The CPI inflation rate for May, to be published at 9:30 am tomorrow by the Office for National Statistics, is 3.1%. That is more than one percentage point above our target of 2%. Under the terms of the remit you have given us, I am, therefore, writing an open letter to you today on behalf of the Monetary Policy Committee. As requested by the National Statistician, in order to avoid conflict with the release of the official statistic, in this case the CPI, the Bank of England will publish this open letter at 10:30am.
Our remit specifies that an open letter should explain why inflation has moved away from the target, the period within which we expect inflation to return to the target, the policy action that the Committee is taking to deal with it, and how this approach meets the Government’s monetary policy objectives.
Why has inflation moved away from the target?
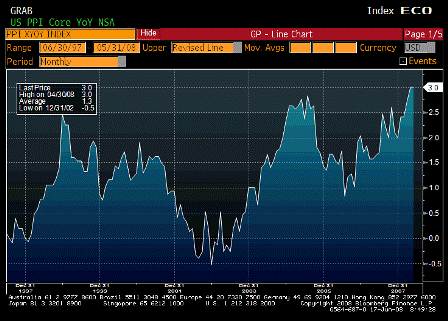
Inflation has risen sharply this year, from 2.1% in December to 3.3% in May. That rise can be accounted for by large and, until recently, unanticipated increases in the prices of food, fuel, gas and electricity. These components alone account for 1.1 percentage points of the 1.2 percentage points increase in the CPI inflation rate since last December. Those sharp price changes reflect developments in the global balance of demand and supply for food and energy.
In the year to May:
- world agricultural prices increased by 60% and UK retail food prices by 8%.
- oil prices rose by more than 80% to average USD123 a barrel and UK retail fuel prices increased by 20%.
- wholesale gas prices increased by 160% and UK household electricity and gas bills by around 10%.
The global nature of these price changes is evident in inflation rates not only in the UK but also overseas, although the timing of their impact on consumer prices differs across countries. In May, HICP inflation in the euro area was 3.7% and US CPI inflation was 4.2%. As described in our May Inflation Report, inflation is likely to rise significantly further above the 2% target in the next six months or so.
The May Report set out three main reasons for this:
- The increase in oil prices will continue to pass through to the costs faced businesses.
- Rising wholesale gas prices are expected to lead utility companies to announce further tariff increases. There is considerable uncertainty about their size and timing.
- The depreciation of sterling, which has fallen some 12% since its peak last July, has boosted the prices of imports and will add to the pressure on consumer prices.
The Committee’s central projection, described in its May Inflation Report, was for CPI inflation to rise to over 3 1/2%% later this year. But in the past month, oil prices have risen by about 15% and wholesale gas futures prices for the coming winter have increased by a similar amount. As things stand, inflation is likely to rise sharply in the second half of the year, to above 4%. I must stress, however, that there are considerable uncertainties, in both directions, around this, and any such projection is particularly sensitive to changes in domestic gas and electricity charges.
There are good reasons to expect the period of above-target inflation we are experiencing now to be temporary. We are seeing a change in commodity, energy and import prices relative to the prices of other goods and services. Although this clearly raises the price level, it is not the same as continuing inflation.
There is not a generalised rise in prices and wages caused by rapid growth in the amount of money spent in the economy. In contrast to past episodes of rising inflation, money spending is increasing at a normal rate. In the year to 2008 Q1, it rose by 5 1/2%, in line with the average rate of increase since 1997 – a period in which inflation has been low and stable. Moreover, in recent months the growth rate of the broad money supply has eased and credit conditions have tightened. This will restrain the growth of money spending in the future.
Over what period does the MPC expect inflation to return to the target?
It is possible that commodity prices will rise further in the coming months – oil prices have now been rising for four years. But in the absence of further unexpected increases in oil and commodity prices, inflation should peak around the end of the year and begin to fall back towards the 2% target. Nevertheless, each monthly rise in food, energy and import prices will, by pushing up the overall price level, affect the official twelve-month measure of inflation for a year. So CPI inflation is likely to remain markedly above the target until well into 2009.
I expect, therefore, that this will be the first of a sequence of open letters over the next year or so. The remit for the Monetary Policy Committee states that:
“The framework takes into account that any economy at some point can suffer from external events or temporary difficulties, often beyond its control. The framework is based on the recognition that the actual inflation rate will on occasions depart from its target as a result of shocks and disturbances. Attempts to keep inflation at the inflation target in these circumstances may cause undesirable volatility in output”.
