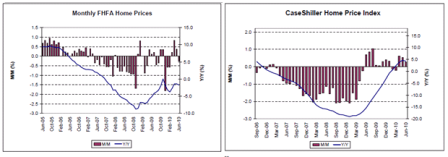
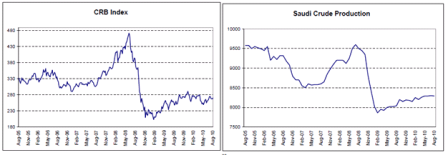
All looking very L shaped to me, with a hint of growth.
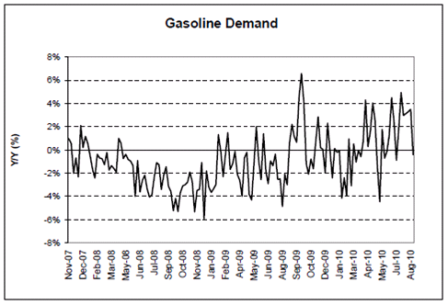
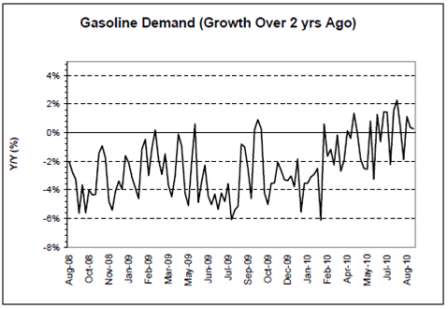
Gasoline consumption has recovered and showing signs of growth year over year, but very modest.
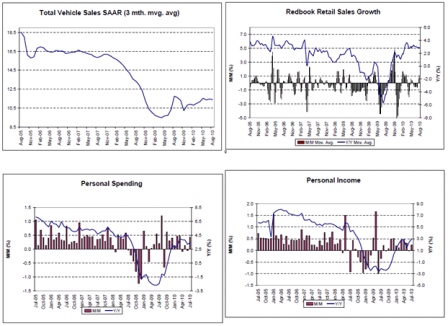
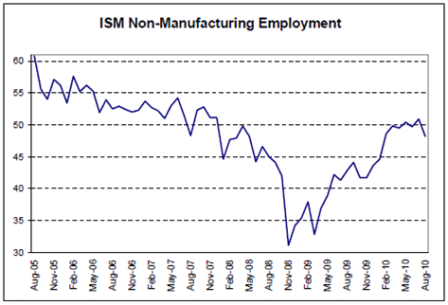
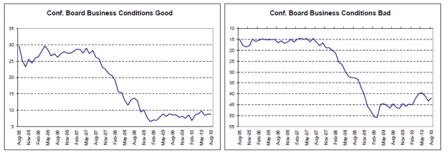
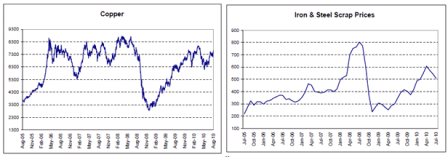
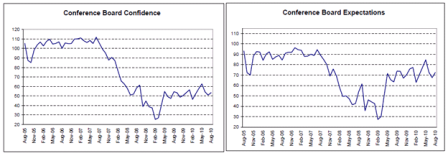
Modest recoveries from the lows and leveling off.
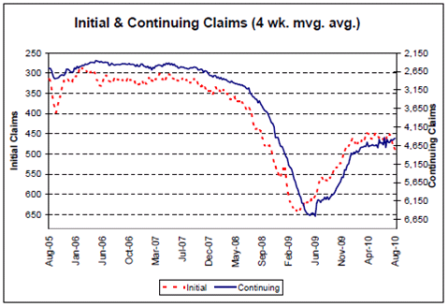
Continued modest improvement from the lows
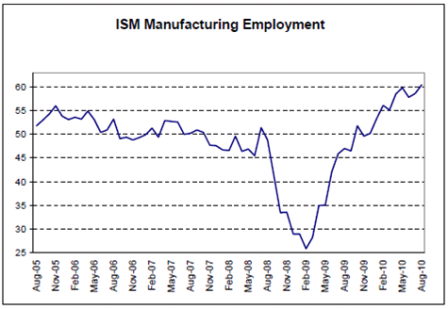
Manufacturing, the smaller component of GDP, led from very low levels
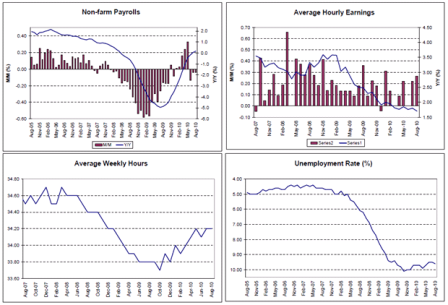
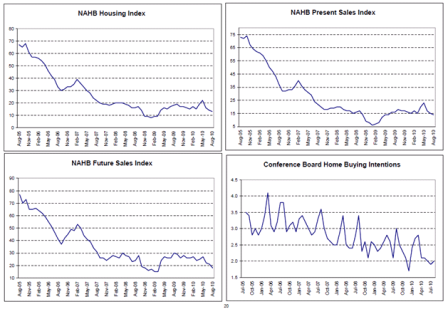
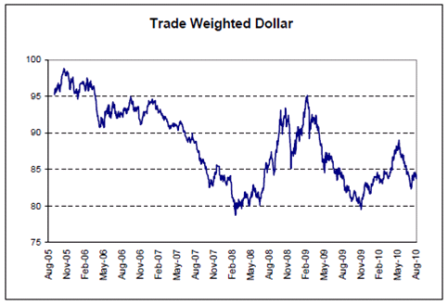
Looking very L shaped.
