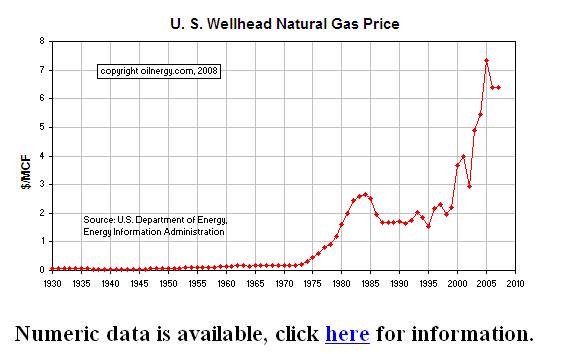
[Skip to the end]
I hadn’t noticed this back then, but Vince got it right: The Fed purchased the $30 billion of securities from JPM/Bear Stearns, with JPM agreeing that if there were any net losses it would be responsible for the first $1 billion.
It’s very odd that the Fed would call this a non-recourse loan, as they cut a better deal than that.
Unlike a non-recourse loan, if the securities turn out to be profitable, the Fed gets those funds.
So why would the Fed use language that implies the transaction was worse for the Fed than it actually was?
Perhaps there was a legal or some other restriction that prevented the Fed from purchasing the securities?
Seem there is a lot more to the story than has been revealed?
March 24, 2008
The Federal Reserve Bank of New York (“New York Fed”) has agreed to lend $29 billion in connection with the acquisition of The Bear Stearns Companies Inc. by JPMorgan Chase & Co.
The loan will be against a portfolio of $30 billion in assets of Bear Stearns, based on the value of the portfolio as marked to market by Bear Stearns on March 14, 2008.
JPMorgan Chase has agreed to provide $1 billion in funding in the form of a note that will be subordinated to the Federal Reserve note. The JPMorgan Chase note will be the first to absorb losses, if any, on the liquidation of the portfolio of assets.
The New York Fed loan and the JPMorgan Chase subordinated note will be made to a Delaware limited liability company (“LLC”) established for the purpose of holding the Bear Stearns assets. Using a single entity (the LLC) will ease administration of the portfolio and will remove constraints on the money manager that might arise from retaining the assets on the books of Bear Stearns.
The loan from the New York Fed and the subordinated note from JPMorgan Chase will each be for a term of 10 years, renewable by the New York Fed.
The rate due on the loan from the New York Fed is the primary credit rate, which currently is 2.5 percent and fluctuates with the discount rate. The rate on the subordinated note from JPMorgan Chase is the primary credit rate plus 450* basis points (currently, a total of 7 percent).
BlackRock Financial Management Inc. has been retained by the New York Fed to manage and liquidate the assets.
The Federal Reserve loan is being provided under the authority granted by section 13(3) of the Federal Reserve Act. The Board authorized the New York Fed to enter into this loan and made the findings required by section 13(3) at a meeting on Sunday, March 16, 2008.
Repayment of the loans will begin on the second anniversary of the loan, unless the Reserve Bank determines to begin payments earlier. Payments from the liquidation of the assets in the LLC will be made in the following order (each category must be fully paid before proceeding to the next lower category):
- to pay the necessary operating expenses of the LLC incurred in managing and liquidating the assets as of the repayment date;
- to repay the entire $29 billion principal due to the New York Fed;
- to pay all interest due to the New York Fed on its loan;
- to repay the entire $1 billion subordinated note due to JPMorgan Chase;
- to pay all interest due to JPMorgan Chase on its subordinated note;
- to pay any other non-operating expenses of the LLC, if any.
Any remaining funds resulting from the liquidation of the assets will be paid to the New York Fed.
Where No Fed Has Gone Before
Why the Federal Reserve’s ‘loan’ for the Bear Stearns deal looks like an investmentâ€â€Âand faces serious scrutiny
March 26, 2008
by Peter Coy
The Federal Reserve has stretched its mandate up, down, and sideways to prevent a financial market deluge. Now it appears to be stretching the English language a bit as well. What the Fed is calling a $29 billion “loan” to help finance JPMorgan Chase’s (JPM) purchase of Bear Stearns (BSC) looks much more like a $29 billion investment in securities owned by Bear. Although the Fed insists that it isn’t technically buying any assets, in practical terms it’s doing exactly that. All this adds up to a big and unacknowledged step up in the central bank’s financial intervention with Wall Street investment banks.
The Fed, of course, is the only part of government with the speed, power, and flexibility to arrest a bout of market panic. By rapidly intervening in mid-March to keep Bear from filing for bankruptcy, it may well have prevented a series of cascading failures that could have severely damaged the financial system and the economy. Many economists and analysts are happy that the Fed stepped into the breach. Nevertheless, now that things have quieted down a bit, the Fed is likely to face some tough questions about the precise nature of its actions as well as the legal justification for them.
The second-guessing has already begun. On Mar. 26, Senate Banking, Housing, and Urban Affairs Chairman Christopher Dodd (D-Conn.) announced an Apr. 3 hearing to explore the “unprecedented arrangement” between the Fed, JPMorgan, and Bear. Top officials from the Fed and other regulators, as well as Bear Stearns CEO Alan Schwartz and JPMorgan CEO Jamie Dimon, will likely be grilled about the details.
“That Looks Like Equity”
Meanwhile, Treasury Secretary Henry Paulson gave the Fed a gentle prod on Mar. 26 in a speech to the Chamber of Commerce. While saying he fully supported the Fed’s recent actions, Paulson stressed that “the process for obtaining funds by nonbanks must continue to be as transparent as possible.” He also urged the Fed to continue to work with other agencies to get the information necessary for “making informed lending decisions.”
So far, few people have focused on what exactly the Fed is getting in exchange for supplying $29 billion to JPMorgan Chase. That’s a bit surprising because whatever the deal is, it’s far from a standard loan. The strangest twist is that even though the money goes to JPMorgan, that firm isn’t the borrower. So the Fed can’t demand repayment from JPMorgan if the Bear assets turn out to be worth less than promised.
What’s also odd is that if there’s money left after loans are paid off, the Fed gets to keep the residual value for itself. That’s what one would expect if the Fed were buying the assets, not just treating them as collateral for a loan. Vincent R. Reinhart, a former director of the Fed’s Division of Monetary Affairs and now a resident scholar at the American Enterprise Institute, said in an interview on Mar. 26: “The New York Fed is the residual claimant. That doesn’t look to me like a loan. That looks like equity.”
[top]