The Committee believes that, if Bank Rate were set to bring inflation back to the target within the next 12 months, the result would be unnecessary volatility in output and employment. So the MPC is aiming to return inflation to the 2% target within its normal forecast horizon of around two years, when the present sharp rises in energy and food prices will have dropped out of the CPI inflation rate. Nevertheless, the Committee is concerned about the present and prospective period of above-target inflation. It is crucial that prices other than those of commodities, energy and imports do not start to rise at a faster rate.
That would happen if those making decisions about prices and pay began to expect higher inflation in the future and acted on that. It could also happen if employees respond to the loss of real spending power that results from higher commodity prices by bidding for more substantial pay increases. Pay growth has remained moderate. But surveys indicate that higher inflation has already had an impact on the public’s expectations of inflation. For that reason, the Committee believes that, to return inflation to the target, it will be necessary for economic growth to slow this year.
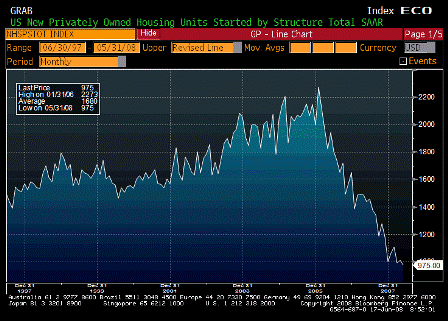
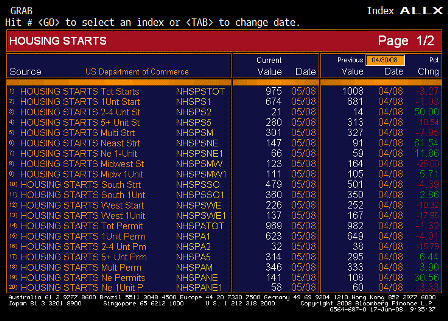
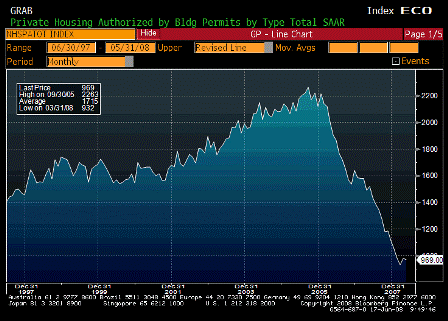
A slowdown is already in train. Moreover, as described in the Committee’s May Inflation Report, the prospective squeeze on real incomes associated with higher inflation, together with the reduced availability of credit, is likely to lead to a further slowing in activity this year. This will reduce pressure on the supply capacity of the economy and dampen increases in prices and wages. What policy action are we taking? Since December, Bank Rate has been reduced three times, to stand at 5%. When setting Bank Rate the Committee has faced a balancing act between two risks. On the upside, the risk that above-target inflation could persist explains why the Committee has not responded more aggressively to signs that the economy is slowing. On the downside, the risk is that the slowdown could be so sharp that inflation did not just return to the target but was pulled below. This explains why Bank Rate has been reduced at a time when inflation is above the target.
The MPC will discuss at its July meeting the implications of the latest inflation and other economic data for the balance of these risks. That analysis will be described in the minutes, published two weeks later, and a fully updated forecast will be presented in the August Inflation Report. The path of Bank Rate that will be necessary to meet the 2% target is uncertain. The MPC will continue to make its judgement about the appropriate level of Bank Rate month by month.
How does this approach meet the Government’s monetary policy objectives?
Over the past decade, inflation has been low and stable. Volatility in commodity, energy and import prices means that inflation will now be less stable but it does not mean that inflation will persist at a higher rate. The Committee will maintain price stability by ensuring that the rise in inflation is temporary and that it returns to the 2% target. In the short term, this commitment should give those setting prices and wages some confidence that inflation will be close to the target in the future. That will minimise the slowdown in economic activity that will be necessary to ensure that inflation does fall back. In the longer term, price stability, as our remit states, is “a precondition for high and stable levls of growth and employment”.
We have seen in the past how the need to reduce inflation from persistently high levels has required prolonged periods of subdued economic growth. The resulting instability in our economy deterred investment and contributed to poor economic performance over a longer period. The Monetary Policy Committee remains determined to set interest rates at the level required to bring inflation back to the 2% target, and I welcome the opportunity to explain our thinking in this open letter.
I am copying this letter to the Chairman of the Treasury Committee, through which we are accountable to Parliament, and will place it on the Bank of England’s website for public dissemination.
Thanks, seems the risk of crude rising continuously due to demand continues to be downplayed by the world’s central bankers even though it has been the case for several years, so they continue to pursue policies that in their models are designed to at least support demand.
I continue to suggest mainstream history will not be kind to them.