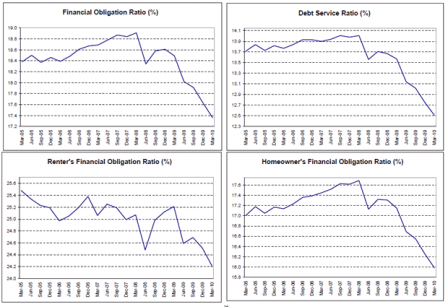
These are March numbers, June should be out soon and show further balance sheet repair as deficit spending continues are relatively high levels, adding income and net financial assets to the non govt. sectors.
Lots of signs of leveling off at modest levels of top line growth.
Waiting for the handoff to private sector credit expansion as balance sheets repair, or another fiscal adjustment.
GS Skinny: The Administration’s New Fiscal Proposals
(CLEARED FOR EXTERNAL USE)
September 7, 2010
The White House has announced three new measures to stimulate growth: 100% up-front depreciation of capital investments; a permanent and slightly expanded R&D tax credit; and $50 bn in infrastructure spending. They could be helpful but are unlikely to have a large effect on growth for four reasons: (1) some of them cover multiple years, spreading out the fiscal impulse; (2) the incremental effect is smaller than the headline numbers imply, as some are modifications of existing proposals or policies and one is essentially an interest free loan; (3) the president proposes offsetting the cost of some of the proposals with targeted corporate tax increases of an equal amount; and (4) the likelihood of enactment of some of these proposals is low.
Key points:
1. Bonus depreciation. The president proposes to allow companies to deduct 100% of the cost of capital investments (not including real estate) made in 2010 and 2011. Press reports cite White House estimates that the proposal would lower corporate tax receipts by $200bn. However, almost all of this revenue loss would be temporary, since the additional deductions taken now would lower deductions in future years, effectively making this an interest free loan. Given current low levels of capacity utilization, the benefit of additional investment is low to begin with. Our previous analysis indicated that the 50% bonus depreciation provision effective for 2008 and 2009 had a relatively small effect on investment. To the extent it does have an effect, it is likely to pull forward demand into the quarter just before expiration (in this case Q4 2011) so the near term effect should be even more modest (and indeed the effect in early 2012 would be negative). Whatever effect the provision would have would also be weakened somewhat by the proposal to raise corporate tax revenues (through closing of “loopholes”) to offset the proposal’s cost.
2. R&D Tax credit. The president is expected to propose to increase and make permanent the research and development tax credit, at a cost of $100bn over ten years. This proposal is somewhat less than meets the eye, since the president has already proposed to make the credit permanent at a cost of $80bn. This leaves an incremental proposal worth around $20bn, or $2bn per year. Nevertheless, enactment of this proposal would be helpful on the margin, since the existing R&D credit lapsed at the end of last year and has yet to be renewed by Congress.
3. Infrastructure. The president proposes to spend $50bn on transportation infrastructure projects, as part of a six-year plan. We take this to mean a front-loading or incremental investment on top of the six-year reauthorization of surface transportation spending programs that has been pending in Congress for most of the year. For context, a $50bn addition to infrastructure spending is roughly on par with the investments made in that sector in the 2009 Recovery Act. If enacted, this could provide an important boost to growth, particularly in 2011. However, the likelihood of enactment in the near term appears low. Also, offsetting the otherwise positive effect is the proposal to offset the entire cost with the repeal of tax incentives for oil and gas companies.
4. Process from here. There are two likely scenarios for consideration of the tax-based measures. First, the Senate will vote on small business legislation next week, which already includes a 50% depreciation bonus for 2010. This provision could simply be modified, to bring it into line with the president’s depreciation proposal, in which case it could be enacted in the next few weeks. The second scenario is that the tax measures could be added to upcoming legislation to extend the expiring 2001/2003 tax cuts, which will be debated in late September. Adding corporate tax cuts to that legislation might allow Democratic leaders to attract enough votes for passage without extending the upper-income tax rates that most Republicans support. However, given that legislation’s uncertain prospects, adding these measures to it could also risk delaying enactment until after the November election. Infrastructure spending would be dealt with separately from the tax measures; the most likely scenario is that it could be considered after the election as part of the next stop-gap extension of the highway program, which expires December 31.